Leaves
advertisement

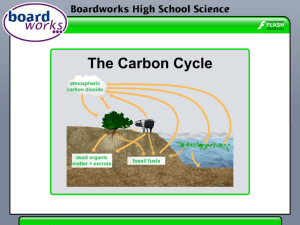
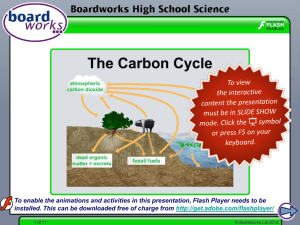
Leaves 1 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 2 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 How do leaves maximize photosynthesis? Leaves are the most efficient solar panels on Earth! What does this mean? Like solar panels, leaves convert energy from the Sun into usable chemical energy. This is through the photosynthesis reaction. Leaves come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but they share certain features that maximize photosynthesis. 3 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Photosynthesis 4 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 How are leaves adapted for photosynthesis? 5 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Structure of a leaf activity 6 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Photosynthetic pigments 7 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 8 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Take a look inside a leaf 9 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Looking at real leaves 10 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Palisade cells 11 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 How do gases enter and leave plants? On the underside of leaves are small holes, or pores, called stomata. A single hole is called a stoma. Each stoma is surrounded by two guard cells. When guard cells gain water, they curve outwards. This opens the stoma, allowing carbon dioxide in and oxygen out. Losing water causes the guard cells to come closer together, closing the stoma. This stops the movement of gases, but also prevents water loss. 12 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Water As well as carbon dioxide, photosynthesis also requires water. Water is taken in by the roots and travels up the stem of the plant. It is distributed to the leaves through the veins. Water is also needed to hold the plant upright so that it can absorb more light. 13 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Leaf adaptations 14 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 15 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Glossary 16 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011 Multiple-choice quiz 17 of 17 © Boardworks Ltd 2011



![Direction_and_Scale[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005432475_1-80ce3065f13008250a8cdec135db9846-300x300.png)