vietnam_war_-_overview_ppt

Case Study: Vietnam
How was a small country like Vietnam able to win a war against the USA?
Essay Question
This section includes:
• Background
• 1957 to 1965 – Struggle in Vietnam between the
South Vietnamese army and the communist-trained rebels (Viet Cong)
• 1965 to 1969 – North Vietnamese-USA struggle
• The war from the Vietnamese and USA perspective
• The war as a world issue
• 1969 to 1975 – USA withdrawal from Vietnam
• Conclusion: How the war is remembered today
2
(Refer to CAPS, p26)
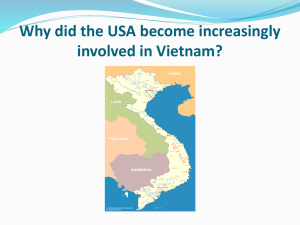
Where in the World is Vietnam?
Vietnam USA
Background
• In the 19 th century France colonised a large part of SE
Asia including modern day
Vietnam.
• 1941: Japan invaded and occupied SE Asia.
• 1941: Two communists /
Vietnamese nationalists (Ho
Chi Minh and Nguyen Vo Giap) set up Viet Minh (League for the Independence of Vietnam)
• Viet Minh funded by the US.
Post-War Settlement 1945-1954
• 1945: Japan was defeated in
WWII, withdrew from SE Asia
• September 1945 Ho Chi Minh announced Vietnam was an independent and democratic republic.
• The French attempted to reestablish their empire and took back control of the south
• Vietminh continued to fight for full independence and a united Vietnam
• 1954 French surrendered
The Geneva Agreement
In May 1954, Britain, France, China, the
Soviet Union, the USA and Vietnam met in
Geneva to decide the future of Vietnam
1954-1965 struggle between South Vietnamese army and communist trained rebels (NFL / Viet Cong)
• 1955 Diem (supported by
USA) officially elected president of South
Vietnam in rigged elections
• Diem was a dictator. He was a Catholic and persecuted the Buddhist majority. Land was taken from peasants and given to
Diem’s supporters
• Diem refused to allow elections to re-unite North and South Vietnam.
Opposition to Diem’s Government
• 1959: Vietminh supporters in South Vietnam formed the National Liberation
Front (NFL) Diem and USA called them ‘Viet Cong’
(Vietnamese Communists)
• 1963: an elderly monk named Thich Quang Duc, set himself ablaze in protest against Diem’s corrupt regime .
• 1963: a CIA funded coup in
South Vietnam which overthrew and killed Diem.
Malcolm Brown who took this photograph
Why did America become involved in a war in Vietnam?
American Presidents during the period of US involvement in Vietnam:
Dwight D Eisenhower (Rep): 1953- 1961
John F. Kennedy (Dem): 1961-1963
Lyndon B Johnson (Dem): 1963-1969
Richard Nixon (Rep): 1969- 1974
The ‘Domino Effect’
(Strategic importance of Vietnam)
In 1949 the Chinese Communist Party, led by Mao Zedong won their civil war and established a communist government. USA feared that other countries in the region would fall to communism unless the USA actively prevented it.
Gulf of Tonkin Incident (Trigger)
• On 2 August 1964 the US destroyer Maddox was fired at by North Vietnamese patrol boats in the Gulf of Tonkin. The Maddox was gathering intelligence information. Two days later there was a second alleged attack.
Evidence has since shown that this did not happen. US President Johnson used these attacks to persuade Congress to support greater US involvement in Vietnam.
• 1965 – by end of year 200,000 US combat soldiers had been sent to Vietnam.
1965 - 1969: North Vietnamese-USA struggle
USA’s Tactics
• 7 Feb 1965: USA launched
‘Operation Rolling Thunder’:
- Widespread aerial bombing using cluster bombs and
Chemical weapons (‘Agent
Orange’ and Napalm used)
• Search and Destroy (used airmobility to move troops)
• 16 March 1968: My Lai massacre
• Defence of South Vietnamese government against North
Vietnamese expansion.
North Vietnamese Tactics
• Winning South Vietnam hearts and minds
• Guerrilla tactics
• Booby traps and mines
• Suicide squad fought their way into US embassy
• 31 January 1968 Vietcong launched an attack on over
100 towns and cities in the south during New Year (or
Tet) holiday – (Turning point:
US public realised that US was
NOT winning the war!)
