Sol REVIEW - Loudoun County Public Schools
advertisement

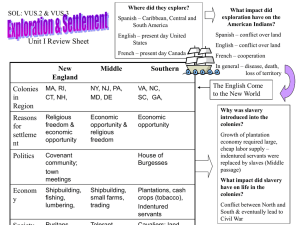
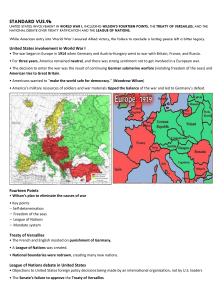
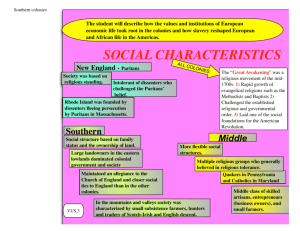
SOL REVIEW VUS.2 – The student will describe how early European exploration and colonization resulted in cultural interactions among European, African, and American Indians European exploration and colonization resulted in redistribution of world’s population Exploration led to commercial expansion (i.e. Columbian Exchange) Settlements New England Settled by Puritans Formed covenant community Mayflower Compact Intolerance of religions Mid-Atlantic Settled by English, Dutch, and German Sought religious freedom, economic opportunity Virginia and South Virginia Cavaliers: English nobility Shenandoahs: poor immigrants Jamestown 1607 1st permanent English Settlement House of Burgesses (1st assembly) Known as General Assembly of Virginia VUS.3: The student will describe how the values and institutions of European economic and political life took root in the colonies and how slavery reshaped European and African Life in the Americas Economic Activity of Colonial Settlements New England Ship-building, small-scale farming, and trading New York and Philadelphia grew as trading ports Foothills (Appalachia) had small-scale farming Mid-Atlantic Based on religious standing Intolerant of dissenters Multiple religious groups, Quakers Flexible social structures, developed Middle class South Based on family status and ownership of land Closer ties to Britain Incorporated number of democratic principles that reflected the rights of Englishmen South Town meetings Mid-Atlantic Rice, indigo, and tobacco New England New England Social characteristics of Colonial Settlements Religious movement, swept Europe and Colonies Mid-1700s Growth of evangelical religions (Methodist/ Baptist) and challenged traditional order Political Life in Colonies Developed plantations, grew cash crops South 1st Great Awakening Shipbuilding, fishing, lumbering, subsistence farming, manufacturing Reflected Puritans values of hard work Mid-Atlantic Stronger ties with Britain Planters led representative legislatures Slavery Growth of plantations led to growth of slavery Replaced indentured servants “middle passage” brought Africans to colonies Eventually led to conflict (Civil War) VUS.4 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the Revolutionary Period American Revolution inspired by ideas concerning natural rights and political authority centuries, Europe Influences Thomas Jefferson, Declaration of Independence “natural” rights of man All original power resides in the people Influenced by Locke and Paine Authored by Thomas Jefferson Grievances against the King French/Indian War Proclamation of 1763 Taxes Patriots- complete independence Patrick Henry: “Give me Liberty” Loyalists- loyal to Britain Neutrals- uninvolved Victory Diplomatic Events leading to Revolution Boston Massacre Minutemen – Lexington/ Concord Challenged the rule of the American Colonies by the King of England 1st time colonies worked together Minus GA Colonists during Revolution Declaration of Independence Boston Tea Party 1st Continental Congress Common Sense Thomas Paine 18th John Locke 17th/ Resistance of British Rule Enlightenment Benjamin Franklin negotiated a Treaty of Alliance with France No popular support in Britain Military George Washington’s abilities Benefit from presence of French Navy and Army at Yorktown VUS.5: Student will demonstrate knowledge of the issues involved in the creation and ratification of the Constitution Two attempts made to establish a working government American political leaders fearful of a powerful central government Articles of Confederation Strengths Land Ordinance 1785 Northwest Ordinance 1787 Got colonies through Revolution Weaknesses Weak national government No power to tax, regulate commerce No common currency One vote per state, regardless of size No executive or judicial branches Constitutional Convention Made federal laws supreme, but gave states leeway to govern themselves Senate balanced power between small and big states 3/5ths compromise to appease the South (House of Representatives) Avoided too powerful central government with 3 branches Limited powers of federal government to only those in Constitution Key Leaders George Washington James Madison Virginia Declaration of Rights Authored by George Mason Reiterated rights of man Virginia Statue of Religious Freedoms Authored by Thomas Jefferson Outlawed established church Federalists/ Anti-Federalists Federalists Importance of strong government Promotion of economic development/ public improvements George Washington, James Madison Anti-Federalists Led the debate, kept copious notes “Father of the Constitution” Authored the Virginia Plan,much of the Bill of Rights Virginia President of Convention Feared overly powerful central government Wanted protection of individual rights Patrick Henry, George Mason Marshall Court Strengthened role of Supreme Court