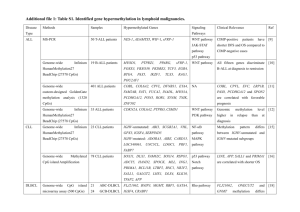
ISCModel6
advertisement
Introduction to the ISC Model Marti Blad NAU College of Engineering Model Overview The Industrial Source Complex (ISC) model version 3--key regulatory model developed by EPA Gaussian plume model appropriate for complex mixture of sources Chemical reactions can only be treated in rudimentary way, thus… Model best applied to non-reactive pollutants 2 Model Overview Short-term and long-term versions of ISC3 model Differ in averaging times available for data output Short-term model also has more sophisticated capabilities for estimating effects of terrain and deposition ISC-PRIME ISC-AERMOD Plume Rise Model Enhancements Based on more-sophisticated treatment of boundary layer dynamics than possible with Gaussian plume model GUI Courtesy of Lakes Environmental 3 Applications ISCST3 Model widely used by EPA, state and local environmental agencies Models effects of various pollution sources Model can calculate average concentrations over time periods of an hour to a year Appropriate modeling uses include Demonstrating sufficiency of proposed State Implementation Plans (SIPs) for criteria air pollutants Predicting air quality impact of new regulated sources Supporting assessment of health impacts of air toxics 4 History Several revisions to model, each adding new capabilities (without changing Gaussian plume assumptions at heart of model) ISCST3 has new Algorithms for wet and dry deposition Way of simulating area sources Method for simulating complex terrain 5 How To Get the Model Primary source for most up-to-date model is EPA’s Support Center for Regulatory Air Quality Models (SCRAM) website www.epa.gov/ttn/scram Site includes compiled, executable version of model for running on Microsoft Windows operating system 6 How to Get the Model (cont.) EPA version not particularly user-friendly No graphical interface--everything done with input/output files More user-friendly interfaces designed by several private vendors To locate, Web search “ISCST3” 7 ISC Model outline Screens with multiple tabs for multiple inputs Control Pathway Source Pathway Receptor Pathway Meteorology Pathway Terrain Grid Pathway Output Pathway See each piece now in detail 8 Pathways in detail Control Pathway Dispersion options, specify pollutant, averaging times, terrain height options Source characteristics Source type: point, volume, open pit source release parameters Variable emission rate: season, month, hour Variables for deposition, settling & removal Variable source groups: single, combined 9 Pathways in detail (cont.) Receptor Pathway Network of gridded receptors Cartesian & polar Where to calculate concentrations Specify discrete receptor location Flagpole Elevated receptors: terrain above stack base Plant boundary distances 10 Pathways in detail (cont.) Meteorology Specify met data input files Station location and other indicators Anemometer height Wind speed categories Wind profile exponents Vertical temperature gradients Data time period to process 11 Pathways in detail (cont.) Terrain Grid Used to calculate dry depletion in elevated or complex terrain Output Pathway Summary of high values by receptor For each averaging period and source group Overall maximum values Find all occurrences over threshold value Plot files 12 Site Maps for Modeling One degree DEMs http://edcwww.cr.usgs.gov/glis/hyper/guide/1_dgr_ dem 7.5 degree DEMs http://edcwww.cr.usgs.gov Format notation DXF. = autoCAD DLG. = USGS digital line graph LULC.= USGS land use and land coverage BMP.= Bitmap images SHP. = ArcView shapefiles 13 Dispersion Coefficients 14 Met Data Needed for the ISCST3 15 Surface Roughness 16 Noontime Albedo 17 Albedo Values for Model Inputs 18 Daytime Bowen Ratios by Land Use 19 Parameters not Frequently Seen Anthropogenic heat flux Surface heating caused by humans Rural = 0.0 Watts/m2 Urban (large) = 20 Watts/m2 Rammet View has many inside program Fraction of net radiation absorbed @ ground Rural = 0.15 Urban = 0.27 20 Other Dispersion Models Models-3 CMAQ Will provide more advanced chemistry for reactive pollutants Plume within grid to more realistically simulate dispersion at multiple scales 21