Summary Presentation - Kimley-Horn
advertisement
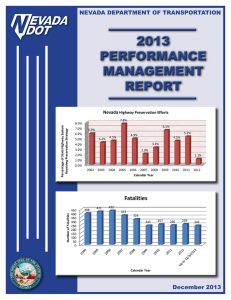
Statewide Integrated Transportation Reliability Program Executive Summary Presentation Overview Project Highlights Addressing Reliability in Nevada Key Outcomes Call to Action What is Congestion? Recurring – Day-to-day bottlenecks – We know when to expect them – Often a capacity issue Non-recurring – Unexpected – Delays that exceed typical congestion levels – Compounds the capacity issue Causes of Congestion The Reliability Connection Congestion Typical Measures: Level of Service Volume/Speed Delay Travel Time RELIABILITY Impacts of Congestion on the Traveler ITRP Development Process Reliability Focus Regions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Las Vegas Metropolitan Area Reno/Sparks/ Carson City/Tahoe I-80 Corridor Rural Corridors Statewide Stakeholder Involvement Introductory Presentations – to stakeholders in northern and southern Nevada as part of already established meetings One-on-One Meetings – with Cities, Counties, MPOs, and Highway Patrol in the state to better understand the current plans and processes Stakeholder Workshops – to gather stakeholders together to review existing conditions, best practices, and strategize about potential integration needs within Nevada A Project Website – to provide a one-stop resource for project deliverables, meeting dates, and important links to other web sites – Website is: http://www.kimleyhorn.com/projects/NevadaITRP/index.shtml – can be accessed through the NDOT website (www.nevadadot.com) and clicking on the ‘Major Projects & Corridor Studies’ link ITRP Focus Area Intersection Diagram ITRP Focus Area Intersection/Resource Diagram Reliability Issues and Impacts Las Vegas Metropolitan Area – Recurring congestion • Unique peak travel periods • Capacity – – – – – – – – Infrastructure deployment Incident management – TIM Coalition Land use planning and future expansion Regional systems and coordination with local systems Access management Traveler information Transit/Multimodal FUNDING Reliability Issues and Impact Reno/Sparks Metropolitan Area – Recurring congestion – Infrastructure deployment and integration – Incident management – Capacity – Land use planning – Regional systems – Access management – Traveler information – Transit/Multimodal – FUNDING Reliability Impacts/Issues I-80 Corridor – Weather/fire/disaster response – Freight traffic – Limited infrastructure – CA/UT coordination – Limited alternate routes – Traveler information – FUNDING Gap Analysis Category ID by Region GAP = a system, functional, or policy deficiency that is impacting the ability of agencies to provide reliable travel time Gap Analysis Category ITRP Regions Statewide (including Rural Corridors) Southern Nevada (Las Vegas Metro) Northern Nevada (Reno/Sparks /Carson City/ Lake Tahoe) I-80 Corridor Capacity Improvements and TDM Traffic Incident Mgmt Work Zone Mgmt Traveler Information Planning and Policy Operations and Mgmt * * * Trends in Gaps Across all regions: Sharing incident and weather information with multiple agencies Lack of detour route planning Need to get more information out to travelers Inability to address near-term operations needs Operations and process issues Equipment lifecycle/replacement Performance Measurement – How is it Defined ? Collection, analysis, and reporting of data to track and assess resources used, outcomes, and if goals are achieved Why measure performance? Internal Benefits – Set quantifiable goals and document accomplishments – Improve operations by understanding impacts – Improve information provided to decision-makers to support more effective long-range planning External Benefits – Evaluate conditions from a customer/traveler perspective – Provide public accountability/traceability Outcome-Based Performance Measures Outcome-based performance measures provide policy makers, elected officials, and the public with information regarding the reliability of roadways in Nevada. These measures describe the ‘state of the roadway system’. Activity-Based Performance Measures Activity based performance measures are designed for use by NDOT staff responsible for operating and maintaining the state roadway system These are measures of activities that indirectly improve the reliability of the transportation system Reporting Can be done on an annual or semiannual basis Reporting should include: – An overview of goals – Key progress and improvements made during the reporting periods – Overview of trends affecting transportation Current reporting – FAST OMC – NDOT publications Reliability Focus Areas What are the issues? Large gaps associated with the reliability focus area What needs to happen? Strategies for addressing the gaps How do we get there? Processes, policies, and projects Why are we doing this? Anticipated benefits on reliability How do we measure our success? Performance measures for monitoring success Incident Management Infrastructure Sharing Resources Transportation Policy Traveler Information Work Zone Management What does “effort” mean? Factors to determining level of effort involved in implementing a strategy: – Number of agencies involved – Required data that needs to be collected from different sources – Changes to legacy processes, policies, or procedures – Level of approval required in each agency – Cost requirements What does “impact” mean? Factors to determining level of impact involved in implementing a strategy: – Measurable reduction in delay – Measurable improvement to LOS – Enhances information to travelers – Tangible improvements on a regional level – Implements policies that have a direct impact on improved