Integrated Catchment Management Key Elements
advertisement
Integrated Catchment Management Key Elements - Julie Burke Integrated Catchment Management: What is it? › Management of a watershed › Taking account of all competing interests: Economic use of land and water Environmental concerns Social and cultural uses and values › Taking advantage of knowledge in all disciplines: Water engineering, economics, ecology, agricultural studies, forestry, sociology etc Integrated Catchment Management: Key Elements › driving issues › identification of assets to be protected › mechanisms to manage trade-offs and processes to manage negotiations › measurable and simple objectives set › Assessment of scenarios against objectives › clear roles, responsibilities and accountabilities › capacity of partners to carry out roles › mechanisms to monitor, evaluate and improve the approach In the Murray-Darling Basin, the Driving Issues are › Water sharing › Water quality › Riverine Ecosystem Health › Biodiversity Basin assets in the Broad (Goals) › Healthy Rivers › Healthy Ecosystems › Productive and Innovative Industries › Healthy regional communities Some Specific Basin assets › Adelaide’s drinking water › Barmah-Millewa Forest and Narran Lakes (Ramsar sites) › Murray Irrigation Districts › Lake Victoria (cultural site) Charleville Warrego Balonne QUEENSLAND Brisbane Border Barwon Moree Bourke SOUTH AUSTRALIA Darling Meninde Lakes Morgan Macquarie Dubbo Menindee NEW SOUTH WALES Forbes Lake Vi ctoria Lachlan Mildura Adelaide Murray Sydney Murrumbidgie Murray Bridge Canberra Swan Hill Albury VICTORIA Melbourne 200 km Managing Trade-offs › Need to limit degradation of assets › MDB will set limits on degradation of: » » » » Water quantity and flow Water quality Riverine health Biodiversity › MDBC calls these limits “targets” › These targets are a numerical form of objective against which all scenarios can be tested Managing Trade-offs – Targets to protect assets Within-valley target at site 4: Protects town water supply 5. Management target for sub-catchment: Revegetation of 20% of sub-catchment area 4 Within-valley target at site 2: Protects irrigation water supply Major Town 5 2 Basin objective Major Wetland 3 Catchment objectives Irrigation District 1 Within-valley target at site 3: Protects wetland ecosystem End of valley target at site 1 Protects downstream Achievement of the target is the OBJECTIVE Protection of the assets is the desired OUTCOME Assets identified and targets set at different scales Scale determines who manages negotiations and agrees targets Basin -------------------------------- Commission Catchment---------------------- States Sub-catchment --------- CMOs Managing Negotiations › Identify stakeholders relevant to the issues and the scale › Involve them in setting of targets, scenario development and assessment › Everyone must have access to the same information Assigning Roles › Assign and agree roles and responsibilities › Ensure mechanisms for reporting against responsibilities to all stakeholders › Accountability, not blame Capacity Building › Capacities must match roles and responsibilities › Capacities include: › › › › › › leadership legal and institutional financial technical knowledge base cultural Knowledge Required at many stages › Assessment of concerns (audit) › Understanding of processes and drivers (economic, environmental, social) › Modeling of scenarios, including “do nothing” › Monitoring and Evaluation Monitoring and Evaluation › Monitor progress towards Objectives and Outcomes › Monitor and evaluate the PROCESS › Inform all stakeholders › Learn from successes and failures to inform future actions › all decisions are “interim” and must be tested Issues Assets Trade-offs Measurable and simple objectives Scenario Assessment
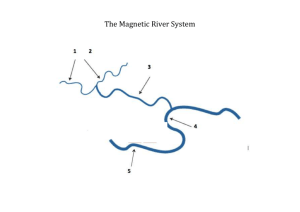






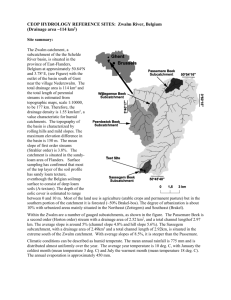

![Georgina Basin Factsheet [DOCX 1.4mb]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006607361_1-8840af865700fceb4b28253415797ba7-300x300.png)

