Concept list 6 is due on Thursday, March 17th.
Forum post 6 (Freudian Slip) is due on Friday, March
18th by 8am.
Quest 4 will be on concept list 5 and ethics and
morality.
Interpret the following psychological quote in your
mini-notebook:
“Evil men do what good men only dream of.”
Share your thoughts with a partner.
Be prepared to share out with whole group.
(6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939)
An Austrian neurologist who founded the discipline of
psychoanalysis
Best known for his theories of the unconscious mind
and the mechanism of repression
Created the clinical method of psychoanalysis for
investigating the mind through dialogue between a
patient and a psychoanalyst
Freud believed that our behavior and behavior
disorders are determined mainly by basic drives and
past psychological events.
Proposed that people may not know why they feel,
think, or act the way they do because activities are
partly controlled by the unconscious part of the mind.
Id – The unconscious portion of personality
containing basic impulses and urges
Pleasure principle – The id’s operating principle, which
guides people toward whatever feels good.
Ego – The part of personality that mediates conflicts
between and among the demands of the id, the
superego, and the real world.
Reality principle- The ego functions in reality and
creates comprises between the id and the superego.
Superego – The component of the personality that tells
people what they should and should not do.
A verbal or memory mistake that is believed to be
linked to the unconscious mind.
Examples
Calling his or her spouse by an ex's name
Saying the wrong word(s)
News Station and Freudian Slips
Log the following clip in your video source graphic
organizer:
Title
Id, Ego, and the Superego
Unit: Theoretical Foundations
Theme: Psychodynamic approach
Thread: Personality
Answer the following writing prompt in your mini-
notebook:
Create an example when your thoughts are guiding by
the id and explain how the superego represses those
actions.
Log the following clip in your video source graphic
organizer:
Title
Id, Superego, and Ego Version 2
Unit: Theoretical Foundations
Theme: Psychodynamic approach
Thread: Personality
Concept list 6 is due on Thursday, March 17th.
Forum post 6 (Freudian Slip) is due on Friday, March
18th by 8am.
Quest 4 will be on concept list 5 and ethics and
morality.
WEAR RED on Friday for extra credit.
Answer the following question in your mini-notebook:
What role do your parents play in your moral
development?
Explain by using specific examples.
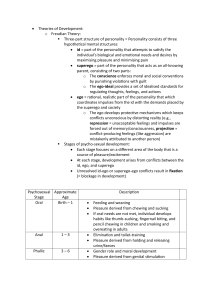
Periods of personality development in which conflicts
focus on particular issues.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Oral Stage
Anal Stage
Phallic Stage
Latency period
Genital Stage
The first psychosexual stage, in which the mouth is the
center of pleasure and conflict.
Birth to 18 months
Example
Sucking fingers
Biting and chewing
Breast feeding
The second psychosexual stage that focuses on
pleasure and conflict that sifts from the mouth to the
anus.
18 months to 3 years old
Examples
Toilet Training
Too harsh or too early can produce stinginess and
neatness in adults
Too late or too lax can produce disorganized or
impulsiveness in adults
The third psychosexual stage that focuses on pleasure
and conflict shifts the genital area.
3 years old to the age of 6
Example
Oedipus Complex–Boy experiences sexual desire for his mother
and wants to eliminate father. (Male superego developed)
Electra Complex –Girl develops penis envy and transfer love from
mother to father.
The fourth psychosexual stage which sexual impulses
lie dormant.
Age 6 through Age 12
Example
Children at this age hang out with groups of friends
that are of the same sex.
The fifth psychosexual stage, which begins during
adolescence, when sexual impulses appear at the
conscious level.
Puberty till Death
Example
Pleasure is focused on the genitals of an individual.
Log the following clip by using your video source log
graphic organizer:
Title
Freud's Psychosexual Stages
Unit: Theoretical Foundations
Theme: Psychodynamic approach
Thread: Personality