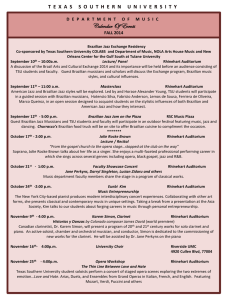
brazil nowadays
advertisement

Brazil's Infrastructure Framework AGENDA 1. BRAZIL NOWADAYS 2. BRAZILIAN GOVERNMENT'S STRATEGY 3. INVESTMENT OPPORTUNITIES 4. OVERVIEW OF BRAZILIAN BID PROCEDURES FRAMEWORK 5. PUBLIC AGREEMENTS 6. COMPLIANCE STRUCTURE BRAZIL NOWADAYS BRAZIL NOWADAYS Brazilian economy produces a wide range of manufactured goods: Many factors have forced the country to accelerate investments especially in infrastructure, such as: automobiles (3.3 million units in 2012) The Brazilian income growth aircraft sophisticated machines The social inclusion process BRAZIL NOWADAYS Joined the group of the most dynamic emerging countries of the world The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is currently among the ten largest in the world, either in nominal terms or in purchasing power parity Unemployment rate below 5% Living a period of rapid and sustained economic development, based on: production growth, soundness of fiscal and monetary institutions and investment, credit and consumption expansion; Market of over 100 million consumers with huge growth potential Vitality of entrepreneurial class and technological advances in the agriculture industry BRAZIL IN NUMBERS INCREASED INVESTMENT AS A PRIORITY INFLATION UNDER CONTROL STRENGTH OF THE EXTERNAL SECTOR 5th LARGEST GLOBAL MARKET IN 2020 MIDDLE CLASS SOCIETY LOWER INTEREST RATE REDUCED COSTS FOR INVESTMENTS The Government has put in place several measures aiming to reduce investments costs, among which the following stand out: FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENTS HIGH LEVELS EXPECTED GROWTH IN BUSINESS BRAZILIAN AGRICULTURE: NEED OF LOGISTICS source: http://www.estadosecapitaisdobrasil.com/mapas-do-brasil.php BRAZILIAN POPULATION: NEED OF LOGISTICS source: http://www.scp.rs.gov.br/upload/mapa_popula%C3%A7%C3%A3o_absoluta_brasil_2010(1).gif DEMAND FOR INFRASTRUCTURE LARGE INVESTMENT PROGRAMS Several major infrastructure programs were announced over the last two years, with investments adding around US$ 235 billion over the coming years, not to mention the major urban infrastructure works required for the 2014 World Cup and 2016 Olympics CHALLENGES Threats •Urge to keep up with the dynamism - ex. foreign trade of the country (which quadrupled from 2002 to 2012); the passenger flow of its airports (doubled in the same period); and the traffic on its highways (also doubled over the last ten years, as did the number of licensed vehicles); •The new cycle of economic expansion will require even greater investments in logistics and energy Needs Actions in course •The Government needs to provide the infrastructure the Brazilian Economy needs to continue on its path of economic and social development •Infrastructure investments have tripled in real terms over the last ten years, reaching about $ 100 billion in 2012 BRAZILIAN GOVERNMENT STRATEGY BRAZILIAN GOVERNMENT STRATEGY Investment stimulus measures that include: (i) reducing interest rates; (ii) enacting tax cuts; and (iii) launching a new strategy for recovery of logistical planning and execution of major infrastructure works Launch of Logistics Investments Programs in 2012: a strategic partnership with the private sector, focused on the renewal and integration of the Brazilian transportation network Government has enacted a number of tax and bureaucratic benefits, including for nonresident investors, as well as innovative financing instruments such as infrastructure debentures and Receivables Investment Funds (FDICs). BRAZILIAN GOVERNMENT STRATEGY LOGISTICS INVESTMENTS PROGRAMS OIL, GAS AND ENERGY •The Program consists of a wide concession set in transportation logistics, which implies large private investment in infrastructure •In oil and gas, 2013 will see the 11th and 12th Bidding Rounds (in concession regime) and the 1st Bidding Round of the Pre-Salt Layer •Make concession auctions for large projects for highways (7,500 km), railways (10,000km), airports (Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte) and ports •In electricity, a series of auctions will be carried out between 2013 and 2017 for the generation of 33,000 MW from hydropower, wind