2011 Scaling Up Nutrition Cambodia ppt
advertisement

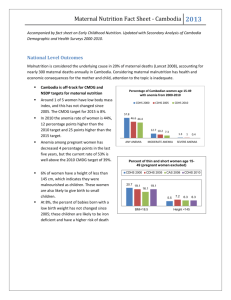
Country Challenges and Achievements for Food Security & Nutrition Prepared for Scaling Up Nutrition Meeting August 2011 Cambodia Delegation Trends in U-5 Child Malnutrition from 2000-2010 Cambodia Millennium Development Goal Percentage of U-5 children underweight (weight-for-age < - 2 SD) 2000-2010 CMDG 2010 Target=24.5% CMDG 2015 Target=19% Past and Current Achievements in Coordination • National Council for Nutrition established; National Plan of Action on Nutrition (1996-2000) and Cambodia Nutrition Investment Plan developed (2003-2007) • Interministerial National Sub-Committee on Food Fortification, Provincial Nutrition Coordination Committees, Ministry of Health National Nutrition Program, and private sector Salt Producers Community (focusing on iodization) established • Food Security and Nutrition Technical Working Group chaired by CARD (Council for Agricultural and Rural development) is one of 18 current official coordination bodies of the government • Strategic Framework for Food Security and Nutrition, National Nutrition Strategy, and Social Protection Strategy (including nutrition) currently in-place Achievements in the Health Sector Early initiation of breastfeeding and exclusive breastfeeding show great progress (CDHS 2010) Anaemia among children 6-59 months reduced from 62% in 2005 to 55% in 2010 and from 47% to 44% among women of reproductive age Coverage of IFA supplementation for pregnant women is over 85% Coverage of deworming and vitamin A supplementation for postpartum women and children climbing to above 50% (CDHS 2010) Agricultural & Multisectoral Achievements Increases in productivity and cultivated area has led to a surplus paddy of over 3.5 million tones Eight out of ten households consume iodized salt (CDHS 2010) Household dietary diversity is improving with a higher percentage of calories from animal sources, especially in urban areas. Protein consumption increased from 54.5 g/person/day in 2004 to 62.8 g/person/day in 2009 (CSES 2009) The poorest households are consuming 13% more calories (CSES 2009) and spending a lower percent of overall expenditure on food Rice Paddy Production and Surplus, 2000-2009 Challenges for Current Priorities • Integrate nutrition in national development strategy; provide more operational guidance for policy and strategy documents • Sub-national coordination structures for nutrition are not currently active • Some current programmes have not been adequately evaluated; improve national monitoring systems • Increased agricultural productivity and economic growth is not sufficient for changing the diet of young children; improved feeding practices is needed Emerging and Long-Term Challenges • Comprehensive policy and legislation is lacking for food fortification • Fluctuating food prices require different strategies, including nutrition-sensitive social safety nets, targeted to most vulnerable (net food buyers, urban poor) • Unclear future financial support to scale up interventions; link investment now with economic cost of malnutrition on development • Postgraduate degrees in agriculture are available in-country, but still lacking for nutrition