ENERGY POLICY IN SOUTH EAST EUROPE
advertisement

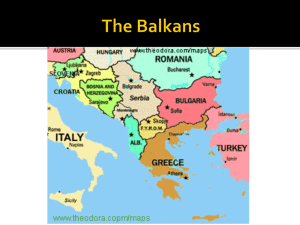
ENERGY POLICY IN SOUTH EAST EUROPE VENELIN TSACHEVSKY SAPPORO 2012 AIMS OF THE STUDY “ENERGY ECONOMICS IN SOUTH EAST EUROPE” • Analysis of the energy characteristics and energy development of the region • Review of the energy trends and the energy policy of the twelve SEE countries • Development and significance of the nuclear energy production in SEE • Trends and results of the regional energy cooperation • Role of the Energy Community • South East Europe as a transit corridor for the Europe-bound exports of oil and natural gas from Russia and the Caspian region. • In-depth analysis of the headway achieved in the implementation of the regional and Pan-European energy infrastructure projects • South East Europe’s prospects in terms of energy policy and development. TABLE OF CONTENTS PREFACE PART I: SOUTH EAST EUROPE AT THE START OF 21st CENTURY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. WHICH COUNTRIES CONSTITUTE SOUTH EAST EUROPE? SPECIFIC PLACE OF THE REGION IN EUROPE GOVERNANCE AND POLITICAL TRANSFORMATION ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT REGIONAL COOPERATION PARTICIPATION IN THE EUROPEAN INTERGATION TABLE OF CONTENTS PART II: SOUTH EAST EUROPE’S ENERGY POTENTIAL 1. ENERGY RESOURCES 2. PRODUCTION, CONSUMPTION, IMPORTS AND EXPORTS OF ENERGY RESOURCES 3. ELECTRICAL ENERGY PRODUCTION 4. NUCLEAR ENERGY 5. OTHER SOURCES OF ELECTRICITY 6. ENERGY MIX AND ENERGY IMPORT DEPENDENCE 7. ENERGY SECTOR OF SEE ECONOMY TABLE OF CONTENTS PART III: SOUTH EAST EUROPE’S ENERGY SECTOR AND ENERGY POLICY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. ALBANIA BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA BULGARIA CROATIA GREECE KOSOVO REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA MONTENEGRO ROMANIA SERBIA SLOVENIA TURKEY TABLE OF CONTENTS PART IV: REGIONAL COOPERATION IN THE ENERGY DOMAIN 1. 2. EVOLUTION OF THE REGIONAL ENERGY COOPERATION THE ENERGY COMMUNITY PART V: REGIONAL ENERGY INFRASTRUCTURE PROJECTS 1. 2. 3. 4. SEE AS A TRANSIT ENERGY CORRIDOR THE BIGGEST OIL INFRASTRUCTURE PROJECTS THE SOUTHERN GAS CORRIDOR SOUTH STREAM GAS PIPELINE PROJECT CONCLUSION THE BALKAN PENINSULA SOUTH EAST EUROPE (SEE) COUNTRIES* * Without Kosovo that is in process of international recognition COUNTRIES WITH TERRITORIES FULLY OR PARTIALLY BELONGING TO THE BALKAN PENINSULA COUNTRY Albania Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Kosovo Republic of Macedonia Montenegro Greece Serbia Croatia Slovenia Romania Turkey Italy Territory situated within the Balkan peninsula (%) 100 100 100 100 100 100 84 74 49 27 9 3 0.2 BASIC DATA FOR SEE COUNTRIES (2010) COUNTRY Territory Population GDP in PPP/ GDP per capita (1000 km2) (mln Nominal value in PPP/Nominal inhabitants) ($ bln) value ($) Albania Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia Greece Kosovo Montenegro Republic of Macedonia Romania Serbia Slovenia Turkey SEE 28.7 51.1 110.9 56.6 131.5 10.9 13,8 25.7 238.4 77.5 20.3 783.6 1549.0 3.2 3.8 7.3 4.4 11.3 2.2 0.6 2.1 21.5 7.3 2.1 72.5 138.3 26.3/11.6 30.2/16.2 90.8/44.8 78.0/59.9 322.5/305.4 4.4/3.2 6.5/3.9 19.3/9.6 252.2/161.6 79.9/38.9 56.3/46.4 960.5/741.8 1926.9/1443.2 7 400/3 700 7 800/4 300 12 800/6 300 17 700/13 700 28 400/27 300 6 600/3 100 10 700/6 000 9 700/4 400 11 900/7 500 10 800/5 200 28 000/23 700 13 500/10 400 13 800/9 630* SEE share in Europe (%) 7.7 11.0 5.7/3.7 49.0/35.0** * Average level ** Percentage of the average level in Europe Source: National Statistics of the SEE countries; IMF, 2012 GDP PER CAPITA* IN SEE ( Index ЕС = 100 ) Country 2000 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 Greece Slovenia Romania Bulgaria Croatia Turkey Republic of Macedonia Montenegro Serbia Bosnia and Herzegovina 84 80 26 28 