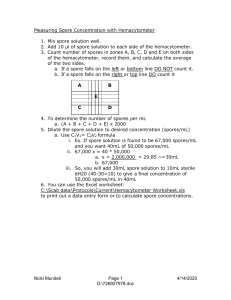
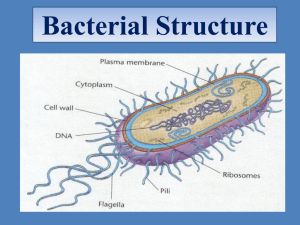
Practical seminar 5/05 capsules, sporulation
advertisement

Practical seminar 5/05 capsules, sporulation Spores - endospores • Some pathogenic Gram positive bacteria from genus Bacillus and Clostridium - can forme spores. Their localisation is diagnostic • In unfavorable conditions the vegetative cell forms one spore (sporulation, dormant phase of life cycle) – formation of multiple layers – coat – dipicolin acid and Ca • Resistance to environmental extreme conditions • Germination – return to vegetative phase of lifecycle – breaking of coat, water intake • Activation – 1st step of germination – changes in environmental condition – mild temperature, alanin Wirtz Conklin • • • • Differencial staining form spores Spore forming bacteria – red Spores – green Susspension dried on the air, heat fixed and stained with 5% malachit green. Heating untill evaporation for 3-6 minutes. Rins under water flow, add 0,5% water solution of safraninfor counter staining (30 sec.) Rinse with water, dry and read in 400-1000 times magnification Bacillus cereus - spóry Burri´s method for capsule detection Prepare the suspension of the colony and destilled water on the slide Add one drop of inkand make a thin smear Dry on air and fix with heat Counterstain with crystalin violte , rinse very carefully with water , let dry on air and read with immersion Capsules • Extracellular structures overlying the cell wall • Polysaccharide ( exception B. antracis – polypeptid) • Tool of virulence – antifagocytic properties, act as adhesin • Some bacteria can be present in form of encapsulated and nonencapsulated strains • Strains loose capsule in older cultures or can gain it by transformation from encapsulated strains when cultivated together Hemofilus influenzae b acc.Burri • On black smear capsules are represented by uncolored space in forme of rod In the white space the cristalin violet counterstained rods can be indentified - blue Encapsulated rod - scheme