The Neuropsychology of Learning Disabilities
advertisement

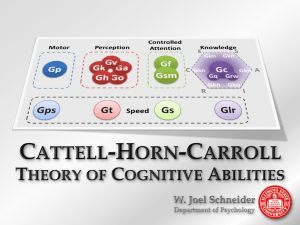
Advanced Cross-Battery Assessment Using CHC Theory and Neuropsychological Measures Catherine A. Fiorello, Ph.D., ABPP Temple University September 30, 2011 Workshop Objectives Participants will be able to: • Use XBA to detect processing deficits in identifying students with LD and ADHD • Describe how processing assessment can be integrated within an RtI model • Understand how CHC Theory and neuropsychological assessment work together Cognitive Product or Process: Synthesizing Paradigms Nomothetic Assessment Idiographic Assessment • Compares individual to norm • Focuses on score: Assessment Product • Interpret levels of performance • Compares individual to self • Focuses on performance: Assessment Process • Interpret patterns of performance BOTH essential for effective assessment and intervention IDEA 2004: The Impetus for Developing Better Assessment and Intervention Strategies Identifying Children with Learning Disabilities: IDEA Definitions and Practices Defining Learning Disabilities • Learning Disabilities is a disorder of one or more of the basic psychological processes that adversely affects educational achievement in one or more academic domains Determining Learning Disabilities • Discrepancy between “ability” and “achievement” (typically using cut-off points and global IQ) • Failure to respond to scientific research-based intervention • May permit the use of other alternative research-based procedures for determining whether a child has a specific learning disability, as defined in §300.8(c)(10) (OSERS Final Regulations-8/06) RtI as Prereferral Process • Prereferral interventions, with good progress monitoring, are essential to serving children. • Interventions may help a large number of children (e.g., Torgeson, early reading, 9496%). • Tracking response to intervention provides good information about what works and what doesn't. • Avoids “waiting to fail.” Problems with RtI • Established interventions for many referral problems do not exist. • Agreement on goal setting (what is failure to respond?) can be problematic. • Many children are referred for multiple areas of difficulty. • Failure to respond may be due to many reasons other than disability. RtI and LD • RtI provides valuable information as part of an evaluation for learning disabilities • A failure to respond to interventions is not, by itself, diagnostic of a learning disability. • Cognitive and neuropsychological processing is critical to identifying LD. • School psychologists can and should evaluate processing. Fiorello Comprehensive RTI Model High quality research-based teaching ~85% Universal screening Protocol-based interventions ~10% Individual screening Personalized interventions Comprehensive assessment: cog/neuro/ach ecobehavioral personality etc. IEP ~3 % ~2% Implications for Assessment and Intervention Cognitive Hypothesis Testing Model Theory 1. Presenting Problem 5. Cognitive Strengths/Weaknesses 9. Intervention Consultation Interpretation Hypothesis 13. Continue/Terminate/Modify 4. Interpret IQ or Demands Analysis 2.Intellectual/Cognitive Problem 8. Interpret Constructs/Compare 6. Choose Related Construct Test 12. Determine Intervention Efficacy Data Collection 10. Choose Plausible Intervention 3. Administer/Score Intelligence Test 7. Administer/Score Related Construct Test 11. Collect Objective Intervention Data Source: Hale, J. B., & Fiorello, C. A. (2004). School Neuropsychology: A Practitioner’s Handbook. New York, NY: Guilford Press. Processing and LD • Literature in cognition, cognitive assessment, neuropsychology, and learning disabilities links cognitive processing with achievement and LD. • Regular education curricula tend to focus on a few areas of processing (e.g., phonemic awareness) to the exclusion of many others. • Once there has been failure to respond, process assessment can be used to develop interventions. School Neuropsychology: The Key to Reconceptualizng Cognitive Processes for Assessment and Intervention The Two Axes Interpretation Anterior -Executive Functions -Motor Output Posterior -Sensory Input -Comprehension