49 42 27 35 30 20 90 88 42 40 60 45 31 40 33 29 93 91 47 44 63 47 34 43 36 30 94 87 46 44 62 46 36 41 36 31 90 85 47 44 61 49 36 41 34 30 82 84 49 45 61 52 36 43 35 29 Albania SEE 18 43 23 47 26 50 28 48 28 48 31 50 * Evaluated on Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) basis Source: Eurostat, GDP per capita in PPS, 2012 SEE COUNTRIES AND EU • Four countries (Greece, Slovenia, Bulgaria and Romania) are members of the EU. Their accession has extended the EU boundaries to the Black Sea and has increased the Union’s policy potential in SEE. The total size of territory and population of those four countries constitute one-third of SEE and their gross product accounts for more than 35% of the region’s volume. • Croatia has concluded its accession negotiation and has signed the Accession Treaty. It will join the EU as the 28th member state upon the completion of the ratification process which is expected to happen on 1 July 2013. • Turkey is currently conducting accession negotiations with the EU. There has been specified no closing date. Its membership is uncertain since some EU member states consider that Turkey should be granted privileged partner status instead of a full-fledged EU membership. • Four countries (Republic of Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia and Albania) have filed an application for EU membership. Three of them (except for Albania) have already been granted EU candidate country status. The next step is the start of formal negotiations on EU membership. • The only countries that haven’t submitted applications for EU membership are Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kosovo . SEE ENERGY PROFILE • SEE is relatively poor in natural energy resources. Only coal reserves are larger, whereas discovered oil and natural gas reserves are small and constantly diminishing as a result of their exploitation • About two-thirds of lignite coal deposits are in six countries Kosovo, Turkey, Greece, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia and Bulgaria. • Almost 90% of the oil reserves are in Romania, Turkey and Albania • About 95% of the natural gas deposits are in Romania, Serbia and Croatia • Between 2000-2010, the tendency was toward increasing the share of oil (4%) and natural gas (3%) in the energy balance at the expense of the use of coal • In 2011 oil and petroleum satisfied 33% of energy consumption, coal 30 %, natural gas 22%, hydro power 6%, nuclear power 4%, and other sources (biofuel, geothermal, wind, solar, etc.) 5%. ENERGY SOURCES IN SEE (Proven reserves, Production, Consumption, Imports, Exports) INDICATOR COAL OIL Proven reserves Share in Europe (%) Production Share in Europe (%) Consumption Share in Europe (%) Imports Share in Europe (%) Exports Share in Europe (%) 3326 (1) 15.0 282982 (2) 28.0 321363 (2) 27.0 40797 (2) 15.0 653 (2) 0.2 1284 (3) 3.5 220.3 (4) 2.5 1726.7 (4) 9.5 1783.0 (4) 2.5 469.0 (4) 0.2 NATURAL GAS 278.5 (5) 7.0 15700 (6) 3.0 66345 (6) 6.0 47075 (6) 8.5 1250 (6) 0.1 (6) (1) Million tons (2) 1000 tons (3) Billion barrels (4) 1000 barrels per day (5) Billion cubic meters (6) Million cubic meters Source: Compiled by the author on data from the National Energy Statistics of SEE countries, 2012; International Energy Statistics,U.S. Energy Information Administration, 2012; CIA World Factbook, 2012 NUCLEAR ENERGY IN SEE (2011) Country Number of reactors Capacity (МW) Output (billion kWh) Share in electricity production (%) Bulgaria 2 1920 16.3 32.6 Romania 2 1400 11.7 19.0 Slovenia / Croatia 1 730 5.9 43 / 15 SEE 5 4050 33.9 7.4**** SEE share in Europe (%) 2.7* 2.5** 3.0*** * In 2012 the number of functioning nuclear energy reactors in 17 European countries was 186, including 5 in Russia’s territory within Asia. The SEE share is percentage of the number of nuclear energy