Eutrophication
advertisement

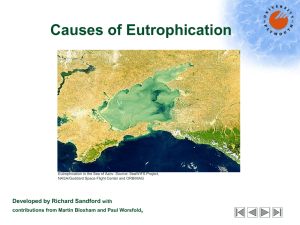
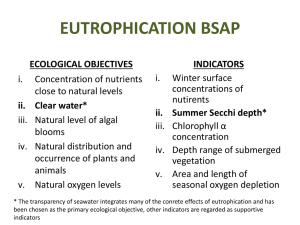
Eutrophication Menkov, Peter Stamatova, Zhanet Tantcheva, Christina Section 10/1 http://www.marietta.edu/~biol/biomes/images/mangroves/florida_eutrophication_7536.jpg What is eutrophication? A process whereby water bodies receive excessive amounts of nutrients, which results in excessive plant growth (aka algal bloom) (1) Anthropogenic eutrophication – the pollution that humans cause with the release of sewage effluent and fertilizers into natural waters. (2) What does eutrophication cause? Reduced oxygen concentration (hypoxic water) by the decomposition of dead plant materials (1) This can result in the death of other organisms (1) http://library.thinkquest.org/04oct/01590/pollution/culturaleutroph.jpg Algal Bloom (3) • Algal/marine/water bloom=“rapid increase in the population of algae in an aquatic system” –green, yellowish-brown or red • In fresh water and marine environment • Caused by excessive nutrients (P and N mainly) …So what? (3) The more algae grow, the more other organisms die. Bacteria feed on the dead organic matter. Thus, bacteria increase in number. More oxygen dissolved in water used Fish and aquatic insects die And then…? (3) Neurotoxins Biological impact on wildlife HABs –Harmful Algal Blooms (toxins produced by phytoplankton) Accumulations of foams, scums, and discoloration of the water (4) http://www.macalester.edu/environmentalstudies/thr eerivers/studentprojects/ENVI_133_Spr_08/Phosph orus/eutrophication.gif http://www.seos-project.eu/modules/oceancolour/images/algal-bloom-warning-sign.jpg Problems… Species diversity decreases Dominant biota changes Competition for resources, predator pressure Turbidity increases – less transparency Rate of sedimentation increases High chemical or physical stress Algal blooms (9, 10) http://www.jamstec.go.jp/jamstece/tech/tech_3g/rtdeadfish.jpg http://sevenhillslake.com/CulturalEutrophication.jpg Water - injurious to health, decline in value Disturbance in water flow and navigation Commercially important species of fish may disappear Problems with drinking water, bad taste or odor after treatment (10) Blue baby syndrome (methemoglobinemia) - nitrate levels above 10 mg/l in drinking water, may be life-threatening (8) http://www3.aims.gov.au/ibm/pages/news/images/figure1-bc.jpg http://openlearn.open.ac.uk/mod/resource/view.php?id=171951 http://medicalimages.allrefer.com/large/shaken-baby-symptoms.jpg Prevention (5, 6) Reduce the input of nutrients into the water basins (for example, Baltic Sea) Fertilization balance Reduction in P and N load Monitoring to predict eutrophication Hydrodynamics of the water body – especially information about nutrients Precision agriculture – accurate irrigation Sewage treatment – removal of nutrients Prevention of erosion of soil Unfertilized buffer zones near water bodies http: //lan dsat .gsf c.na sa.g ov/g raph ics/n ews/ soc 001 7b_l g.pn g How to deal with the effects (5) Algaecides - copper sulphate, chlorine, citrate copper; kill algal and cyanobacterial cells Filtration – micro-, ultra-, nano Coagulation-clarification Activated carbon adsorption Oxidation Disinfection with chlorine Examples of Eutrophication (7) The Baltic Sea In the Baltic Sea, all the areas are affected by eutrophication Number of phytoplankton increases (especially cyanobacteria) This bacterium has increased, because of the increase in nutrient concentrations and due to the changes in the seasonal availability and large nutrient proportions Cyanobacteria bloom (Nodularia spumigena) in the western Baltic http://www.eutro.org/documents/EEA%20Top ic_Report_7_2001.pdf The Baltic Sea (6) Since harmful and toxic species are parts of the phytoplankton, the blooms of harmful algae have also increased Blooms - caused losses to fish farming, deaths of fish, sea birds, dogs and cattle, and some damage to human health Source of eutrophication in this area – increase in phytoplankton, consisting of many harmful bacteria causing damage to the environment Impacts include: reductions in biodiversity reductions in the natural resources of dermersal fish and shellfish reduced income from maricultures of fish and shellfish reduced recreational value and income from tourism increased risk of poisoning of animals including humans by algal toxins http://www.rahulbasu.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2008/05/baltic_sea_map.png Solutions (6) The Baltic Sea states and the North Sea states decided to aim at a 50 % reduction of the N and P load from land compared to the level in the middle of the 1980s. It is expected that the directives and especially the recently decided water framework Directive (the urban wastewater treatment directive, 2000/60/EC) will reduce the nutrient loads to the European coastal areas and the eutrophication impacts to an acceptable level. Mediterranean Sea (7) Mediterranean surface waters in the open sea are classified among the poorest in nutrients (oligotrophic) of the world oceans Mediterranean coastal zone important for human activities like habitation, industry, agriculture, fisheries, military facilities, and tourist resorts Most of these activities contribute to coastal eutrophication in the Eastern Mediterranean http://www.iasonnet.gr/abstracts/fig_kar1.jpeg Works Cited "Algal bloom." Science Daily. N.p., n.d. Web. 5 June 2010. <http://www.sciencedaily.com/articles/a/algal_bloom.htm>. (3) "Algal Blooms in Fresh Water." Water Encyclopedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 5 June 2010. <http://www.waterencyclopedia.com/A-Bi/Algal-Blooms-in-FreshWater.html#ixzz0qB5cw2ci>. (4) "Eutrophicatio and Health." European Commission. N.p., n.d. Web. 6 June 2010. <http://ec.europa.eu/environment/water/water-nitrates/pdf/eutrophication.pdf>. (5) "Eutrophication." Guide to Water Pollution. N.p., n.d. Web. 6 June 2010. <http://www.waterpollution.org.uk/eutrophication.html>. (7) "Eutrophication." USGS. N.p., n.d. Web. 5 June 2010. < http://toxics.usgs.gov/definitions/eutrophication.html>. (1) "Eutrophication." Wikipedia. N.p., n.d. Web. 5 June 2010. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eutrophication>. (2) "Eutrophication in Europe’s coastal waters." ASSETS. N.p., n.d. Web. 6 June 2010. <http://www.eutro.org/documents/EEA%20Topic_Report_7_2001.pdf>. (6) "General effects of eutrophication." Water Treatment and Purification - Lenntech. N.p., n.d. Web. 6 June 2010. <http://www.lenntech.com/eutrophication-waterbodies/eutrophication-effects.htm>. (10) "Problem: Eutrophication ." Wingolog. N.p., n.d. Web. 6 June 2010. <http://wingolog.org/writings/water/html/node27.html>. (9) "Why Is Eutrophication Such a Serious Pollution Problem?" IETC. N.p., n.d. Web. 5 June 2010. <http://www.unep.or.jp/ietc/publications/ short_series/lakereservoirs-3/1.asp>. (8)