VUS.6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from the last decade of the 18th century through the 1st half of the 19th century Development of 1st political parties Controversy over the Federalists’ support for the Bank of the United States, the Jay Treaty, issues with France Democrat-Republicans Weak national government Farmers, artisans, and settlers Thomas Jefferson Federalists Strong national government, commercial economy John Adams, Alexander Hamilton Territorial Expansion Stirred by Manifest Destiny Louisiana Purchase 1803 (Jefferson) American victory in War of 1812 Oregon, Florida Monroe Doctrine 1823 No colonization by European powers Westward Movement Moved for economic opportunity Growth of railroads and canals Eli Whitney’s Cotton Gin Mexican War victory 1840s Slavery spreads in south California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico American Indians Manifest destiny supported claims to land Indians forcibly moved “Trail of Tears” VUS.6 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from the last decade of the 18th century through the 1st half of the 19th century War of 1812 British interfered with U.S. shipping and western expansion Federalists opposed war, talked of secession Political Changes Sectional “Westward” Tensions Missouri Compromise 1820 Compromise of 1850 Kansas-Nebraska Act 1854 Political Tensions Jacksonian Era Emphasis on equality for white males Rise of interest groups and sectional issues A changing style of campaigning Increased voter participation Federalists disappeared, new parties emerged “Age of the Common Man” Sectional Economic Tensions Industrial north favored high protective tariffs Agricultural south opposed high tariffs South Carolina, nullification Nullification Crisis Whigs and Know-Nothings Tariff of 1832 President Jackson threatened to send in troops to collect tariffs Slavery Slave revolts: Nat Turner, Gabriel Prosser William Llyod Garrison’s The Liberator Fugitive Slave Law outraged North Women’s Movement Seneca Falls Declaration 1848 Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Susan B. Anthony VUS.7 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the Civil War and Reconstruction Era Causes of Civil War Sectional disagreements over tariffs, extension of slavery, nature of the Union Dred Scott Case Uncle Tom’s Cabin Ineffective leadership during the 1850s Failed compromises Events of the Civil War Emancipation Proclamation Freed slaves in rebelling states Abolition of slavery a war aim Discouraged interference from Foreign governments Enlistment of African-American soldiers Gettysburg Address Election of Lincoln 1860 Preserving Union important Fort Sumter Emancipation Proclamation (Antietam 1862) Battle of Gettysburg War fought to fulfill the promise of the Declaration of Independence, a second American Revolution Appomattox: Lee’s surrender Survival of nation was at risk Key Leaders Abraham Lincoln Ulysses S. Grant, Robert E. Lee Frederick Douglass Reconstruction Political Union, Civil War Amendments,Ended 1877 Economic South embittered North and mid-West growing industrial economies Transcontinental Railroad VUS.7 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the Civil War and Reconstruction Era Social Impact of Reconstruction African-Americans Emancipation allowed for enlistment No full equality for 100 years Post-war Contributions Common Soldiers Ulysses S. Grant Urged Radical Republicans to not be harsh Elected President Hand-to-hand combat Advocated rights of freedman Harsh reality of war Opposed retribution to South Women Robert E. Lee Managed home and families Urged Southerners to reconcile Often faced poverty and hunger Assumed new roles in agriculture, nursing, and war industries President of Washington College (Wash & Lee) Emphasized importance of education Frederick Douglas Supported full equality Advocated passage of 14th and 15th amendments Ambassador to Haiti VUS. 8 The student will demonstrate knowledge of how the nation grew and changed from the end of Reconstruction through the early 20th century Westward Movement Growth of Cities Intensified after civil war Era immediately after, Era of the Cowboy (1860s-1880s) Chicago, Detroit, Cleveland, Pittsburgh, and New York grew Housing shortages Need for public services Homestead Act 1862 encouraged settlement New technologies Railroads, reaper Removal of Native Americans New Immigration Prior 1871: Immigrants from Northern and Western Europe “New” immigrants from Southern and Eastern Europe and Asia Made valuable contributions to society U.S. became “melting pot” Fear and resentment from “natives” Limitations like Chinese exclusion Act 1882 New States Great Plains, Rocky Mountains U.S. underwent economic transformation that involved the development of an industrial economy, the expansion of big business, the growth of large-scale agriculture, rise of national labor and industrial conflict New Technology Corporations, Bessemer process, Light bulb, Telephone, Airplane, Assembly-line VUS. 8 The student will demonstrate