reactors in Europe. ** In 2012 the total capacity of NPP in operation in Europe, including Russia, was 162 000 MW. The SEE share is percentage of the total capacity of NPP in operation in Europe. *** In 2011 the total electricity production in Europe, including Russia, was 1136.8 billion kWh. The SEE share is percentage of the electricity production in Europe. **** Share of nuclear energy generation in the total electricity production in SEE (%). Source: Compiled by the author from data of the European Nuclear Society (ENS), Nuclear Power Plants in Europe, 2012, Nuclear Energy Institute (NEI), World Nuclear Generation and Capacity in 2011, Energy Statistics of the SEE countries, 2012. TOTAL PRIMARY ENERGY SUPPLY IN SEE COUNTRIES Country Total primary energy (KTOE)* Oil share (%) Natu Hydro ral Share gas (% ) share (%) Albania Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia R. Macedonia Montenegro Serbia Slovenia Greece Romania Turkey 1717 49.6 0.4 5953 17480 8702 2781 750 14450 6969 29436 34406 97661 23.9 37.1 52.0 35.5 37.0 27.1 35.6 53.3 23.2 29.8 3.0 14.7 29.3 2.4 0 9.6 11.5 10.0 30.6 29.6 Biofuels and Waste Share (%) Nuclear Share ( %) Coal and Peat share (%) - Geother mal/ Solar/ Wind Share (%) 0.2 26.2 13.4 8.6 1.2 7.0 4.1 20.5 6.0 5.6 1.5 12.0 3.2 2.9 3.8 4.4 7.4 5.0 2.0 5.0 3.4 11.2 4.8 20.9 20.7 8.9 - 1.2 0.2 0.4 0.5 0.3 1.9 1.5 0.1 2.2 65.2 37.9 6.2 52.0 37.0 55.0 19.7 28.6 21.4 30.5 4.4 * 2009, in Kilotons of Oil Equivalent (KTOE) Source: Compiled by the author from data of the National Energy Statistics of SEE countries, 2012; 2009 Energy Balances for the countries in the World, International Energy Agency, 2012; Energy profiles of SEE countries, Clean Energy Information Portal, 2012. SHARE OF RENEWBLE ENERGY (in gross final energy consumption) Country 2005 2009 2010 Albania Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia Greece Republic of Macedonia Romania Slovenia Serbia Turkey SEE 38.0 11.0 9.5 14.5 7.0 11.5 17.6 16.0 7.5 9.0 11 39.5 11.5 11.9 13.2 8.1 12.0 22.4 18.9 8.0 10.0 12 39.5 11.5 13.9 14.6 9.2 12.0 23.4 19.8 8.5 10.5 12.5 EU 9.0 11.7 12.5 *Renewable Energy Sources (RES) cover solar thermal and photovoltaic energy, hydro (including tide, wave and ocean energy), wind geothermal energy and biomass (including biological waste and liquid biofuels) ** Author’s assessment from data of the Energy National Statistics. Source: Eurostat, June 2012. ENERGY DEPENDENCE* OF SEE COUNTRIES COUNTRY Bulgaria Greece Slovenia Romania Croatia Republic of Macedonia Turkey Bosnia and Herzegovina Albania Montenegro Serbia Kosovo SEE 2000 46.5 69.5 52.5 22.0 53.0 2005 47.5 68.5 52.0 27.5 58.5 2008 52.0 73.5 55.0 28.0 60.0 2009 45.34 68.0 48.0 20.0 51.0 2010 40.5 69.0 49.0 22.0 52.0 40.5 66.0 43.5 72.0 46.0 72.0 45.0 70.5 44.0 69.0 30.0 25.0 34.0** 34.0** 30.0 55 32 28.0 42.0** 35.0** 32.0 62 36 30.0 52.0 36.0 32.0 65 34.0 28.0 51.5. 36.0 34.0 60 33.0 27.0 51.3 37.0 35.0 60 * Energy dependence shows the extent to which an economy relies upon imports in order to meet its energy needs. The indicator is calculated as net imports divided by the sum of gross inland energy consumption plus bunkers. ** The data is for the former state Serbia and Montenegro. Source: Compiled by the author from data of the National Energy Statistics of SEE countries, 2912; Eurostat, Energy Dependence, 2012. ENERGY SECTOR IN THE SEE ECONOMY (2010) • The energy sector’s share in the SEE Gross Product is about 7%. Its share in the total annual regional investments accounts for 15-16% • The total turnover of all SEE energy companies is EUR 100 – 120 billion. Companies from seven SEE countries ranks among the 20 leading energy companies in the region. Turkey, Greece and Romania provided four companies each, Bulgaria – three, Serbia and Croatia – two each and Slovenia – one. As many as