Regression Discontinuity Design Can Be Your Friend: Developing
advertisement

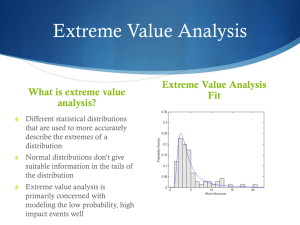
REGRESSION DISCONTINUITY DESIGN CAN BE YOUR FRIEND: DEVELOPING EVIDENCE IN THE REAL WORLD Applied Research Seminar David Kimball Adriano Udani Department of Political Science, UMSL RD Design and Applications Public Policy Research Center 1 AGENDA Purpose Scholarship and Contributions Design Application RD Design and Applications 2 REGRESSION DISCONTINUIT Y DESIGN Method to estimate treatment ef fects in natural setting Observed continuous variable and causal variable of interest exhibit a discontinuous increase at a certain threshold Address confounding factors influencing control and treatment Empirically verify assumptions strengthens internal validity Applies to observations only near “cutof f point” limits external validity RD Design and Applications 3 THISTLEWAITE AND CAMPBELL (1960) Impact of scholarships on future academic outcomes Awards based on test scores, measured against cutoff point (c) If score > c, then individual receive an award Estimated treatment effect applies to individuals near the cutoff point Assume these individuals have similar characteristics EXCEPT receipt of award RD Design and Applications 4 T YPES OF RD STUDIES Source of RD Threshold Treatment Outcome Performance Test score Team standings Scholarship Relegation Achievement Club revenues Population City/County Size Federal funds Election rules Official salaries Voting behavior Turnout Candidate entry Size threshold School size Firm size Class size Anti-bias law Achievement Productivity Anti-poverty program High security Voting behavior Recidivism Eligibility criteria City poverty rank Prisoner index Age threshold Voting age Past voting Student birth month Years of education Turnout Earnings Close elections Vote majority Incumbency Politician behavior Income Annual income Health insurance Health RD Design and Applications 5 STUDIES THAT USE RDD Health Low birth weight babies (Almond et al. 2010) Young adults who lose health insurance (Anderson et al. 2012) Education U.S. School Bond Referenda (Cellini, Ferreira, and Rothstein 2010) Management studies Yelp.com ratings (Anderson and Magruder 2012; Lucas 2012) Political Science Split tickets in the Senate (Butler and Butler 2005) Incumbency effect (Snyder 2005) * Coattails of Members of Congress (Broockman 2009) U.K. House of Commons (Eggers and Hainmueller 2009) Close House Races (Caughey and Sekhon 2011) U.S. mayoral races (Gerber and Hopkins 2011) RD Design and Applications 6 RDD: TREATMENT EFFECT RD Design and Applications Source: Perraillon (2013): http://home.uchicago.edu/~mcoca/docs/hrs_rdd_slides_f.pdf 7 BLACK MAYORS HIRE MORE BLACK POLICE Source: Hopkins and McCabe 2012 RD Design and Applications 8 EVALUATE RD ASSUMPTION THEORETICALLY Be wary of RD design if there is strategic behavior or manipulation near threshold. Information Incentives Capacity RD Design and Applications 9 TEST RD ASSUMPTIONS EMPIRICALLY Balance test: Plotting means of pre -treament covariates in control group vs. treatment group (dif ference of means). Density test: Examine distribution of observations just above and just below threshold. Test causal direction (outcome or treatment DOES NOT predict pre-treatment DV or other covariates) Placebo test: Look for other discontinuities in the range of scores. RD Design and Applications 10 CHECK STABILIT Y OF RD RESULTS Test dif ferent specifications. Linear Polynomial Local regression Test dif ferent “discontinuity samples” (dif ferent bandwidths). Test sensitivity to inclusion of pretreatment covariates RD Design and Applications 11 0 10 20 30 MISSOURI SCHOOLS APPLICATION 0 50 100 150 MSIP 2014 Score RD Design and Applications 12 IMPLICATIONS FOR POLICY ANALYSIS RD design is an appealing form of natural experiment. Weak assumptions compared to other empirical methods In many cases the assumptions are plausible Policymakers might consider a threshold for policy applications – this would favor empirical analysis of the policy’s impact. RD Design and Applications 13 REFERENCES Joshua D. Angrist and Jörn-Stef fen Pischke, Mostly Harmless Econometrics (Princeton University Press, 2008). Thad Dunning, Natural Experiments in the Social Sciences (Cambridge University Press, 2012). Andrew C. Eggers, Anthony Fowler, Jens Hainmueller, Andrew B. Hall, and James M. Snyder, Jr. 2014. “On the Validity of the Regression Discontinuity Design for Estimating Electoral Ef fects: New Evidence from over 40,000 Close Races.” American Journal of Political Science (May 2014). RD Design and Applications 14