Resource Stream
advertisement

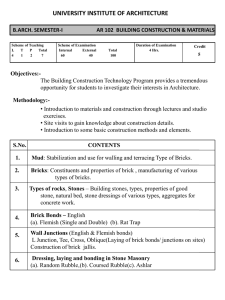
Resource Stream Clay Brick By Bob Fromtling Resource Acquisition Materials Required: clay, sand, fuel (varies), and manpower. Clay is extracted/mined from clay quarries Soil must contain from 25 to 50% clay and silt Copyright 1997 Haruhiko Suga Environmental Impacts of Extraction New extraction sites can have adverse impacts on local landscape, habitats, animals, and plants Quarrying process produces silt laden waters that can escape through storm runoff to contaminate surrounding surface and ground waters Clay particles also enter the air surrounding a quarry Many extraction sites are used as landfills after the clay has all been extracted, which has significant environmental impacts Brick Production The clay soils are mixed with water for plasticity and sand to keep them from sticking to the brick molds The material is then extruded through a large opening making a sheet that can be cut into bricks Through new Stiff Extrusion technology, the bricks contain much less moisture, shortening the drying and heating processes and reducing the wastage of bricks through handling Production Continued After being cut, bricks are stacked and dried, either by open air or by the excess heat from the brick kilns Once they have dried sufficiently to remove moisture, the bricks are heat treated It is through this heating that the alkalis in the clay and the oxides from iron and other metals join with the alumina and silica in the clay to give the bricks their desired hardness Property of www.aureka.com/eceguj.htm Production: Kilns A kiln is an oven or furnace where bricks are fired or heat treated to develop their hardness Brick production is a very energy intensive process and large amounts of fuel must be burned to acquire the correct hardness in the bricks Openings are left in the kiln to release the combustion gases and pieces of metal can be slid on and off of these openings to control the rate at which the fire burns Depending on the technology being used the fuels for a kiln vary from wood and charcoal (most commonly) to natural gases or even waste materials, such as sawdust, pecan shells, plastic wastes, agricultural wastes, and scrap tires Kilns Continued Depending on fuels used, the heating process can go on from anywhere between 17 hours and 8 days and the prime heat level is about 885° Celsius If the fuel runs out and the temperature falls under the correct level, the entire load of bricks could be lost Property of www.gtz.de/basin/gate/ vertical.htm Environmental Impacts of Production The dangerous pollutants emitted by brick kilns are numerous and varied These emissions are produced from the burning of the fuels as well as from the bricks themselves as they are heated These emissions can be extremely unhealthy to kiln workers as well as the surrounding flora, fauna, and residents Environmental Impacts: Air Pollutants Nitrogen oxides are produced by the burning of hydrocarbon fuels and cause acid rain as well as local air pollution Sulfur dioxides are produced by the heating of the clay and the burning of any oils or coals as a fuel source Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide are produced when hydrocarbon fuels are burned and CO causes local air pollution while CO2 causes global warming Air Pollutants Continued Other organic compounds, even toxins such as dioxin can be released if waste compounds are used to fuel a kiln Particulate matter is produced by the firing of the bricks themselves and from the burning of heavy fuel oil, coal, and waste materials Many of these problems could be greatly remedied and reduced by the use of better technology, which reduces waste and increases efficiency Disposal The only options in brick disposal are landfills or recycling Bricks are often moved to landfills where they serve no purpose other than to take up space Bricks can be recycled in a variety of ways ranging from being reused as whole bricks in future construction projects to being crushed and graded for use in road construction, driveways, or as sand or river gravel Environmental Impacts of Disposal The only problem with the disposal of bricks is when they are put into landfills Recycling is an excellent cost efficient way to reduce the amount of brick material that ends up in landfills Ways to Increase Energy Efficiency and Reduce Waste Brick kilns use a large amount of energy and emit a large amount of pollutants By using new and inexpensive technology both of these factors can be significantly improved In India the brick industry is huge and steps are being taken to improve their emissions and energy use Vertical Shaft Brick Kilns VSBK save between 30 and 50% more energy than traditional brick kilns Because of its roof VSKB can operate in all weather conditions year round instead of only 6 months per year Because of energy efficiency and improved combustion air flow efficiency the amount of suspended particulate matter in the emitted flue gases and other pollutants are greatly reduced Vertical Shaft Brick Kiln: Statistics and Picture Property of Teri Organization Other Simple Means of Increasing Environmental Performance By drying the bricks for extended periods of time fuel requirements are reduced By preheating kilns with cleaner burning propane or natural gas before switching to waste fuels such as sawdust, production speed and quality can be increased By simply raising the bricks on a metal grill above the fuel, air flow and combustion increase, reducing particulate matter and other emissions By reducing air leaks and controlling the size of the kiln opening, combustion can be improved, hence leaving less partially burned fuels Environmental Benefits of Brick Production Fly-ash is a byproduct of the burning of soft coals such as Bituminous coals. It consists of the lighter particles of ash that fly into the air, hence the name Fly-ash is a known carcinogen and can cause skin and lung diseases. It also reflects infra-red rays, contributing to global warming. It is being produced in huge quantities in such countries as India and Australia, who both have large brick industries If stiff extrusion technology is used, maximum amounts of non-plastic (clay) material can be used With this technology 30-60% of fly-ash can be used in the production of bricks. This is a wonderful way to recycle a substance that has no other use, is very hard to dispose of, and has terrible environmental and health effects Sources Used http://www.teriin.org http://www.hinduonnet.com/thehindu/mp/2002/ /10/07/stories/2002100701530400.htm http://www.priyabrick.com/mbp.htm http://www.cleanerproduction.com/sectors/subs ectors/clay.html http://www.fao.org/inpho/vlibrary/s1250e/S1250 E07.htm http://www.ebrd.com/about/policies/enviro/sect oral/construc/brick.pdf http://www.scerp.org/scerp/projects/AQ95_9.ht ml