1969 to 1975 – USA withdrawal from Vietnam
“From 1964-1972, the wealthiest and most powerful nation in the history of the world made a maximum military effort, with everything short of atomic bombs, to defeat a nationalist revolutionary movement in a tiny peasant country – and failed”.
(H. Zinn, A People’s History of the USA, (New York, 1980, p460)
WHY?
A Soviet cartoon mocking the large number of US casualties in Vietnam. c. 1968
Deforestation caused by USA spraying
Agent Orange (TCDD Dioxin)
The Vietnamese Red Cross estimates that up to three million Vietnamese have suffered health effects from dioxin exposure, of whom
150,000 are children with birth defects
Ten year old Phan Thi Kim Phuc running naked down a street having torn off her burning clothes after an American Napalm attack.
The Massacre at
My Lai -
16 March 1968
Women and children shot dead by American soldiers lie
We made them squat down. I poured about four clips into the group. in the road at the village of My Lai, 1968
.
While we kept on firing .
(
An extract from the evidence of Paul Meadlo who was a US soldier at My Lai.)
Conscripted Soldiers: ‘Cherries’
• Of the 3 million
Americans involved in
Vietnam war – about two-thirds were conscripts (‘cherries’)
• Average age of conscript = 19 years
• 12 month – ‘tour of duty’
• Anti-conscription campaign in USA
A student burns his draft card during an anti-war demonstration. Over 200,000 young men dodged the draft.
Kent State Massacre (4 May 1970)
National Guardsmen opened fire on student protestors in Ohio, killing four. This picture shows one of the dead students,
Jeffrey Miller.
Casualties of War
Category Year Range
North Vietnamese civilian deaths from bombing
North Vietnamese soldiers killed
Viet Cong deaths
Viet Cong and North
Vietnamese soldiers deaths combined
South Vietnamese civilian deaths from gunfire / bombing
South Vietnamese soldiers killed
US military deaths
1965-72
1965-72
1960-75
1960-75
1960-75
1960-75
1960-73
Low estimates
172,000
533,000
361,000
219,000
46,000
Medium estimates
65,000
500,000
251,000
1,011,000
391,000
266,000
47,000
High estimates
329,000
1,489,000
720,000
313,000
58,000
Source: Rudolph Rummel, Statistics of Vietnamese Democide: Estimates, Calculations and Sources, 1997.
Why did the USA lose the Vietnam War?
• US Army’s military tactics - ineffective and unpopular
• Growth of the anti-war movement in USA.
• Media coverage of the war – 1 st TV war
• Unpopularity of South Vietnamese Government
• North Vietnamese soldiers’ Guerrilla warfare tactics
• North Vietnam and NLA were fighting a war of liberation to free their country from foreign intervention.
• Support for North Vietnamese from China and USSR
How has the Vietnam War been remembered?
• Memorials in USA and Vietnam
• Film (Hollywood has presented different views of war in different periods)
• Music
• Personal accounts / Auto-biographies
• Academic histories
• Tourist sites
Impact of Vietnam War
• For Vietnam – Horrific: 5 Million Vietnamese peasants displaced, Large numbers killed, or maimed. Huge areas of forest destroyed by
American chemicals – long term implications for agriculture.
• For America - A major psychological as well as military defeat. Probably sped up the ‘Domino effect’ ie lots of other countries in Asia ‘went red’
(ie became communist) A propaganda disaster
(US troops involved in human rights violations, massacres, use of chemical weapons)
Audio-Visual Resources
BBC – News coverage of Vietnam War
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Et9w2YPf3Wk
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qTFnYl7vWyA
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B3CXZCoQPrU
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SeMDPB0-HOY
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xX5lesv49B4
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-7Y0ekr-3So
Anti- Vietnam war songs
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CvwQmxLaknc&list=PL7FAC1A0
A55CDC6F3
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wbQECHzMhXo
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H2FEjGB0ZVU
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b8JlTIo--CQ
![vietnam[1].](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005329784_1-42b2e9fc4f7c73463c31fd4de82c4fa3-300x300.png)