Secondary Treatment Configurations SOP Pretreatment 2012
advertisement

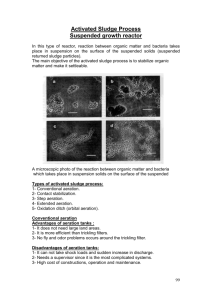
Secondary Treatment Configurations SOP Pretreatment Workshop August 2011 NDWRCDP Disclaimer This work was supported by the National Decentralized Water Resources Capacity Development Project (NDWRCDP) with funding provided by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency through a Cooperative Agreement (EPA No. CR827881-01-0) with Washington University in St. Louis. These materials have not been reviewed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. These materials have been reviewed by representatives of the NDWRCDP. The contents of these materials do not necessarily reflect the views and policies of the NDWRCDP, Washington University, or the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, nor does the mention of trade names or commercial products constitute their endorsement or recommendation for use. CIDWT/University Disclaimer These materials are the collective effort of individuals from academic, regulatory, and private sectors of the onsite/decentralized wastewater industry. These materials have been peer-reviewed and represent the current state of knowledge/science in this field. They were developed through a series of writing and review meetings with the goal of formulating a consensus on the materials presented. These materials do not necessarily reflect the views and policies of University of Arkansas, and/or the Consortium of Institutes for Decentralized Wastewater Treatment (CIDWT). The mention of trade names or commercial products does not constitute an endorsement or recommendation for use from these individuals or entities, nor does it constitute criticism for similar ones not mentioned. Pretreatment components Section objectives Describe various engineered systems that maintain high-rate aerobic digestion of organic compounds found in domestic wastewater Provide an understanding of the typical issues associated with these components Describe basic operation and maintenance procedures required to keep these systems functional Basic aerobic treatment environments Saturated Suspended growth Fixed/attached growth Integrated fixed/activated sludge (IFAS) Unsaturated Media filters Trickling filters Saturated treatment Suspended growth Fixed/attached growth Integrated fixed/activated sludge (IFAS) Saturated aerobic units: Primary distinctions Packaging Flow of effluent Aeration method Biomass management Suspended growth reactors Activated sludge process Biomass is thoroughly mixed with nutrients and biodegradable compounds Organisms flocculate and form active mass of microbes - biological floc Extended aeration to limit biomass wasting Endogenous respiration Suspended Growth Suspended growth Suspended growth Suspended growth USEPA Manual, 1980 Sequencing Batch Reactor Suspended growth treatment process Utilize a single chamber for achieving aeration, clarification and anoxic conditions Flow equalization chamber for dosing effluent into the treatment chamber Sequencing batch reactors Sequencing batch reactors Fixed/attached growth reactors Fixed-film process Inert medium is submerged in the aeration chamber Effluent circulated through media and attached microbes Colloidal and dissolved organics compounds absorbed by biological film Extended aeration to limit biomass wasting Food brought to bugs Fixed-film reactors Rotating Biological Contactor (RBC) Membrane bioreactors Wikipedia Flow schemes Continuous inflow Batch processes Aeration Air supply and delivery component Distribution device Venting device Air supply delivery Methods Aspirator/Aerator Compressor Blower Free Air Aerator/Aspirator Aerator/Aspirator Spinning shaft or impeller creates a vacuum (venturi) Vacuum pulls air into the water Compressor Two distinct types of compressors Rotary Linear Both types fitted with filters Relative to blowers: Rotary Greater pressure Lower air flow Linear Blowers Fitted with inlet screens/filters Relative to compressors: Lower pressure Greater air flow Air distribution device Introduces air into the water Includes any supply line(s) Various methods Aspirator/aerator Shaft piping delivers the air supply Distribution relative to pressure Diffused air distribution Compressor or blower delivers air Mode of distribution is manufacturer specific Solid pipe Perforated pipe • Holes • Slots Porous material Diffused air distribution Perforated Pipe Diffused air distribution Porous ceramic diffuser Diffused air distribution Spargers small interconnected passageways inside a ceramic matrix Oxygen transfer into solution Small diameter bubbles More surface area per unit volume Oxygen transfer takes place across interface between air and water Point of injection Usually near bottom of tank more time for oxygen to go into solution more hydrostatic pressure on bubble more mixing of contents “Free” air Alternately rotates media through air space in top of unit and down into effluent in basin Water accepts oxygen from air Aeration and Mixing Aeration system also encourages mixing displacement of water as air is introduced causes turbulence Air supply operation Continuous Timed Venting Air entering system Air must exit somewhere Unit House vent Biofilter Biomass management Returning sludge to a previous point in treatment system Keeps the biological processes working At some point, accumulated solids will have to be removed Passive sludge return system Settled material automatically returns to the aeration chamber No moving parts Limited flexibility for including anoxic treatment process Active sludge return system Pump on bottom of settling chamber Control panel with timer Timing of return Volume returned Location for returned material Proprietary configurations Modular units with complete configuration Subcomponents installed in prefab tanks Specific to proprietary products Basic aerobic treatment environments Saturated Suspended growth Fixed/attached growth Integrated fixed/activated sludge (IFAS) Unsaturated Media filters Trickling filters Unsaturated treatment Media filters Trickling filters Media filters A container or lined excavation containing a specific media through which wastewater flows Treatment occurs in unsaturated conditions Designed to follow primary treatment Flow regimes for media filters Single pass Recirculating Single-pass media filter NSFC Recirculating media filter schematic Recirculating Media Filter Filter Drainage From House Septic Tank Final Effluent Tank Recirculation Tank To Soil Effluent Filter Float Valve in Tank Dosing Pump Effluent Pump Typical configuration – 36 inches of media Methods of distribution 24 Pressure distribution - most common • Spray nozzles • Driplines Gravity Typical configuration Increasingly, timer-controlled dosing is being used Usually lined to collect filtrate for external dispersal May be configured to drain into rock pad beneath unit in certain soil/site conditions Typical hydraulic loading 1 – 2 gal / ft2 /day Multiple-pass filters: up to 5 gal / ft2 /day Increased loadings may be allowed for certain proprietary designs Single-pass: Dosing frequency Single-pass filters: Historically - 4 times/day Current recommendations - as high as 12-24 times/day Multiple-pass: 12-72+ times/day Treatment process Wastewater applied in small doses Percolates over media in thin film Organisms on media contact wastewater Air is maintained in media pores Oxygen is transferred into the thin film and to organisms Aeration typically passive PRO CE SSE S A T W OR K LI Q U I D W A S T E S O R G A N IC S A IR M E D IA B IO L O G IC A L M ASS P A T HO G E N S E X CE SS CE L L M A SS E N D PR O D U C T S B.O .D . SS N U TR IE N T S Treatment occurs by: Filtration and trapping Adsorption Biological decomposition Biochemical transformation Nitrification Denitrification (especially if recirculated) Types of media Washed, graded sand Gravel Foam chips and cubes Expanded polystyrene Peat Synthetic textile materials Bottom ash from coal-fired plants Crushed glass Other Sand and gravel filters Single pass or recirculating mode Sand/Gravel media specifications Must (generally) be processed to provide the right gradation Screened for proper gradation Washed Must be handled carefully after processing to maintain the specification and remain free of fines Cutaway demo Single pass sand filter with pump basin Questions?