knowledge of how the nation grew and changed from the end of Reconstruction through the early 20th century Industrial leaders Progressive Movement Rose because of social problems in rural and urban settings Causes Economic transformation Laissez-faire capitalism Increasing labor supply Natural resources African Americans Discrimination intensified “Jim crow” laws, lynching Plessy v. Ferguson, separate but equal Andrew Carnegie (Steel), J.P. Morgan (finance), John D. Rockefeller (oil), and Cornelius Vanderbilt (railroads) Excess of Gilded Age Income disparity, Robber Barons Working Conditions Child labor, dangerous conditions, long hours, low wages, Accomplishments Government reforms Referendum, initiative, recall Direct election of Senators, secret ballots Labor unions “Great Migration” of African- Americans Responses to discrimination Ida B. Wells, Booker T. Washington, W.E.B. du Bois Knight of Labor, American Federation of Labor (Samuel Gompers), American Railway Union (Eugene V. Debs) Antitrust laws Sherman Anti-Trust : restrains monopolies Clayton Anti-Trust : strengthened Sherman Act Women’s suffrage- 19th Amendment VUS.9 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the emerging role of the United States in world affairs Creation of International Markets Open Door Policy (China) Plan to eliminate causes of war Dollar Diplomacy (Taft) Key points: Growth of international trade Expanded influence in Latin America Wilson’s 14 points Spanish American War Puerto Rico annexed Right to intervene in Cuba Panama Canal Encouraged Panama’s independence from Columbia Built canal (T. Roosevelt) Expanded influence in Asia and Pacific Hawaii: deposed monarchy, annexed Philippines: annexed after S.A. war WWI Began in 1914, assassination of Arch Duke Ferdinand U.S. neutral for three years U.S. entry a result of german sub warfare, U.S. ties to Britain Self-determination Freedom of the seas League of Nations Mandate system Treaty of Versailles French and English insisted on punishment of Germany League of Nations created National boundaries redrawn, new nations League of Nations U.S. objected to foreign policy decisions being made by international organization not U.S. leaders Senate failed to approve Treaty of Versailles VUS.10 The student will demonstrate knowledge of key domestic events of the 1920s and 1930s Mass Media created popular culture Radio: jazz and fireside chats Movies: escape from Depression era realities Consequences of Crash Newspapers and magazines: shaped cultural norms and sparked fads Traditional values challenged Bankers panicked, withdrew deposits Causes of Great Depression Stock market crash Failure of Federal Reserve, then constricted $ supply High protective tariffs Religion: Darwin and the Scopes Trial Women: Flappers, 19th amendment Unemployment, homeless Immigration: rise of new KKK Collapse of financial system (banks) Prohibition: smuggling alcohol and speakeasies Decline in demand for goods Political unrest, farm foreclosures, migration Global Power U.S. emerged from WWI a global power Causes of Stock Market Crash Impact of Great Depression New Deal Change role of government, more activist Overspeculation, credit, business failures Relief, Recovery, Reform When market collapsed, banks out of money Social Security Act VUS.11 The student will demonstrate knowledge of WWII WWII in Europe Major battles Began with Hitler’s invasion of Poland 1939 U.S. neutral 1st two years El Alamein= Egypt (oil) 1941 Hitler invaded Soviet Union Stalingrad= prevented loss of Soviet Union U.S. helped Britain Normandy= D-day 6/6/1944 Lend-lease act WWII in Asia Japan’s aggressiveness in Pacific Pearl Harbor 12/7/1941 Strategies Allied 1st” “defeat Hitler pacific= island hopping Axis Defeat Soviet Union, oil Japanese- invade Hawaii and Australia Europe/North Africa Pacific Midway= defeat of Jap. Navy Iwo Jima/ Okinawa= closer to Japan, hari-kari Atomic bomb= Hiroshima and Nagasaki Contributions Tuskegee Airmen (African-American) Nisei Regiments (Asian-American) Navajo Code talkers Mexican-Americans Geneva Convention Attempted to ensure fair treatment for POWs Bataan Death March- Philippines VUS.12 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the effects of World War II on the home front Holocaust African Americans Genocide, final solution Migrated to cities for jobs Jews, Poles, Slavs, Gypsies, undesirables (mentally ill, homosexuals, political dissidents) Campaigned for equality Nuremberg trials Demand for Jewish homeland Home front effort Economic resources Gov’t and industry worked together Rationing War bonds, income tax Human resources Women/ minorities Military resources The draft Women Rosie the Riveter Japanese Americans Relocated to internment camps Kormatesu case Media/Communications Strict censorship over reporting of war Public morale and ad campaigns to support war Movies, plays, shows to boost morale VUS. 13 Student will demonstrate and knowledge of United States foreign policy since WWII Political, economic, and social consequences of WWII