fifteen of them operates in the field of oil and natural gas, the remaining in the electricity sector. Each of them have an annual turnover of more than EUR 1 billion. • The top 20 SEE energy companies have a total annual turnover of around EUR 70 billion. • The six out of the ten biggest SEE companies in the economy operates in the energy sector • The majority of the SEE big energy companies are either affiliates or having a large investment participation of non-SEE energy companies – Gazprom, Lukoil, OMV, RWE, Shell, Chevron, MOL, etc. • Due to the economic recession since 2009 the energy consumption dropped by one third, the energy imports by one fifth. The investments decreased more than twice. At the beginning of the present decade the energy sector is in stagnation or in a slow and unstable recovery THE BIGGEST ENERGY COMPANIES IN SEE (2010) Company Country Field Sales (EUR billion) 1.Tüpraş 2. Hellenuc Petroleum 3. Aegean Marine Petroleum 4. Motor Oil Hellas 5. Public Power Corporation 6. Eüaş Elektrik Üretim A.S. 7. OMV Petrom SA 8. INA Industrija Nafte 9. Lukoil Neftochim Burgas 10. Petrol Group Turkey Greece Greece Greece Greece Turkey Romania Croatia Bulgaria Slovenia Petrol/natural gas Petrol/natural gas Petrol/natural gas Petrol/natural gas Electricity Electricity Petrol/natural gas Petrol/natural gas Petrol/natural gas Petrol/natural gas 10.8 8.5 7.5 6.2 5.8 4.5 3.6 3.3 2.8 2.5 Source: Compiled by the author from data of the National Energy Statistics of SEE countries, 2012 THE ENERGY COMMUNITY ENERGY COMMUNITY (BASIC INFORMATION) • • • • Energy Community Treaty was signed on 25 October 2005 and entered into force on 1 July 2006 Institutions: Ministerial Council; Permanent High Level Group; Electricity, Gas, Oil and Social Forums; Energy Community Regulatory Board; Energy Efficiency, Renewable Energy, Environment and Regional Energy Strategy Task Forces; Secretariat Membership: 28 countries, incl. Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Republic of Macedonia, Serbia, Croatia, Montenegro, Kosovo (contracting parties), Greece, Slovenia, Bulgaria, Romania (participants) and Turkey (observer) Aims: – create a stable regulatory and market energy framework capable of attracting investment in gas networks, power generation, and transmission and distribution networks – create a single regulatory space trade in Network Energy – enhance the security of supply of the single regulatory space – improve the environmental situation in relation to Network Energy and related energy efficiency, foster the use of renewable energy, and set out the conditions for energy trade in the single regulatory space – develop Network Energy market competition on a broader geographic scale and exploit economies of scale THE ACHIVEMENTS OF THE ENERGY COMMUNITY (2006 – 2012) • • • • • • • Adoption of a Common Energy Community Framework Program prescribing measures for adaptation and implementation of the acquis, liberalization of the electricity and natural gas market and establishment of a trans-national energy market in SEE region. Progress in the implementation of Directive 2001/77/EC on the promotion of electricity production from RES in the internal electricity market, Directive 2003/30/EC on the promotion of the use of bio fuels or other renewable fuels for transport, Directive 2003/54/EC on the creation of a single electricity market, Directive 2003/55/EC on the creation of a single natural gas market, Directive 2004/67/EC concerning measures to safeguard security of natural gas, Regulation 1775/2005/EC on conditions of access to the natural gas transportation networks, etc. Adoption of a list of 10 major Energy Investment Projects in SEE. Another 22 projects are carried out with the technical assistance within the Western Balkans Investment Framework (2010). Proposal