Environmental Problems
advertisement

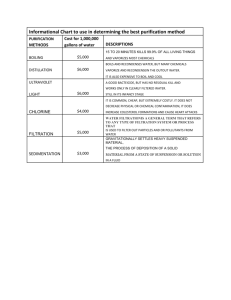
Environmental Problems, economics and cows. Chapter 1 Exponential growth You’ve probably seen the equation used in calculating compound interest: FV= Future Value PV= Present value i= Interest rate n= Number of terms (usually years) Calculate: If you owe $500 on a credit card that has a 13.5% interest rate, how much more will you owe after a year? $567.5 If you owe $150,000 to the bank on a loan with 3.75% interest, how much will you have paid after 30 years? $452,620 ($1257/month payment) Economics of life Not unlike interest compounding, the populations of organisms tend to grow at an exponential rate. Between 1950 and 2005 the world population increased from 2.5 billion to 6.5 billion. Haves vs. Have nots Regardless of the great (8-fold) economic growth between 1950 and 2000,wealth and resources are not evenly distributed. Literally, 1 of 2 of the world’s workers tries to live on less than $2 a day. (Data from World Bank and UN). Survival The problem lies in that in order to survive, many of the poor must deplete and degrade local forests, grasslands, and soils and wildlife. Degrade? But…How? How do people in poverty stricken areas degrade their environment? – Bushmeat – Cutting wood for fuel – Clearing land for agriculture – Poor crop choice – “Feast & Famine” lifestyle. Sustainability None of these practices is sustainable. Sustainability is the ability of the earth’s systems, including human economies, to survive and adapt over time. Sustainability is only achieved through careful management of the earth’s natural resources. Natural Capital Natural Capital refers to the natural resources and services that help keep us and other species alive, and support our economies. For most people, capital is wealth that is used to sustain a business and generate more wealth. Natural Capital is different, but functions the same. Investing in nature… Smart people invest capital to provide themselves with financial income. Smart societies invest in natural capital to provide themselves with biological income. – – – – – – – – This includes: Air purification Water purification Food production Pollination Waste treatment Climate control Soil renewal (sustainable agriculture) Natural Capital Natural Capital can be summed up as the combination of Natural resources + Natural Services. Natural Capital = Natural Resources Air Soil Land Life Minerals Renewable energy NonRenew. energy Natural Services + Air Purification Water Purification Soil Renewal Food Climate control Pest control Environmentally Sustainable An environmentally sustainable society meets the basic resource needs of its people indefinitely without degrading or depleting the natural capital that supplies these resources.