Structural Hemispheric Differences Left Hemisphere Right Hemisphere More Grey Matter More White Matter More Primary Cortex More Association Cortex More Intramodal Connections More Intermodal Connections Source: Goldberg, E., & Costa, L. D. (1981). Hemispheric differences in the acquisition and use of descriptive systems. Brain and Language, 14, 144-173. The Two Axes Interpretation Anterior -Executive Functions -Motor Output Left Hemisphere Right Hemisphere -Routinized/Detailed/Local -Convergent/Concordant -Crystallized Abilities -Novel/Global/Coarse -Divergent/Discordant -Fluid Abilities Posterior -Sensory Input -Comprehension Is There Evidence? • • • • • Newborn language processing Musician processing of symphonies American Sign Language in the deaf Brain activation in novice-new learning vs. expert-learned Bilateral fMRI activation: Left and right for Verbal; Right and left for nonverbal processing Psychological processes matter more than stimulus input or response output! Source: Hale, J. B., & Fiorello, C. A. (2004). School Neuropsychology: A Practitioner’s Handbook. New York, NY: Guilford. Hemispheric Functions and Language Left Hemisphere Right Hemisphere Source Routinized/Automatic Novel/New Learning Goldberg/Costa, 1981 Low Demand High Demand Belger & Banich, 1998 Local/Detailed Global/Holistic Delis et al., 1986 Microstructural Macrostructural Glosser, 1993 Fine Processes Coarse Processes Beeman/Chiarello, 1998 Close Semantic Distant Semantic Chiarello, 1998 Simple Syntax Complex Syntax Cooke et al., 2001 Concordant/ Convergent Discordant/ Divergent Bryan & Hale, 2001 Comprehensive Assessment Model HOME SCHOOL Family Constellation Instruction Siblings Attachment Parental Mental Health Parental Educational Background Resources Interventions Language History Language Development Background Knowledge Structure Supports Services Motivation STUDENT Developmental Status Physical Health Economic Resources Social Resources Role Models Violence COMMUNITY Cognitive Abilities Emotion Regulation Psychopathology Friendship Role Models Bullying PEERS The Cattell-Horn-Carroll (CHC) Model Achievement Basic Reading Reading Comprehension Written Expression CHC Factors Ga-PC Phonetic Coding (Phonemic Awareness) Ga Auditory Processing -Phonetic Coding Ga-PC Phonetic Coding Gsm Short-Term Memory -Memory Span -Working Memory Gsm Short-Term Memory -Memory Span -Working Memory Glr Long-Term Storage and Retrieval Glr Long-Term Storage and Retrieval -Naming Facility (RAN) -Meaningful Memory Gs Processing Speed -Perceptual Speed Gs Processing Speed -Perceptual Speed Gs Processing Speed Gc Crystallized Ability -Vocabulary -Listening Skills -Language Development -General Knowledge Gc Crystallized Ability -General Knowledge -Listening Skills Gc Crystallized Ability -Vocabulary -Language Development -General Knowledge Gf Fluid Reasoning CHC Model, cont. Achievement Basic Math Math Reasoning CHC Factors Ga-PC Phonetic Coding Ga-PC Phonetic Coding Gsm-MW Working Memory Gsm Short-Term Memory -Memory Span -Working Memory Gs Processing Speed -Perceptual Speed Gs Processing Speed -Perceptual Speed Gc Crystallized Ability Gc Crystallized Ability Gf Fluid Reasoning Gf Fluid Reasoning Gq Math Knowledge Gq Math Reasoning Gv Visual Processing? (Higher Math?) Oral Language/Listening Comprehension Gc Crystallized Ability The Neuropsychology of Reading Disorders Word Recognition • Phonological Awareness • Symbolic Representation • Phoneme-Grapheme Correspondence • Timing/Automaticity • Word Attack vs. Sight Word Strategies Reading Comprehension • • • • Semantics Syntax Pragmatics Timing/AutomaticityFluency • Explicit-Factual vs. Implicit-Inferential Comprehension Double-Deficit or multiple subtypes? Source: Hale, J. B., & Fiorello, C. A. (2004). School Neuropsychology: A Practitioner’s Handbook. New York, NY: Guilford. The Neuropsychology of Math Disorders Computation • Quantitative Knowledge • Value-Grapheme Correspondence • Sequential/Working Memory • Visual-PerceptualSpatial (higher only) • Graphomotor Word Problems • • • • Auditory Processing Verbal Comprehension Quantitative Knowledge Word/Symbolic Representation • Sequential/Working Memory • Fluid/Quantitative