of the Gas Ring Concept providing for an increase of the share of the natural gas in the power generation mix and a help for the Western Balkan countries to comply with their environmental obligations in the context of the Common Energy Community framework (2010). Adoption of the EU’s third internal energy package including rules on unbundling, certification of the transmission system operators from third countries and clarification of the Energy Community institutions’ role in their implementation (2011). Adoption of a Plan for Gas Infrastructure Development (2011) Initiative for adoption of Comprehensive long term energy strategy (2011) THE GAS RING IN THE WESTERN BALKANS RUSSIA’S SHARE IN THE OIL AND NATURAL GAS IMPORTS OF SEE COUNTRIES (2010)(in %) Country Albania Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia Greece Republic of Macedonia Montenegro Romania Slovenia Serbia Turkey Crude oil 20 100 100 60 40 60 65 35 20 70 35 Natural gas 100 100 96 57 100 90 100 47 99 46 ROUTE OF NABUCCO AND NABUCCO WEST PIPELINES KEY FACTS ABOUT NABUCCO WEST • Participant countries: Turkey, Bulgaria, Romania, Hungary, Austria, Germany • Route: From the Turkish – Bulgarian border across Bulgaria, Romania and Hungary to Austria • Length: 1 300 km • Capacity: 10 - 16 billion cubic meters of natural gas per year • Cost: EUR 5 billion • Phase of implementation in mid-2012: In preparation • Construction period: Second half of 2013 - end of 2017 ROUTE OF THE TRANS – ADRIATIC GAS PIPELINE FROM GREECE TO ITALY KEY FACTS ABOUT TRANS-ADRIATIC PIPELINE • Participant countries: Greece, Albania, Italy, Switzerland, Norway, Germany • Route: From Thessaloniki in Greece through Albania and across the Adriatic Sea to the Italian city of Brindisi • Length: 520 km • Capacity: Up to 20 billion cubic meters of natural gas per year • Cost: $ 2.3 billion • Phase of implementation in mid-2012: In preparation • Date of completion: 2017 ROUTE OF THE TRANS-ANATOLIAN GAS PIPELENE (TANAP) KEY FACTS ABOUT TRANS-ANATOLIAN PIPELINE • Participant countries: Azerbaijan, Georgia, Turkey • Route: From Shah Deniz-II gas field in Azerbaijan across Turkey to the Turkish – Bulgarian border • Length: 2 000 km • Capacity: 16 - 24 billion cubic meters of natural gas per year • Cost: EUR 5 - 7 billion • Phase of implementation in mid-2012: In preparation • Construction period: Fourth quarter of 2013 – end of 2017 ROUTE OF SOUTH STREAM GAS PIPELINE KEY FACTS ABOUT SOUTH STREAM PIPELINE • Participant countries: Russia, Italy, Turkey, Bulgaria, Greece, Serbia, Hungary, Slovenia, Austria, Croatia, possibly Romania, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republic of Macedonia • Route: From Russia across the Black Sea to Varna, through Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovenia and Austria to Northern Italy. Deviations to Greece, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, possibly Republic of Macedonia • Length: 3 500 km • Capacity: 16 - 63 billion cubic meters of natural gas per year • Cost: EUR 16 billion • Phase of implementation in mid-2012: In preparation • Construction period: End of 2012 – 2015 ENERGY POLICY STRATEGIC PRIORITIES IN SOUTH EAST EUROPE (2010-2020) • Increasing and diversifying the production of the country’s own energy resources; • Reducing energy import dependency; • Energy market restructuring according to the market principles; • Increasing energy sector efficiency in conformity with the environmental requirements; • Increasing the share of RES in the energy balance; • Broadening the energy sector cooperation with the countries from SEE and the EU, participation in regional and European energy infrastructure projects. The financial costs related to the national energy strategies objectives by 2020 amount to EUR 150 - 180 billion. Up to 2020, the SEE energy