U.S involvement reflected containment policy Germany partitioned U.S. led U.N forces to drive back North Korea Japan occupied by U.S. Ended in stalemate Europe in ruins Korean War Marshall plan United Nations formed Cold War set framework for Global politics for next 45 years Origins of Cold War Vietnam War Reflected containment policy U.S. helped South Vietnam resist North Build-up began under Kennedy’s term Scale of war grew during 1960s America divided over War Nixon- Vietnamization War ended in 1976, North took over South Different fundamental values Truman Doctrine NATO Castro led communist revolution 1950s Communist takeover of China Failure of “Bay of Pigs” Massive retaliation 1962- Cuban Missile Crisis, Soviets “blinked” Cuba Confrontation VUS. 13 Student will demonstrate and knowledge of United States foreign policy since WWII Impact of Cold War at home Fear of communism Internal pressures on Soviet Union Rising military expenses Raid drills, bomb shelters Rising nationalism in republics Alger Hiss/ Rosenbergs Economic reforms, economic inefficiency McCarthyism Gorbachev’s glasnost and perestroika Senator Joseph McCarthy Heavy military expenditures Foreign policy an issue in every election Key to victory= U.S. military Military Forces “Ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you can do for your country” Kennedy’s assassination led to internal strife and divisiveness Vietnam vets faced hostility External pressures on Soviet Union President Reagan’s Role Challenged legitimacy of Soviet Union “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!” Increased U.S. military and economic pressure on Soviet Union VUS. 13 Student will demonstrate and knowledge of United States foreign policy since WWII George H.W. Bush Fall of communism Reunification of Germany Collapse of Yugoslavia Persian Gulf War 1990-1991 Operation Desert Storm Bill Clinton NAFTA Full diplomatic relations with Vietnam Lifting of sanctions against South Africa NATO action in Yugoslavia George W. Bush Terrorist attacks on U.S. soil 9/11/01 War in Afghanistan War in Iraq VUS.14 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the Civil Rights Movement in the 1950s and 1960s Brown v. Board of Education 1954 Desegregation of public schools Thurgood Marshall Civil Rights Act of 1964 Johnson’s presidency Prohibited discrimination based on race, color, religion, gender, or national origin Desecrated public accommodations NAACP Legal Defense team Oliver Hill Legislative Process Individual Roles NAACP Legal Defense team in Virginia Virginia’s Response Voting Rights Act of 1965 Outlawed literacy tests Massive resistance, some school closings Increase in African-American voters Establishment of private academies Registers sent to the south White flight from Urban schools 1963 March of Washington “I Have a Dream” speech MLK Jr. Helped influence public opinion to support civil rights legislation Demonstrated power of non-violence VUS.15 The student will demonstrate knowledge of economic, social, cultural, and political developments in recent decades and today Supreme Court Women: Sandra Day O’Connor, Ruth Bader Ginsberg Advances of Technology Minorities: Thurgood Marshall, Clarence Thomas Civil Rights movement of 1950s and 1960s provided model for other groups to extend civil rights and promote equal justice Immigration Increase from Latin American and Asian nations Rising immigration has increased diversity and redefined American identity Political freedom, economic opportunity Issues with policy Reasons Space Strain on resources, border issues, citizenship Contributions Diversity in music, arts, and literature Labor force 1960s: Space Race John Glenn 1st man in space, orbited Earth Neil Armstrong 1st man on the moon Sally Ride 1st female astronaut Space shuttle Mars Rover Voyager Missions Hubble telescope Communications Satellites GPS Personal communication devices Robotics Change in work, school, health care Telecommuting, growth of service industries Breakthroughs in medical research Outsourcing, offshoring VUS.15 The student will demonstrate knowledge of economic, social, cultural, and political developments in recent decades and today Reagan’s impact of Government Conservative political philosophy prompted reevaluation of size and role of government Federal Government’s influence on economy Bases economic decisions on GDP, exchange rates, rate of inflation, and unemployment Government promotes a healthy economy characterized by full employment and low inflation through: Platform Tax cuts Transfer of responsibilities to state governments Appointment of judges who exercised “judicial restraint” Strengthening of military Reduction in # and scope of government programs Reagan Revolution effects George H.W. Bush elected president Election of centrist Bill Clinton Election of George W. Bush Federal Reserve President and Congress International Terrorism U.S. created domestic and international policies aimed at stopping terrorism Patriot Act: Domestic Use of diplomatic and military initiatives