Reasoning Source: Hale, J. B., & Fiorello, C. A. (2004). School Neuropsychology: A Practitioner’s Handbook. New York, NY: Guilford. Developing and Testing Hypotheses About Cognitive Processes and Achievement • Examine profile for significant subtest or factor scatter • If global scores are invalid, interpret subtest performance within and between subtests • Use Demands Analysis to examine Input, Processing, and Output Demands (Caution: Processing Demands More Relevant) • Demands Analysis is prone to error, must validate with additional measures (Caution: Avoid Cookbook Interpretation) • Data must show convergent, divergent, AND ecological validity Demands Analysis: Block Design Determining InputProcessingOutput Demands Demands Analysis: WISC-IV Block Design Determining InputProcessingOutput Demands Input Demands: • • • • • Models and abstract visual pictures Lengthy oral directions-receptive language Demonstration and modeling Perception of timed task Low cultural knowledge and emotional content Demands Analysis: WISC-IV Block Design Determining InputProcessingOutput Demands Processing Demands: • Novel task for most children (note beginning vs. later task performance-also when lines removed) • Visual processing: Spatial-global • Visual processing: Directional orientation-local • Perceptual analysis (divergent thought) and synthesis (convergent thought) • Planning, strategizing, and monitoring performance: Match to sample • Sustain attention, inhibit impulsive/error responding Demands Analysis: WISC-IV Block Design Determining InputProcessingOutput Demands Output Demands: • Fine motor response, arrange manipulatives • Bimanual sensory (visual-somatosensory) – motor coordination • Processing speed Processing Assessment Using Specific Tests DAS-II Copying Gv:Vz Early Number Concepts Gq:A3, KM Receptive language, spatial and numerical concepts Matching Letter-Like Forms Gv:Vz Visual perception, orientation, attention to details Matrices Gf:I Inductive reasoning, multiple choice Naming Vocabulary Gc:VL, LD Expressive naming Pattern Construction Gv:SR Visual-spatial processing, constructional praxis, planning, bimanual coordination Phonological Processing Ga:PC Phonological awareness, segmentation, assembly Picture Similarities Gf:I Fluid reasoning, visual perception Rapid Naming Glr:NA Gs:Pc Fluent retrieval from LTM; automaticity of visual-auditory associations Recall of Designs Gv:MV Visual and spatial memory Recall Digits-Forward Gsm:MS Visual-motor integration, graphomotor skills Rote auditory memory, sequencing DAS-II, cont. Recall Digits— Backward Gsm:WM Working memory for auditory material Recall Objects— Immediate Glr:M6 Memory for verbal and pictorial stimuli Recall Objects— Delayed Glr:M6 Longer-term memory, verbal and pictures Recall Sequential Order Gsm:WM Short-term memory for verbal and pictorial stimuli, sequencing Recog. of Pictures Gv:MV Nonverbal visual memory, recognition Seq. & Quant. Reasoning Gf:I, RQ Fluid reasoning, sequential reasoning, figural and numeric Verbal Similarities Gc:LD Verbal knowledge, verbal reasoning Speed of Info Processing Gs:N, R9 Processing speed, graphomotor Verbal Comp. Gc:LD, LS Receptive language, basic language concepts Word Definitions Gc:VL, LD Verbal knowledge, oral expression KABC-II Simultaneous/Gv Triangles Visual-spatial processing, constructional praxis, planning, bimanual coordination Face Recognition Visual facial memory (ventral stream) Pattern Reasoning (5-6) Inductive reasoning, visual processing, figural Block Counting Visual-spatial processing, quantitative knowledge Story Completion (5-6) Reasoning, sequencing, attention to visual details Conceptual Thinking Inductive reasoning, visual processing, pictorial Rover Planning, inhibition, spatial processing Gestalt Closure Visual processing, holistic perception Sequential/Gsm Word Order Short-term auditory memory for unrelated words, nonverbal response, later items interference task Number Recall Short-term auditory memory Hand Movements Short-term visual memory, sequencing, praxis KABC-II, cont. Planning/Gf Pattern Reasoning (7-18) Inductive reasoning, visual processing, figural Story Completion (7-18) Reasoning, sequencing, attention to visual details Learning/Glr Atlantis +Delayed Associative memory, meaningless symbols and names, syllable length cues Rebus +Delayed Associative memory, rebus clues to meaningful sentences Knowledge/Gc Riddles Receptive language, reasoning, long-term memory retrieval Expressive Vocabulary Word knowledge, oral expression Verbal Knowledge General knowledge, multiple choice, pictorial representations CAS Planning Planned Codes Gs:R9 Sustained attention, psychomotor speed, strategy use Matching Numbers Gs:P Sustained attention, visual scanning, psychomotor speed, strategy use Planned Connections Gs:P Sustained attention, visual scanning, psychomotor speed, strategy use NV Matrices Gf:I Inductive reasoning, multiple choice Verbal/Spatial Relations Gv:SR Gc:LS Receptive language, working memory, grammatical relationships, visual scanning/discrimination Simultaneous Figural Memory Gv:MV, CF Visual perception, spatial relationships, visual memory, graphomotor reproduction, constructional skills, figure-ground relationships CAS, cont. Attention Expressive Attention Glr:NA Inhibition of automatic response; similar to Stroop Number Detection Gs:P Cancellation task, sustained attention, visual scanning, visual discrimination, inhibition, psychomotor speed Receptive Attention Gs:P Sustained attention, visual scanning, attend to perceptual, then shift set to meaning Word Series Gsm:MS Word span, rote auditory memory Sentence Repetition Gsm:MS Gc:MY Rote recall of meaningless sentences, grammatical structure important Sentence Questions Gsm:WM Gc:LD Language comprehension based on grammatical structure with meaningless content Speech Rate Gps:PT Oral praxis Successive WISC-IV Integrated Verbal Comprehension Verbal Subtests Multiple Choice Long-term memory retrieval; compares free-recall and recognition memory Working Memory Visual Digit Span (Forward) Compare visual to auditory memory span Spatial Span (Forward and Backward) Compare visual to auditory working memory Letter Span (Forward) Compare numbers to letters (familiarity) L-N Seq Process Approach Arithmetic Process Approach Compare working memory effects Written Arithmetic Compare arithmetic knowledge WISC-IV Integrated, cont. Perceptual Reasoning Block Design Multiple Choice Visual discrimination and spatial perception; removes v-m integration and speed demands Block Design Process Approach Comparison of orientation (LH) versus configuration (RH) errors Elithorn Mazes Executive funtions—planning, organization, monitoring, inhibition; graphomotor skills Processing Speed Coding Copy Visual-motor integration, graphomotor skills, processing speed Coding Recall Paired-associate symbol and digit recall, free recall CMS Auditory/Verbal Stories Glr:MM Auditory attention, semantic long-term memory encoding and retrieval, sequencing/grammar, verbal comprehension, expressive language Word Pairs Glr:MA Paired-associate task; auditory attention, learning novel word pairs Word Lists Glr:M6 Selective reminding task; long-term memory encoding, storage and retrieval of unrelated words Visual/Nonverbal Dot Locations Gv:MV Visual-spatial memory encoding and retrieval (dorsal stream); susceptibility to interference Faces Gv:MV Facial memory encoding and retrieval (ventral stream) Attention/Concentration Sequences Gsm:WM Rote recall followed by mental manipulation-executive function (working memory) NEPSY-II Executive Functions/Attention Animal Sorting Gf:I Problem-solving, verbal and spatial concept formation, categorical thinking, flexibility of thinking Auditory Atten & Response Set Gs Sustained auditory atten., vigilance, inhibition, set maintenance, flexibility Clocks Gv:Vz Gc:K0 Telling time, reading analogue clocks, visual-spatial processing, graphomotor Design Fluency Glr:FF Visual-motor fluency, flexibility, divergent thinking, graphomotor Inhibition Glr:NA Naming fluency, inhibition, shifting set Knock and Tap Gsm:WM Self-regulation, inhibition, maintaining set Statue Resistance to distraction, inhibition, motor persistance NEPSY-II, cont. Language Body Part Naming Gc:K0 Knowledge of body parts, receptive and expressive Comprehension of Instructions Gc:LS Receptive