Buffer - Arkansas Forest Resources Center

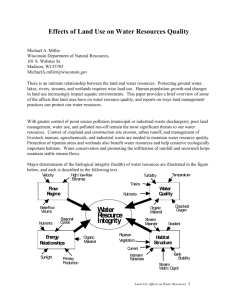
Riparian Buffers for Water and Stream Protection
Hal O. Liechty
Arkansas Forest Resources Center
School of Forest Resources, UAM liechty@uamont.edu
What is a riparian area?
Latin word “riparious”~ belonging to the bank of a river
“The riparian corridor encompasses the stream channel and the portion of the terrestrial landscape from the high water mark toward the uplands….. Naiman et al.
1993
Stream channel and land that interacts with the stream
What is a riparian area?
Area within the channel but also land that is flooded outside the channel
--Flooded 1 out of 100 years--
--Flooded 2 out of 3 years--
What is a riparian area?
What is a riparian area?
What is a buffer?
Buffer “to lesson the shock” &
“something that separates two items”—Webster Dictionary
Vegetation that separates a field, a managed forest, or an urban development from a stream, lake, etc and reduces the impact of the land management on water quality
What is a buffer?
Separates stream from other landuses
Reduces impact of management practices on stream
What is a buffer?
Separates stream from other landuses
Reduces impact of management practices on stream
What is the purpose of a riparian buffer?
Moderates Stream
Temperature
Food for Aquatic
Organisms
Filter Strip
Wildlife Habitat
Purpose: Filter Strip
Remove nutrients, sediment, chemicals from water before it reaches the stream
Purpose: Filter Strip
Filters Nutrients and Sediment from Surface Water
CROPS
Grass
RIPARIAN
BUFFER
STREAM
Purpose: Filter Strip
Filters Nutrients and Sediment from Surface Water
Purpose: Filter Strip
Filters Nutrients and Sediment from Surface Water
Grass buffers somewhat more effective than trees
Sediment and phosphorus removal
20-85%
Wider buffers better
Purpose: Filter Strip
Nutrient and Chemical Uptake Subsurface Water
CROPS
Grass
RIPARIAN
BUFFER
STREAM
Purpose: Filter Strip
Nutrient and Chemical Uptake
Trees and grass can absorbs nutrients & contaminates
Long-term storage in trees
Important uptake for phosphorus and nitrogen
Purpose: Filter Strip
Degradation and Denitrification
CROPS
N
2
RIPARIAN
BUFFER
N
2
Grass
N0
3
NH
3
Org N
STREAM
Purpose: Filter Strip
Degradation and Denitrification
100
80
60
40
20
0
Fo re st
Fo re st ed
W et la nd
G ra ss
G ra ss/
Fo re st
W et la nd
Source: Mayer et al. 2005, EPA
Purpose: Riparian Protection
Bank Stabilization
Vegetation stabilizes bank maintains stream depth and width
Purpose: Riparian Protection
Bank Stabilization
Removal of vegetation from banks increases sediment in stream and width of stream
Purpose: Modification of Stream Climate
Shading of Stream Reduces Temperature
Removal of vegetation can increase maximum water temperatures 12 o F.
Retention buffer alters temperature <2 o F
Corbett et al. 1978
Purpose: Modification of Stream
Climate
30
25
20
15
15
19
14
21
25
18
21
25
18
16
19
15
10
5
0
Uncut Forest Clearcut Herbaceous Tree Buffer
Mean Max. Weekly Max. Weekly Mean Weekly
Lee and Samuel 1976
Purpose: Modification of Stream
Climate- - Aquatic Organism
Water
Temperature
(F)
Solubility of O
2
(mg/L)
41
50
68
77
12.8
11.3
9.0
8.2
Purpose: Modification of Stream Climate-
- Aquatic Organism
Warm water fish (smallmouth bass, crappie etc.) need temperatures from 65-85 o F --DO needs
Growth of juvenile smallmouth bass decline at temperatures>86 o F
Growth of mature smallmouth bass decline at temperatures >88.7
o F
Cold water fish (trout) need temperatures from
45-65 o F -- high DO needs.
Purpose: Aquatic Organism Habitat
Benthic Invertebrates-Aquatic organisms without backbones
Live the majority of their life as larvae and nymphs in the water and only emerge as adults to mate outside the stream (flying stage)
Bottom of aquatic food chain
Purpose: Aquatic Organism Habitat
Food and Energy for Macroinvertebrates
Leaves and other organic matter source of food for macroinvertebrates:
1) Shredders
2) Filter feeders
Purpose: Aquatic Organism Habitat
Food and Energy for Macroinvertebrates
• 20 to 75% of leaf weight lost in 116 days following input of foliage to stream
• Rapid colonization of the leaves by organisms within
21 days of input to stream
Petty and Brown 1982
Illinois River
Purpose: Aquatic Organism Habitat
Large Woody Debris
• Macroinvertebrates cling to large woody debris for protection and stability
Purpose: Aquatic Organism Habitat
Large Woody Debris
• Macroinvertebrates to cling to large woody debris for protection and stability
• Provides diversity in bed structure and stream flow
Purpose: Aquatic Organism Habitat
Large Woody Debris
• Macroinvertebrates to cling to large woody debris for protection and stability
• Provides diversity in bed structure and stream flow
• Cover from predators
Purpose: Aquatic Organism Habitat
Large Woody Debris
Deflects water and creates slack water
Dissipates stream energy protecting stream banks
Purpose: Wildlife Habitat http://www.sotir.com/publications/retrofit.html
Forest Buffer
Types of Buffers
Use native trees with multiple values.
Typical buffer in managed forests
Types of Buffers
Grass Buffer
Efficient Filter Strip
Utilize Native Grass
Can Benefit Wildlife
Types of Buffers
Three Zone Buffer http://www.cayugawatershed.org/Cayu ga%20Lake/RPP/caywetrip.htm
Types of Buffers
Three Zone Buffer
Undisturbed
Forest http://www.ieaconline.org/
Grass
Managed
Forest
Types of Buffers
Wildlife Buffer
Wildlife Corridor
Plant Species
Beneficial to Wildlife
Wider Buffer
Types of Buffers
Urban Buffer http://www.crjc.org/riparianbuffers.htm
Aesthetics
Recreation
Greenway