Big Idea 18 : Matter and Energy Transformations
advertisement
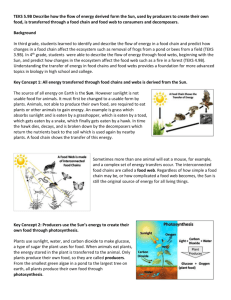
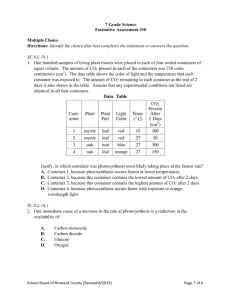
Big Idea 18: Matter and Energy Transformations A. Living things all share basic needs for life. B. Living organisms acquire the energy they need for life processes through various metabolic pathways (photosynthesis and cellular respiration). C. Matter and energy are recycled through cycles such as the carbon cycle. Benchmark Number & Descriptor SC.8.L.18.1 Describe and investigate the process of photosynthesis, such as the roles of light, carbon dioxide, water and chlorophyll; production of food; release of oxygen. SC.8.L.18.2 Describe and investigate how cellular respiration breaks down food to provide energy and releases carbon dioxide. SC.8.L.18.3 Construct a scientific model of the carbon cycle to show how matter and energy are continuously transferred within and between organisms and their physical environment. SC.8.L.18.4 Cite evidence that living systems follow the Laws of Conservation of Mass and Energy. Your Energy is My Energy Cycling of Energy Energy enters the ecosystem from the sun and exits after the organisms have taken as much as they need. Organisms release energy back into the biosphere as heat. This energy cycles round and round in order for the Earth to survive! The Carbon Cycle Carbon is the basis of life on Earth. 99.9% of all organisms on the planet need carbon to survive. Carbon is continuously cycled and reused. Carbon can be found on Earth in the following locations: • in living and dead organisms found in the biosphere • carbon dioxide in the atmosphere • organic matter in soils • sedimentary rock deposits such as limestone, dolomite, and chalk in the oceans as dissolved atmospheric carbon dioxide and as calcium carbonate shells in marine organisms The Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis and respiration are the key processes in the carbon cycle. Carbon Cycle Breakdown Photosynthesis Process by which plants and other autotrophs store the energy of sunlight into sugars Requires sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide Occurs in the leaves of plants in organelles called chloroplasts. The plant’s leaves use the light to make a sugar called glucose. Chemical formula 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + E C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Reactants = carbon dioxide, water, energy (Sun) Products = glucose (sugar), oxygen During the process of photosynthesis, oxygen is produced (We use this oxygen to breathe). Photosynthesis A closer look Carbon Cycle Breakdown Respiration Process by which organisms utilize the products from the process of photosynthesis Requires glucose and oxygen Occurs when consumers eat producers to use the glucose for energy and utilize the oxygen Chemical formula C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy Reactants = glucose, oxygen Products = carbon dioxide, water, energy Respiration – A Closer Look Respiration is the process by which the energy in the bonds of nutrients are used to synthesize ATP. Respiration occurs continuously in all cells of all organisms. Two main types Anaerobic – no oxygen required Aerobic – requiring oxygen Here food is broken down completely into CO2. Other Ways CO2 Enters the Atmosphere Decomposers are also a key partner in the carbon cycle. Decomposers break down organic material such as dead animals or leaves. CARBON CYCLE •A closer look of how Carbon is transported through Earth’s atmosphere. •Carbon Cycle follows Law of Conservation of Mass/Energy •There is a set number of Carbon (C) atoms in Earth’s atmosphere. •This element is recycled through the planet's resources. Plants use Carbon Dioxide and release Oxygen into the atmosphere. Animals eat plants, gain energy (glucose), use oxygen, and release Carbon dioxide. Organisms die and decompose, sending nutrients to soil; plants grow from soil, animals eat plants, etc. Knowledge Check What are some of the contributors to atmospheric CO2? How is some of the CO2 removed from the atmosphere? What is the relationship between producers and consumers? Knowledge Check What are some of the contributors to atmospheric CO2? Animal respiration and factories How is some of the CO2 removed from the atmosphere? Through the process of photosynthesis What is the relationship between producers and consumers? The products that producers create are used for the survival of consumers, visa-versa.