language, sequencing, grammar Oromotor Sequences Gps:PT Oral praxis, sequencing, memory span Phonological Processing Ga:PC Auditory attention, phonological awareness, segmentation, assembly Recognition of Reversals Gv:MV Gc Visual perception of orientation, orthographic knowledge Repetition of Nonsense Words Ga:UM Gsm:MS Phonemic awareness, auditory memory span, sequencing Speeded Naming Glr:NA Naming automaticity, processing speed Word Generation Glr:FW Verbal fluency, integrated RH/LH functioning, compare category with letter responses NEPSY-II, cont. Sensorimotor Functioning Fingertip Tapping Gps:MT Simple motor speed, perseverance Imitating Hand Positions Gp:P2 Visual perception, praxis, kinesthesis Manual Motor Series Gp Imitate a series of rhythmic movements Visuomotor Precision Gp Visual-motor integration, graphomotor w/o construction Affect Recognition Gkn:BC Facial processing (ventral stream), matching emotions Theory of Mind Gkn:BC Perspective taking for knowledge and emotions Social Perception NEPSY-II, cont. Visuospatial Processing Arrows Gv:SR Spatial processing, visualization, line orientation, inhibition, no motor Block Construction Gv:Vz Visual-spatial processing, constructional praxis, planning, bimanual coordination Design Copying Gv:Vz Visual-motor integration, graphomotor skills, local and global processing Geometric Puzzles Gv:Vz Visual-spatial processing; figural, mental rotation, no motor demands Picture Puzzles Gv:CF Visual-spatial processing, pictorial, visual Gc:K0 discrimination, local detail processing, figure-ground Route Finding Gv:SS Visual-spatial processing, orientation NEPSY-II, cont. Memory and Learning List Learning (Delay) Glr:M6 Verbal memory Memory for Designs (Delay) Gv:MV Visual memory, spatial recall and visual details Memory for Faces (Delay) Glr:MA Facial memory (ventral stream) Memory for Names (Delay) Glr:MA Associative memory, names and faces Narrative Memory Glr:MM Meaningful memory Sentence Repetition Gsm:MS Gc:LD Auditory short-term memory, content and grammatical structure important Word List Interference Gsm:WM Auditory memory, short term and working memory (with interference) D-KEFS Sorting Problem-solving, verbal and spatial concept formation, categorical thinking, flexibility of thinking Trail Making Mental flexibility, sequential processing on visual-motor task, set shifting Verbal Fluency Verbal fluency Design Fluency Visual fluency Color-Word Interference Attention and response inhibition Tower Planning, flexibility, organization, spatial reasoning, inhibition 20 Questions Hypothesis testing, verbal and spatial abstract thinking, inhibition Word Context Deductive reasoning, verbal abstract thinking Proverb Metaphorical thinking, generating versus comprehending abstract thoughts CTOPP Phonological Awareness Elision Ga:PC Phonological perception, segmentation Blending Words Ga:PC Phonological assembly Sound Matching Ga:PC Phonological perception, segmentation Phoneme Reversal Ga:PC Phonological perception, segmentation, Gsm:WM working memory Blending Nonwords Ga:PC Phonological assembly Segmenting Nonwords Phonological perception, segmentation Ga:PC Phonological Memory Memory for Digits Gsm:MS Short-term memory, sequencing Nonword Repetition Ga:UM Gsm:MS Phonemic analysis, assembly, working memory CTOPP, cont. Rapid Naming Rapid Digit Naming Glr: NA Number automaticity, processing speed, verbal fluency Rapid Letter Naming Glr: NA Letter automaticity, processing speed, verbal fluency Rapid Color Naming Glr: NA Color name knowledge, naming automaticity, processing speed, verbal fluency Rapid Object Naming Glr: NA Object recognition, naming automaticity, processing speed, verbal fluency Tests Discussed • • • • • • • • CMS Children’s Memory Scale PsychCorp/Pearson CAS Cognitive Assessment System Riverside CTOPP Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing Pro-Ed DAS-II Differential Abilities Scales Second Edition PsychCorp/Pearson D-KEFS Delis-Kaplan Executive Function System PsychCorp/Pearson KABC-II Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children Second Edition Pearson Assessments NEPSY-II PsychCorp/Pearson WISC-IV Integrated PsychCorp/Pearson