File - Professor Fell
advertisement

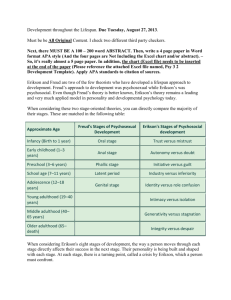
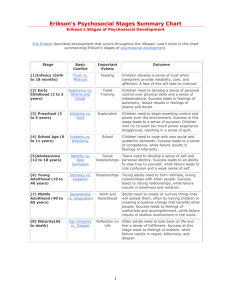
Theories of Development Chapter 2 Theories Help to organize a huge body of info Help to focus our search for new understandings Help us to explain how findings might be interpreted Help to identify major disagreements among scholars The Psychoanalytic Approach 1 Sigmund Freud Structures of the Mind The Developing Personality Psychosocial Crises and Development 2 Erik Erikson Erikson’s Eight Psychosocial Stages Stage One: Infancy Age: 0 to 1 years old Crisis: Trust vs. Mistrust Erikson’s Eight Psychosocial Stages Stage Two: Early Childhood Age: 2 to 3 years old Crisis: Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt Erikson’s Eight Psychosocial Stages Stage Three: Preschool Children Age: 3 to 5 years old Crisis: Initiative vs. Guilt Erikson’s Eight Psychosocial Stages Stage Four: Middle Childhood Age: 6 to 12 years old Crisis: Industry vs. Inferiority Erikson’s Eight Psychosocial Stages Stage Five: Adolescence Age: 12 to 18 years old Crisis: Identity vs. Role Confusion Erikson’s Eight Psychosocial Stages Stage Six: Young Adulthood Age: 18-25 years Crisis: Intimacy vs. Isolation Erikson’s Eight Psychosocial Stages Stage Seven: Middle Adulthood Age: 25-65 years Crisis: Generativity vs. Stagnation Erikson’s Eight Psychosocial Stages Stage Eight: Maturity Age: 65 years until death Crisis: Integrity vs. Despair The Cognitive Development Approach 3 Jean Piaget Stages Functional Invariants •Assimilation •Accommodation The Cultural Framework Approach 4 Three fundamental themes: 1) Concept of development 2) Social & cultural development 3) Speech The Behavioral Approach 5 B.F. Skinner Operant Conditioning Reinforcement Reinforcer Negative=Remove Positive=Add Punishment Negative=Remove Positive=Add Bandura & Social Cognitive Learning 6 Observational Learning Social Cognitive Learning A Bioecological Model • Development depends on context This produces new changes in us Our response causes a change in others Reciprocal Interactions Their responses to us then change 7 Developmental Systems Theory 8 Awareness Test