Chapter 6
Parenting
Impact on Alcohol/Drug Use and Abuse
Chapter Objectives
Explain the role parent-child bonding plays in
preventing problem behaviors and future
alcohol/drug problems.
Define the diagnostic criteria of abandonment
depression.
Describe the child temperaments that may
contribute or make the child at-risk for
substance abuse.
Explain “quality” of parent-child relationship
and its impact on substance use and abuse.
Chapter Objectives
Define shame and describe the domains of
shame and the common affect-shame binds.
Describe rejection sensitivity, difficulty
making decisions, and poor frustration
tolerance.
Classify behaviors that indicate parental
imbalance.
Define and describe boundaries and
boundary inadequacy.
Chapter Objectives
Describe triangulation in the family.
Describe the impact of parental use or abuse
of alcohol/drugs on the child’s future use or
abuse.
Describe the imbalanced life cycles of
families.
Parent-Child Bonding
Abandonment Depression
– An affective disorder with six key
elements:
•
•
•
•
•
•
Homicidal rage
Suicidal depression
Panic
Feelings of hopelessness/helplessness
Emptiness and void
Guilt
– Impact of early abandonment on adult
interpersonal relationships
Parent-Child Bonding
Child’s Temperament
– Evidence that extremes in certain temperament
traits, such as high activity level, emotionality,
attention span, and sociability are associated
with children of alcoholics.
– Aspects of temperament may predict the
behavior problems and substance abuse
problems that frequently arise during
adolescence.
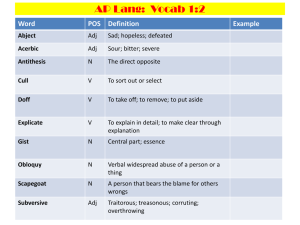
Parenting Styles That Shame Children
Shame
– The self looking at itself, and finding it lacking,
flawed, inadequate.
– Is like a flash flood of emotion that wipes out
the interpersonal connection with people
Differences between a shame-based
system and balanced system
– Shame-based
• No hope, inescapable, and exterior-based
– Balanced system
• Hope-choice, can make amends, internally based
Parents’ Shame
Parents who have not done a good job of
parenting may experience shame.
Shame and Feelings
Shame is a very powerful feeling, and
when it is attached to other feelings, they
are escalated:
– Anger plus shame equals rage
Adolescent sexual identity and shame
Sexual violation and shame
Drug, sex, and shame
Characteristics of Shame and Abandonment
Rejection sensitivity
Fear and difficulty making decisions
Poor frustration tolerance
Other reactions and defenses
–
–
–
–
Overly defensive
Extremely critical or judgemental
Rage or distorted thinking
Masking true feelings and emotions
Parental Imbalance and Boundary Setting
Clear boundaries
– Allow mutual respect and concern
Enmeshed boundaries
– Are inflexible, are unyielding, and leave no
room for differences
Disengaged boundaries
– Are overly rigid, with little or no opportunity for
communication
Boundary Inadequacy
Ambiguous boundary inadequacy
– A pattern of double messages
Overly rigid boundary inadequacy
– Smooth and efficient functioning is a priority
over being responsive and adaptable
Invasive boundary inadequacy
– An imbalance of power is used to objectify
people
Boundary Ambiguity
Stage 1 – Clustering
Stage 2 – Conflict
Stage 3 – Individuation
Stage 4 - Connection
Triangulation
Triangulation is at least two adults
involved in an off-spring’s problem, where
the parent-child dyad is pitted against a
more peripheral parent, stepparent,
grandparent, parent’s lover, or another
relative.
Triangulation
Imbalanced Life Cycles of Families
Relationships between families and the
joining of families
Family and the young child
Family and the adolescent
Launching of children
Later life
Fathers of Alcoholics/Addicts
Dealing with resistance
– Reassure the father that he is important
– Point out that changes depend on his action
– Make the father aware that he has the power to
sabotage treatment
– Note that the father has choices
– Place responsibility for change squarely on
father’s shoulders
– Get the father to consider realigning his
priorities