Tertiary Wastewater Treatment: Effluent Polishing & Removal
advertisement

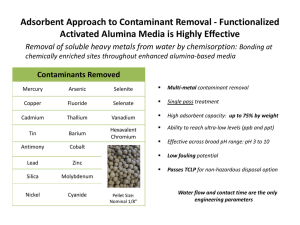
Wastewater treatment steps Primary: solids removal (physical) Secondary: BOD treatment (biological) Tertiary: Effluent polishing, Nutrient and Toxins Removal (chemical, also possibly physical and biological) Tertiary (advanced) treatment Secondary treatment: removes 85% - 95% of BOD and TSS removes 20% - 40% P removes 0% - 50% N Tertiary treatment: removes over 99% of pollutants very high cost Goals of tertiary treatment Effluent polishing (BOD, TSS) Nutrient removal (N, P) Toxin removal (pesticides, VOCs, metals) Effluent polishing Removal of additional BOD and TSS Granular media filter beds gravity or pressurized require frequent backwashing air-washing Microstraining/ microscreens 20-micrometer openings Nutrient management Nutrient = plants require them for growth Potential problems from nutrients: water quality aquatic ecosystem human & animal health Approaches: dilution treatment (biological or physicochemical) plant uptake Nitrogen Biochemically interconvertable forms : organic N (proteins, urea) ammonia gas (NH3) ammonium ion (NH4+) nitrate (NO3) nitrite (NO2) elemental N2 gas (78% of air) Mobile (esp. nitrate) Limiting nutrient in salt waters Nitrification-denitrification Two-step biological method Step 1: Aerobic Nitrification Ammonia to nitrate conversion now nontoxic to fish m.o.s: Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter Step 2: Anoxic-anaerobic Denitrification nitrate to N2 conversion requires carbon source m.o.: Pseudomonas On-site biological methods Upflow anaerobic sand filter uses septic tank effluent as carbon source must monitor and manage recycle ratio: – too low: incomplete denitrification – too high: excess O2 shuts down denitrification 75% removal possible On-site biological methods... Aerobic chamber plus deep sand filter uses methanol as carbon source must manage methanol dosing rate 85% - 95% removal possible On-site biological methods... Bardenpho system uses wastewater as carbon source alternating anoxic and aerobic STRs must monitor and manage sludge recycle ratio Oxidation ditch endless loop of anoxic and aerobic zones less removal efficiency than Bardenpho Physical-chemical N removal Approach: convert all N to ammonia then treat the ammonia Three methods: Breakpoint chlorination Ion exchange Ammonia stripping Often impractical for on-site systems Ammonia stripping Two-step physical-chemical method Step 1: Raise pH to 10.5-11.5 convert ammonium ions to ammonia gas Step 2: Air-strip cascade wastewater countercurrent to air flow ammonia gas escapes to atmosphere Pro: less costly, no sludge or Cl by-products Cons: acids/bases, scale, freezing problems Phosphorus Forms: organic phosphorus orthophosphate (PO4) polyphosphates phosphorus-containing rocks Binds to soils and sediments Limiting nutrient in fresh waters Biological P removal Luxury uptake anaerobically- stressed m.o.s ingest more P than needed Methods: Bardenpho Sequencing Batch Reactor – 1 tank, 5 steps – fill, aerate, settle, decant, idle Physical-chemical P removal Chemical precipitation (3 options) add alum (Al2SO4) to form aluminum phosphate add ferric chloride (FeCl3) add lime (CaO) Coagulation / flocculation Clarifier/settler More on P precipitation Pros: can also serve as effluent polishing step if added after 2ndary treatment lime can aid ammonia stripping too Cons: expensive: more tanks, clarifiers, and filters must closely manage pH, chemical dosing, and precipitate removal produces a LOT of sludge Toxin treatment and removal Types of toxins Organics (pesticides, solvent, petroleum,...) Metals (lead, cadmium, mercury,...) Sources of toxins Impact on wastewater treatment systems when toxins hit Toxicity testing Test for specific chemicals Bioassays (response of fathead minnow, water flea, others, over time) Human toxicity (carcinogenicity, acute or chronic disease) Toxin strategy Prevention Protection equalization basins holding tanks contingency plans Treatment no universal treatment method each toxin different Toxin Tertiary Treatment Organics: Biological treatment (incl. co-metabolism) Oil-water separator Air stripping Thermal treatment (incineration, desorption, distillation, evaporation) Chemical oxidation Sorption (activated carbon, kitty litter) Land farming Toxin Tertiary Treatment Metals: Chemical precipitation and filtration Biological transformation Sorption Solidification (cement, asphalt, plastic polymers) Encapsulation Plant uptake /phytoremediation (note sludge application implications)