sector will require financial resources in the range between EUR 240 and EUR 300 billion MAIN OBJECTIVES OF BULGARIA’S ENERGY STRATEGY BY 2020 - 2030 • Primary energy generation will grow by 10% in 2020 and 16% in 2030 • Energy demand will rise by 7.5% in 2020 and 9.5% in 2030 • The consumption of fossil energy resources and oil will go down, while natural gas use will increase by 6.7% in 2020 and 15.2% in 2030. • The nuclear energy consumption will make the most noticeable leap: 14.3% by 2020 and 35.2% by 2030. • The nuclear power units will account for 22.3% of the generated electricity in 2020 and for 30% in 2030. • The electricity consumption will go up respectively by 9% and by 23%. The production will exceed this rate increasing by 13% and by 32% whereby it will not only meet the national demand but also allow for a surge in exported volumes. • The share of RES in the final energy consumption which was 10.3% in 2005 will climb to 12.7% in 2020 and 13% in 2030. The RES share in electricity consumption will amount respectively to 10.6%, 16.5% and 16.7%, while in the transport sector its distribution will be 1.1%, 1.9% and 2.8% • The energy import dependence will be reduced from 49.5 in 2010 to 45.8% in 2020 and 43.3% in 2030. SCENARIOS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE ENERGY SECTOR IN SEE IN 2010 - 2020 Indicators Annual growth of energy production (% ) Foreign investments and financial aid (billion euro) Number of Regional projects completed New nuclear energy capacities SEE countries having NPP up to 2020 Nuclear energy share in gross electricity production (%) Coal/Oil/Nat.gas/RES share in energy consumption (%) Energy import dependence (%) First (optimistic) scenario 1.5 Second (realistic) scenario 1.0 Third (pessimistic) scenario 0.5 120 - 150 70 - 80 under 50 3 – 4 (incl. South Stream and Nabucco West pipelines) 4 reactors in Akkuyu NPP, 2 reactors in Cernavoda NPP and possibly 2 reactors in Kozloduy NPP Bulgaria, Romania, Slovenia, Turkey and Slovenia - Croatia (jointly), 10 - 12 1 -2 (incl. South Stream or Nabucco West pipelines) 4 reactors in Akkuyu NPP or 2 reactors in Cernavoda NPP none Bulgaria, Romania, Slovenia, Slovenia Croatia (jointly), Turkey Bulgaria, Romania, Slovenia, Slovenia Croatia (jointly) 8-9 5-6 25/28/25/15 28/30/24/12 32/35/22/10 55 – 58 60 65 none TOSHIBA’S ENERGY PROJECTS IN BULGARIA (2011-2012) • • • • • • January 2011: Toshiba and the Bulgarian Energy Holding (BEH) signed a memorandum for the development of “smart electric grids” in Bulgaria and the introduction of electric cars based on renewable energy sources. January 2011: Toshiba announced a project to invest EUR 37.6 million in a 10-MW solar park near the town of Yambol. The solar park will provide electricity to 2000 households. May 2011: Toshiba completed a project for the rehabilitation of part of the production capacity of the largest Bulgarian state-owned thermal power plant Maritsa Iztok 2. The unit’s life span has been extended by 25 years. July 2011: Toshiba made a $ 300 million bid to construct a couple of new thermal power plants in Maritza Iztok with a capacity of 500 MW. April 2012: During her visit to Japan the Chairperson of the Bulgarian National Assembly Mrs Tsetska Tsacheva invited Toshiba to join the construction of an alternative gas power plant at the site of Belene NPP, a project quitted by the Bulgarian government a month earlier. August 2012: An agreement was signed whereby the American energy company Westinghouse will conduct the techno - economic analysis for the construction of a new unit in the Bulgarian nuclear power plant in Kozloduy. One of the options is Toshiba, the main investor in Westinghouse, to provide a nuclear reactor with a capacity of 1 000-1 200 MW. THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION