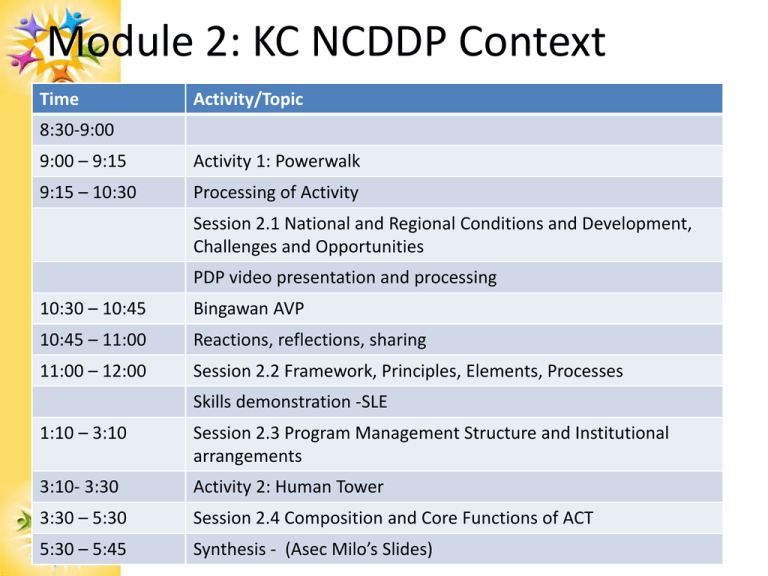
Module 2: KC NCDDP Context
Time
Activity/Topic
8:30-9:00
9:00 – 9:15
Activity 1: Powerwalk
9:15 – 10:30
Processing of Activity
Session 2.1 National and Regional Conditions and Development,
Challenges and Opportunities
PDP video presentation and processing
10:30 – 10:45
Bingawan AVP
10:45 – 11:00
Reactions, reflections, sharing
11:00 – 12:00
Session 2.2 Framework, Principles, Elements, Processes
Skills demonstration -SLE
1:10 – 3:10
Session 2.3 Program Management Structure and Institutional
arrangements
3:10- 3:30
Activity 2: Human Tower
3:30 – 5:30
Session 2.4 Composition and Core Functions of ACT
5:30 – 5:45
Synthesis - (Asec Milo’s Slides)
Session Objectives
Session2.1.Framework, Principles, Elements and Processes
1. To define poor and poverty
2. To know poverty profile, development challenges and
opportunities
3. To know government Social Protection Operational
Framework and
Strategy for development
4. To know DSWD core poverty alleviation programs
Session Activities/Topics
Session2.1.National and Local Poverty Conditions and Development,
Challenges and Opportunities
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
G.
Poverty conditions – who are poor?
Common Definitions on Social Development
Policy Support
PDP Medium-Term Update
Results and Strategic Framework on Social Development
Social Protection Operational Framework and Strategy
Social Reform Agenda and Poverty Alleviation Act
- Local Government Code of 1991
- Grassroots Participatory Budgeting Process (GPBP)
H. DSWD Vision, Mission and Values
E. Challenges to Social Development Sector
F. Poverty conditions in local communities – challenges and
opportunities
Module II: The NCDDP Context
SESSION 2.1:
National and Local Poverty Condition and
Development Challenges and Opportunities
Photo credit: Dennis Bautista, www.allartnews.com
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Message No. 1:
Poverty is a development and
governance issue
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
The Headlines…
“Families rating themselves as “mahirap”
or poor rose to 55%” (SWS, 5/3/2012)
“Hunger at record-high 23.8% of families;
Moderate Hunger at 18.0%, Severe Hunger
at 5.8%” (SWS, 5/8/2012)
“Philippines has a sluggish decline in
Poverty Incidence”
The Language of Poverty…
List terms/concepts in your local language
that would mean or refer to poor
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
SLE: Power Walk
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
1.
2.
3.
4.
If you think you are beautiful step forward.
If you have P500 in your wallet step forward.
If your parent work abroad step forward.
If all of your siblings graduated in college step
forward.
5. If you are a woman step backward.
6. If you are a member of an IP community move
backward.
7. If you have a politician “Ninong”step forward.
8. If you own a property step forward.
9. If you have tuberculosis, step backward
10. If you are not a Roman Catholic step backward
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Poverty is product of social deprivations,
differences in opportunities and inequities
High
Population
Growth Rate
Calamities
Kapigadohon
Social
inequalities
(social
exclusion,
failed asset
reforms
Poverty
Poor
delivery of
social
services
Poor
resources/
economic
management
Corruption
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
High
population
growth rate
and total
fertility rate
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Poor delivery and
access of basic social
services (water,
health, shelter,
education, shelter)
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Disasters
and
calamities
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Unmet
asset
reforms
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Issues of
social justice
and
corruption
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
POVERTY SITUATION IN REGION VI
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Poverty slightly improved in 2006:
there are 31 poor families out of 100 in Region VI!
(Regional Scenario)
Subsistence
Incidence (%)
Region/
200
0
2003
Region VI
17.4
12.9
Aklan
15.1
Antique
Province
Poverty Incidence
(%)
2006
2000
2003
2006
12.5
36.7
31.4
31.1
13.0
17.1
36.3
33.5
42.6
16.7
21.2
23.9
35.1
43.4
43.0
Capiz
17.2
6.3
6.3
40.8
21.6
24.3
Guimaras
6.6
18.3
10.3
22.6
32.7
35.2
Iloilo
13.5
12.5
8.8
29.7
31.1
24.1
Negros
Occidental
21.3
13.0
13.9
41.6
31.4
33.4
19
Region VI
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
36.7
31.4
2000
2003
31.1
2006
Poverty Incidence (%)
Region VI
CAPIZ Poverty Incidence per Municipality
35
32.79
30
25.51
25
20
15.63
17.47
15
10
5
0
20.23
17.75
19.44
20.4
23.11
22.05
24.27
22.19
26.2
26.72
27.25
28.97
Which way we are headed?
•
•
•
•
•
There are signs of “break-out”
There are new growth drivers
How we can ensure inclusive growth?
Yolanda: Development Aftermath
The role of citizens and LGU?
Signs of Breakout: The headlines
• “New Economy to Watch” – PIT (Phil,
Indonesia and Turkey)
• Rising economy in SEA
• High trust rating of political
leadership and agencies.
New growth drivers
•
•
•
•
•
Capital and FDI investments are increasing
GNP is expected at 7%
Economic fundamentals are good
Prices are stable at 3.2 inflation rate
New manufacturing sector/investments are
increasing
• Service sector is doing good (BPO, labor peace)
Is our growth inclusive?
• Few leading sector (manufacturing and service
sectors)
• Is growth geographically spread? All sectors of
the society?
• Why unemployment rate and number of poor
increasing?
Until…Yolanda came..
• 500,000+ HH affected
• 32 sub-projects of KC affected (2 million)
• KC staff responded to relief and disaster
operation
• Estimated 10B for reconstruction and recovery
in FO6.
Spot the Difference?
Ano ang sagot sa
kahirapan?
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Who are poor?
• Disadvantaged Communities* - these have
inadequate resources or facilities such as roads, water
system, electricity and absence of natural resources
• Disadvantaged Families - families belonging to the
bottom 30 percent of the income strata
• Disadvantaged Persons/Groups - individuals or group
of individuals who are considered vulnerable and
marginalized. These include needy family heads and
other needy adults, children in especially difficult
circumstances, out-of-school youths, persons with
disabilities, distressed individuals and families due to
natural and human-induced disasters.
*Definition given by NSCB
Definition
DEVELOPMENT
• is about attaining a full and satisfying
life for all;
• regardless of age, sex, religion,
ethnicity or class. Fairness and equity
demand that everyone in the society,
whether male or female, has the right
to the same opportunities to achieve a
full and satisfying life. (Draft KC-NCDDP
page 22)
Definition
EMPOWERMENT
• the expansion of assets and capabilities of poor
people to participate in, negotiate with, influence,
control, and hold accountable institutions that affect
their lives;
• Multidimensional poverty reduction requires a range
of assets and capabilities at the individual level
(health, education, housing) and at the collective
level (ability or organize and mobilize to take
collective action to solve their problems.
Definition
SOCIAL PROTECTION
”Policies and programs that seek to reduce
poverty and vulnerability to risks and enhance
the social status and rights of the marginalized by
promoting and protecting livelihood and
employment, protecting against hazards and
sudden loss of income, and improving people’s
capacity to manage risks.”
The Philippine Social Protection Framework and Strategy: An
Overview, NEDA SDC Resolution 3, s. 2012, “Approving and
Adopting the Social Protection Operational Framework”
Mainstreaming…
INDIGENOUS PEOPLES (IPRA
LAW)
• Free and prior informed
consent must be obtained
from IP communities who are
directly or indirectly affected
by development interventions
• Thorough consultation
• Participation in planning,
decision-making,
implementation and sustainability of projects that will
affect them.
Mainstreaming…
ENVIRONMENTAL SAFEGUARDS
• a key plank in the nation’s development;
• LGUs are required to comply with
Philippine DRRM Act 2010
– ensure the integration of disaster risk
reduction
– climate change adaptation into local
development plans
– programs and budgets
Mainstreaming…
WOMEN
(RA 9710 Magna Carta For Women)
• Adoption of gender mainstreaming to fulfill
women’s human rights and eliminates gender
discrimination
(From DSWD Memo Circular 007 Series of 2011)
• It is the policy of KALIHI-CIDSS Project to:
– promote active participation of both men and
-women in decision-making within the
opportunities provided by project activities,
– ensure that both have equal access to and
enjoy the benefits of project implementation.
Mainstreaming
AFFECTED BY ARMED CONFLICT AND NATURAL
AND MAN-MADE DISASTERS
• PDPP 46 government efforts focused on:
– subsector outcome: all armed conflicts
brought to a permanent and peaceful closure
– intermediate outcome: negotiated political
settlement of all armed conflicts (conflict
resolution back to the negotiating table and
invests in responsive social programs that will
address root causes of conflict)
Photo credit: EPA
PDP MIDTERM UPDATE
Reflection Questions:
1. How did you feel while watching the
video?
2. What key messages were related by the
video?
3. What poverty reduction programs are
you aware of? Who are their target
groups?
4. Based on your observations/experience
which of these programs appear to be
working? Not working? Why?
Key Message 1
In 2011, the PDP Medium Term
Update goal for incidence of poor
individuals in the country was
pegged at 18.0%-20.0% by 2016 – a
far cry from the original MDG of
16.6% poverty incidence in the
Philippines by 2015
Key Message 2
PDP MIDTERM UPDATE REVEALS THAT
1. Good Governance is an effective platform
upon which strategies should be
implemented
2. Macro-economic and political stability fuel
expectations that led to growth
3. Economic growth is necessary but not
sufficient for poverty reduction
4. Development strategies has to spatial and
sectoral dimension to attain inclusive growth
5. Disaster can reverse the gains and even can
push development
Key Message 3
The 2011 PDP Medium Term Update
multidimensional poverty is manifested by:
lack of education
insufficient nutrition and poor health, inadequate
living standards (e.g. no access to clean water and
sanitation facilities)
no electricity, poor quality of housing, etc.),
low income
social exclusion
Disempowerment
unstable and poor quality of work/employment and
threat of violence.
Key Message 4
The principle of inclusive growth calls
for “preferential attention to the
participation of women and other
highly vulnerable groups (i.e. the
poorest, Indigenous People, youth,
the elderly, and others) in the
planning and implementation of
development projects.
Updated Strategic Framework
PDP 2011-2016 Midterm Update
Results and Strategic Framework on Social Development
PDP 2011-2016 Midterm Update
Social Protection Operational
Framework and Strategy
1. Social Reform Agenda and Poverty
Alleviation Act RA 8425 of 1997
2. RA 7160 Local Government Code of
1991
3. Grassroots Participatory Budgeting
Process (GPBP), formerly BUB
Social Protection Operational Framework
and Strategy
1. Social Reform and Poverty Alleviation Act RA 8425 of
1997
– Integrating multi-dimensional approach to poverty in the
National Anti-Poverty Action Agenda:
(1) Social dimension access to quality basic services. –
Refers to equitable control and access to social services and
facilities such as education, health, housing, and other basic
services which enable the citizens to meet their basic human
needs and to live decent lives;
(2) Economic dimension asset reform and access to
economic opportunities. – Addressing existing inequities in
the ownership, distribution, management and control over
natural and man-made resources from which they earn a living
or increase the fruits of their labor;
Social Reform and Poverty
Alleviation Act RA 8425 of 1997
(3) Ecological dimension sustainable development
of productive resources. – Reforms which ensure the
effective and sustainable utilization of the natural and
ecological resource base, thus assuring greater social
acceptability and increased participation of the basic
sectors in environmental and natural resources
conservation, management and development; and
(4) Governance dimension democratizing the
decision-making and management processes. –
Reforms which enable the basic sectors to effectively
participate in decision-making and management
processes that affect their rights, interests and welfare.
RA 7160, Local Government
Code of 1991
General powers of Local Govt Units
• Section 17 – Local government units shall exercise
such other powers and discharge such functions and
responsibilities necessary to efficient and effective
provision of basic services and facilities at barangay,
municipal and provincial levels
• Section 106 – Local development councils at the
province, municipal or barangay shall assist the
corresponding Sanggunian in setting the direction of
economic and social development, and coordinating
development efforts within its territorial jurisdiction
Grassroots Participatory Budgeting
Process (GPBP), formerly BUB
• Goals and Policy
• To pursue attainment of the PDP goal of
inclusive growth and poverty reduction,
• Promote good governance at the local level,
and
• Ensure inclusion of the funding
requirements for development needs,
identified at the local level, in the budget
proposals of participating agencies
GPBP Implementation
By the Human Development and Poverty
Reduction Cluster (HDPRC) through
a) The Participating National Agencies
b) Oversight: DSWD, NAPC, DBM & DILG
c) Beneficiaries: All cities and
municipalities
Convergence is Our Strategy
POVERTY
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Convergence of
Core Poverty
Reduction
Programs!
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
DSWD VISION
A society where poor, vulnerable
and disadvantaged individuals,
families and communities are
empowered for an improved
quality of life.
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Pathway out of poverty
Community
Development/
• Pantawid
Pamilya
• Social Services
Social
Protection
Chronic Poor
kalahi.dswd.gov.ph
Financial Access
• Kalahi-CIDSS
Project
• Social Services
(Health, Education,
WatSAn)
• Community
Infrastructure
Transition Poor
• Technical
Assistance/Enterprise
Development
• SEA-K
Sustainable
Enterprise
Entrepreneurial
Poor
Challenges to Social Development Sector
1. Unsustained poverty reduction
2. Slow progress towards attainment of
the MDGs
3. Inadequate financing for social services
4. High population growth rate
5. Lack of access to productive resources
and employment opportunities
6. Adverse effects of disasters and shocks
• Bingawan KALAHI-CIDSS EXPERIENCE