power and other sources and the installation of 23,200 kilometers of transmission lines. TAV •The concession auction for the operation of the first high-speed railway in Brazil, which will connect the cities of Rio de Janeiro, Sao Paulo and Campinas, in a total length of 511 km. INVESTMENT OPPORTUNITIES INVESTMENT OPPORTUNITIES Airports Galeão Airport (Rio de Janeiro) – R$ 6,6 billion (announcement scheduled for September/2013) Confins Airport (Belo Horizonte) – R$ 4,8 billion (announcement scheduled for September/2013) Regional Airports – R$ 7,3 billion, in 270 airports (ex: Passos - MG; Cascavel - PR; Linhares - ES) Ports • Investments for over R$ 6,4 billion • Private Terminals already announced • Public Terminal Biddings foreseen October, 2013 Urban transportation - Medium Cities • Target - 75 municipalities (ex: Joinville - SC; Uberaba MG; Ribeirão Preto and Sorocaba - SP; Niteroi and Campos dos Goytacazes - RJ) • Value – R$ 7 billion INVESTMENT OPPORTUNITIES Roads and Railways • Roads – a total of R$ 42 billion, divided in 5 years (R$ 23,5 billion), and 20 years (R$ 18,5 billion) • Highlights: • BR 050 and GO/MG and 262/ES/MG - in Request for Proposals • BR 163-MS in Public Hearing - Request for Information • BR 116/MG - auction scheduled to December/2013 • BR 040 DF/GO/MG/RJ - auction scheduled to December/2013 • Açailandia/Vila do Conde - auction scheduled to September/2013 • Railways – a total of R$ 91 billion, divided in 5 years (R$ 56 billion), and 25 years (R$ 35 billion) • Highlights: • Estrela D Oeste Railway (Group 1) - Auction scheduled to October/2013 • Uruaçu (Group 2) - Auction expected in 2014 Urban transportation - Big Cities • Target - 23 municipalities • Value – R$ 32 billion • Subway, Light rail vehicle (VLT) and urban rails • Highlights: • Salvador Subway: in Request for Proposals • São Paulo Subway - Line 6: Bidding process - rescheduled • São Paulo Subway - Line 18: In public hearing process • São Paulo Intercities Train - Studies proposed in July, 2013 - under analysis OVERVIEW OF BRAZILIAN BID PROCEDURES FRAMEWORK BRAZILIAN BID PROCEDURES FRAMEWORK GENERAL PUBLIC PROCUREMENT • LAW 8.666/1993: General Rules for Bidding and Contracts of the Public Administration • It establish the procedures to be followed by the Brazilian Government federal, state and local level to the selection of the contractor and execution of Public Contracts •Types: •Best price •Technique and price •Best Technique •Best bid or offer •Bidding Modalities: defined by the estimated contract value. •The higher the contract value more complex will be the procedure to be followed price (**it has been changed by the Reverse Auction procedures...) RDC (“Differentiated Regime of Procurement”) • Law 12.462/2011: The Differential Public Procurement Regime - RDC • It was enacted to establish simplified procedures to execute contracts for the 2014 World Cup infrastructure works •Nowadays RDC can also be applied for the PAC (Programa de Aceleração do Crescimento) projects •Main differences between Law 8.666 and the RDC: • Confidential Budget (optional) • Phase inversion: the financial proposal is submitted prior the qualification phase (optional) • Integrated procurement: the contractor is responsible for the whole project (from the engineering / basic project development, work execution and operational process) "REVERSE AUCTION" / "PREGÃO" • Law 10,520/2002: Reverse Auction • Trade-floor Version: performed by the parties in loco (further regulated by Decree 3,555/2000 • Online Auction Version: Comprasnet (further regulated by Decree No. 5,420/2005 • Key dispositions: • The winner will be mandatorily selected based on the lowest price • It is not required the submission of bid bonds/ guarantees and • Only the qualification of the winner is assessed (technical when applicable, financial, and legal) - this is the so-called "reversion of the bidding phases" BRAZILIAN BID PROCEDURES FRAMEWORK Lei de Geral de Concessões (Law 8987/1995): establishes general rules regarding concessions of public services, with no Government Payment Lei de Parceria Público-Privada (Law 11.079/2004): establishes general rules for the concessions with Government