Culture2
advertisement

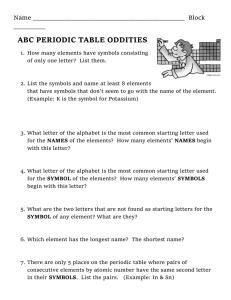
Ch. 2 Characteristics of Culture The Concept of Culture Culture is Learned Culture is Shared Culture is Based on Symbols Culture Gives Meaning to Reality Functions of Culture Culture and Change Ethnocentrism and Cultural Relativism What is Culture? Superstructure: A culture’s worldview, including morals and values, oftentimes grounded in religion Social structure: The rule-governed relationships—with all their rights and obligations—that hold members of a society together. This includes households, families, associations, and power relations, including politics. Infrastructure: The economic foundation of a society, including its subsistence practices and the tools and other material equipment used to make a living. The Barrel Model of Culture What is Culture? The beliefs and behaviors of a society Culture consists of abstract ideas, values, and perceptions of the world that inform and are reflected in people’s behavior Culture is the lens through which we view our world, it “invents” our reality Iceberg example… Culture is like an Iceberg… Culture is Learned Rather than inherited biologically Enculturation: The transmission of culture from one generation to the next Mammals in general display cultural behavior (I.e. we all have the urge to eat/sleep, but when we do/with whom/in what order is determined by our social relationships). With humans, our social rules are more varied and complex. Ex: Social animals…Lions, dogs, chimpanzees… http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-VCJ1ybkjnA (Chimp Culture) If animals display cultural behavior as do we, should we also view animals through an Anthropological perspective? Sub disciplines of Primate Behavior and Animal Communication deal with this question. Culture is Shared By members of a society and produces behavior that is intelligible (able to be understood) to other members of that society Society vs. Culture Society: An organized group or groups of interdependent people who generally share a common territory, language, and culture and who act together for collective survival and well-being. There can be no culture without a society, there are no known human societies that do not exhibit culture. Cultural Anthropologists focus on the Cultural aspect of society. The study of society itself is Sociology (very closely related discipline to Cultural Anthro). Culture is Based on Symbols What are some symbols of U.S. pop culture? What do they mean? Americans! Stereotypes levied at US Peace Corps employees Subcultures Cultural variation between subgroups in societies that share an overarching culture. Ex: Ethnic group (A type of subculture). People who collectively and publicly identify themselves as a distinct group based on various cultural features such as shared ancestry and common origin, language customs and traditional beliefs. Ethnicity: The expression of the set of cultural ideas held by an ethnic group Pluralistic Society: A society in which two or more ethnic groups or nationalities are politically organized into one territorial state but maintain their cultural differences Sometimes can lead to some pretty nasty misunderstandings… Ex: Yearning for Zion Ranch Texas, Warren Jeffs, Polygamy Ex: Branch Davidians, Waco Texas Ex (book –pg 33): Shetland pony seller Salt Lake City/Tongan B-day party Cultures Change In response to environmental or societal pressures. Ex: North American apparel Capitalism, need market growth = fashion changes constantly. Ideas about what is “proper” always evolving. Compare to ancient Egypt: ~3,000 years style of dress pretty much the same. No capitalism, instead a Theocracy. Balance, harmony, emphasis on sameness and repetition of cycles. Ex: New symbols emerge or are invented to convey changed cultural meanings Ex: Religion Osiris + Zeus = Sarapis