operations Effort and Impact on Reliability Low Effort High Impact High Effort High Impact Strategy 2 • Needs training and new staff • Addresses many needs Strategy 1 • Does not require new staff • Does not affect many reliability issues Low Effort Low Impact IMPACT MEASURE EFFORT MEASURE High Effort Low Impact Implementation Strategies Process – programs, actions, change in steps or activities to deliver a specific service or reach a specific goal – Could be high impact and low/no cost – Example: expand TIM to local public safety Policy – formal policy change at organizational, regional, or state level – Potential to be time consuming and challenging to obtain approval – Could make substantial changes to affect reliability Project – capital improvements, tools/technologies, deployments – Potential to have direct effect on levels of congestion – Could require availability of funding Statewide Strategies and Policy Highlights Alternate Route Plan for Freeways and State Highway Diversion Incident Clearance Program/Policy – Shift from “goal” to “policy” Centralized Database for Regional and Statewide Information – Support web, 511, private partner access, regional dissemination Traveler Information Business Plan Access Management Policy Northern Nevada Incident Management Strategies Alternate Route Plan for Freeways and State Highway Diversion Move forward with TIM Multi-state coordination/decision support for I-80 winter operations Northern Nevada Traveler Information Strategies Enhance reporting of real-time data – Urban and rural corridor CCTV Weather conditions reporting (multistate, multi-agency) Freight-focused traveler information Performance measures output document – Internal/external Establish robust local multimodal info for use on NV511 Northern Nevada Other Key Strategies Corridor system management plans – Identify operational gaps, plan for expansion, access management, stakeholder involvement MOUs for resource/land sharing – Equipment storage, faster response in rural areas ITS Infrastructure Plan – Potentially covered in Northern NV TMC project Adaptive strategies – Identify corridors, coordinate with BRT Northern Nevada Policies Regional access management policy Regional standards/joint maintenance of field equipment – NDOT Statewide Contract – Local agency equipment? Develop arterial work zone policies/programs – Inspection, enforcement Land use planning – Link with transportation infrastructure needs Southern Nevada Incident Management Strategies Alternate Route Plan for Freeways and State Highway Diversion – Builds on current FAST project – Agency focused Expand TIM to include local traffic engineering and law enforcement agencies in TIM Coalition – Focused outreach to local LE Arterial Incident Response Team Southern Nevada Traveler Information Strategies Enhance reporting of real-time data – Link travel time, volume and incident data – Expand/enhance automation of ADUS for local agency data Expand travel time program – Strategies for data collection Performance measures output document Establish robust local multimodal info for use on NV511 Southern Nevada Other Key Strategies Corridor communications master plan – Identify gaps, plan for expansion, plan for telecomm alternatives Revisit adaptive signal strategies on different corridors – May be more effective with unpredictable congested conditions Reinstate and revise TCIP program – Allocate funding for near-term operational and capacity enhancements Implement formal meetings with all traffic divisions in each agency – Coordinate on work zones, incident management issues, project development Southern Nevada Policies Regional access management policy – Already underway by RTC Develop arterial work zone policies/programs – Inspection, enforcement Land use planning policy – Link with transportation infrastructure needs Regional road impact fee – Evaluate district vs. regional vs. municipal options Implementation Plan Strategies placed or phased into: – Short-term: 1 to 2 year timeframe – Mid-term: 3 to 5 year timeframe – Long-term: 6 years and beyond The implementation schedule provides NDOT and partner agencies with a guide map for how to improve transportation reliability throughout the state by implementing specific strategies to effect change for the traveler Roles and Responsibilities in Implementing Strategies Lead Agencies – NDOT – RTC of Southern Nevada – RTC of Northern Nevada Lead Agency Responsibilities – Initiate and manage strategy – Allocate internal or external resources to develop strategy – Involve partner agencies – Provide education to key decisionmaking bodies Roles and Responsibilities in Implementing Strategies Partner Agencies – – – – – Cities Counties Public Safety Maintenance Others Partner Agency Responsibilities – Partner with lead agency for ownership of strategy – Provide input to and participate in strategy development – Provide data and inventory information where needed How to Move ITRP Forward Strategies can be shifted – based on changing circumstances surrounding strategy (timing, funding, other strategies to enable, etc.) Determine if strategy is process, policy, or project – guideline for strategies developed in plan or new strategies for future Determine status of implementation steps – that have been completed or ones that need to be completed to initiate strategy Begin process of project implementation outlined in “steps” category of table STATEWIDE SOUTHERN NEVADA I-80 NORTHERN NEVADA Contact Information John Domina – Nevada DOT PM jdomina@dot.state.nv.us Pierre Pretorius – Kimley-Horn pierre.pretorius@kimley-horn.com Lisa Burgess – Kimley-Horn lisa.burgess@kimley-horn.com