fin1_water_supply_slides
advertisement

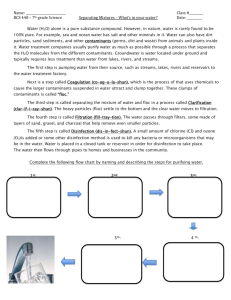
WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM BASIC OPERATIONS Prepared by RCAP Solutions For PADEP Introduction Basics of Water Supply 1 Drinking Water Sources Surface Water Groundwater 2 Surface Water: Advantages Easily accessible Large volumes of water Surface reservoirs for storage 3 Surface Water: Disadvantages Exposure to contaminants Expensive filtration 4 Groundwater: Advantages Less treatment Consistency Availability 5 Groundwater: Disadvantages Chemical contamination Hardness Multiple wells Location 6 Groundwater Treatment Processes 7 Groundwater Treatment Processes Not very complex Mainly disinfection Covered later 8 Surface Water Treatment Processes 9 Racks and Screens 10 Racks and Screens Prevent debris Pipes and pumps Straining pasta 11 Mixing 12 Mixing Coagulant Suspended particles 13 Coagulation and Flocculation 14 Coagulation and Flocculation Reduces solids Prevents bacterial “hiding” Like making cheese 15 Sedimentation 16 Sedimentation Presedimentation Basins Solids loading reduction Sludge removal 17 Filtration 18 Filtration Solids and floc removal Physical Chemical Biological 19 Types of Filtration Slow Sand Conventional Filtration 20 Types of Filtration Direct Filtration Diatomaceous Earth 21 Types of Filtration Membrane Filtration Bag and Cartridge Filters 22 Disinfection 23 Disinfection Disease-causing organisms Chlorine Ozone and Ultraviolet Radiation 24 Disinfection: Chlorine Chlorine Gas Sodium Hypochlorite 25 Disinfection: Chlorine Calcium Hypochlorite Chlorine may form carcinogens 26 Disinfection: Ultraviolet Light Penetrates most cell walls No toxic residuals Short contact times; easy to operate Unsuitable for some water sources 27 Disinfection: Ozone O3 Shorter contact time Capital costs O&M 28 Other Typical Treatment Processes Iron and manganese removal Corrosion control These are source dependent 29 Iron and Manganese Removal Various techniques Aeration Sequestration Ion exchange 30 Corrosion Control Prevents degradation Adjust water characteristics 31 Exercise Exercise!!! Complete the fill-in-the blank questions 32 Distribution System Facilities Pumps Storage facilities Transmission mains Valves and hydrants Meters 33 Pumps Provide lift Do not generally create pressure Major part of O&M costs 34 Storage Facilities Clear wells Stand pipes Elevated storage tanks 35 Clear Wells 36 Clear Wells Large concrete reservoirs Constant rate of operation 37 Stand Pipes Located on the ground Require little maintenance 38 Elevated Storage Tanks Supporting structures Use gravity Filled in off-peak hours 39 Transmission Mains System Design Branching systems Loop or grid systems 40 Transmission Mains Materials Cast iron Ductile iron Plastic (polyvinylchloride – PVC) 41 Valves and Hydrants Valves Wet barrel hydrants Dry barrel hydrants 42 Meters Throughout the system Used for billing and to identify loss Lowers usage Replacement program 43 Exercise Exercise time!!! Fill in the graphic and answer the questions 44 Summary Key points 45 References and Resources See your workbooks for details 46