Payments (public-private partnership contracts - PPP). Types: (i) Sponsored Concession: public work or public service upon guaranteed payments from public administration, in addition to tariffs charged from end-users. Ex.: highways (ii) Administrative Concession: end-user is the public administration and shall provide payment to the private party. Ex.: hospitals, public buildings Selection of Private Partner • subject to public bid Specific Purpose Company (SPE) • establishment of an SPE, under control of private party, in order to manage and implement the project • Mechanism for transfer of control in case of default Guarantees given by the Public Administration • revenues as collateral • establishment or use of special funds • performance bond • guarantees from international organisms or financial institutions Project Aspects • contract value of at least R$ 20MM • minimum term of 5 and maximum of 35 years • Shall not have an exclusive purpose of labor provision, equipment supply or installation and execution of public work www.comprasnet.gov.br > acesso livre > consultas> aviso de licitações PUBLIC AGREEMENTS PUBLIC CONTRACTS INITIATING & PLANNING = BIDDING PROCEDURE • • • • • Its the key phase to negotiate the terms of the Future Contract Request for Information / Quotation Public Hearing Request for Propostal - Bidding Procedure (Request for Clarifications - Risk Breakdown Structure) Administrative and Legal Mesures (Impugnação) EXECUTION & CONTROLLING = CONTRACT MANAGEMENT • • • • • Inaccuracy of the "Statement of Work" / "Services Level Agreement" (TR Termos de Referência, Especificações ) Extra requirements of the Public Client (Was it foreseen in the SOW and Budget?) Penalties due to lack of performance / delays / "redoings" Payments / cash flow of the Governmental Budget Everything shall be written and official - EVER!! CLOSING • Claims and Instruments of Closing (via crucis) PUBLIC CONTRACT According to Federal Law 8.666/93, administrative contract is all and every agreement executed between public agencies and private parties, in which it is established mutual obligations Construction, renovation, manufactoring, recuperation or expansion Service agreement Acquisition for supply of assets, through payment, for one or several opportunities. Construction agreement Purchase agreement TYPES OF ADMINISTRATIVE AGREEMENTS Demolition, repairs, installation, assemble, operation, conservation, adjustments, manteinance, transportation, lease of property, advertisement, ensurance or technicalprofessional works. RISKS AND PROBLEMS The contract terms shall be always observed it can not be changed or turned undetermined! RISKS AND PROBLEMS www.demarest.com.br The contractor is responsible for the quality and delivery 38 PRICE ADJUSTMENT Delay from contractor's fault • if any increase of the index occurs, prevails the index of the date that the agreement should have been executed. • if index decrease, prevails the index of the execution date. Early Conclusion Extension • prevails the index of the date that the agreement should have been executed. • prevails the index of the date agreed for the execution of the agreement. RENEGOTIATION Motivation Principle Legality Principle RESCISSION Agreement rescissions cases must be formally justified in the records, ensuring to the Contractor party the right of defense (adversary system and full defense), in five business days . If the rescission is not due the contractor's fault, and it's duly proven, the Contracting must assure the: • devolution of guarantee • payment of the execution until the date of the rescission • payment of demobilization costs COMPLIANCE STRUCTURE THE NEW COMPLIANCE LAW Law 12.846/2013 (Anticorruption) and Law 12.813/2013 (conflict of interests) provides further regulation regarding the relationship between private and public parties regarding public contracts MAIN COMPLIANCE PRINCIPLES Transparency Equity Accounting SEPTEMBER, 5: Workshop "Compliance and Governmental Relations" Don't miss it! Conformity with rules Ana Bárbara Costa Teixeira (abteixeira@demarest.com.br) Mário Roberto Villanova Nogueira (mnogueira@demarest.com.br) Min Gon Kim (mgkim@demarest.com.br)