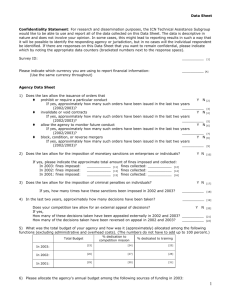
Competition Overview – Barbados Experience

Fair Trading Commission
Overview of Competition Law
The Experience of Barbados
Competition law and Policy Training Workshop
March 30-31, 2011
The Savannah Hotel
Competition Law or Antitrust Law
Law that promotes and maintains market competition by regulating anti-competitive conduct.
Adam Smith: Monopoly - "...great enemy to good
management Competition - medium for "...new divisions of labour, and new improvements of art”
• Competition is not an end in itself but a process that advances goals of economic well being, ultimately for consumers
Competition law or Antitrust law
(Three main elements)
Prohibits agreements/practices that restrict competition between business - price fixing cartels
Prohibits abusive behavior by a dominant firm, - predatory pricing, excessive pricing, refusal to supply
Reviews mergers and acquisitions and joint ventures of large corporations:
• Prohibit potentially anti-competitive mergers
• Prescribe remedies to protect competition
History of Competition Law
1890 — Sherman Antitrust Act (United States) Prohibits agreements in restraint of trade and monopolization
1914 — Clayton Antitrust Act (United States) Prohibits specific types of conduct and mergers that may lessen competition
1957 — (Article 81 and 82) Treaty of Rome established
(European Economic Community) Promoting economic integration to promote free trade
1976 — Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvement Act (United
States) investigate mergers
1980 —Policies to tackle restrictive practices (UNCTAD)
Growth of Competition Law World wide
( 2010 - over 90 countries, 110 Authorities)
1900 Influence of monopolies United States
1960 Economic integration, free trade
1980 Economic efficiency, Privatization
2008 Transition from state control, Eastern
Europe, also Latin America/Barbados
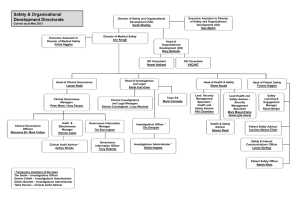
Fair Trading Commission Barbados
Requirement of Ch. 8 –Treaty of Chaguaramas
Public Consultation
Fair Trading Commission - Established 2001
1.
2.
3.
Utilities Regulation Act 2001 To Ensure Efficient
Utility Services
Fair Competition Act 2003 To Promote and
Maintain Competition
Consumer Protection Act 2003 To Protect
Consumer Rights
Fair Competition act
(Scope of Coverage)
Similar to Treaty of Chaguaramas / EC Article 81 and 82
• EC Anti-Competitive Agreements
(Horizontal/Vertical)
• Abuse of Dominance
• Interlocking Directorates
• Includes Merger Control Provisions
• Provides for Authorisations
• Includes all domestic markets
• Includes Statutory Corporations
Initial Challenges Faced by
Commission
○
Reaction of Business Community
Over regulation,
○ Lacking the necessary expertise,
○ Restricted ability to expand/compete internationally
Lack of Competition Culture and infrastructure
Inexperienced Staff
Inexperienced Judiciary/Legal/Technical
Inadequacy of legislation/administrative procedures
Limited financial resources
Initial Approach Adopted
Informal Grace Period
Took on selected matters
Sought technical Assistance
Inform and educate public
Special Stakeholder Seminars (business/Consumers etc.)
Guidelines, Articles in press, Fliers
Website
Radio and TV
Subsequent Approach Adopted
(to Develop Competition Culture)
Enforcement/Education
Expanded Education Programme
Internal Research studies
Expand Range of Investigations
Own Initiative Sector Investigations
Specific Training Programmes
Build Alliances - Business/Public Sector
Develop International Linkages
Industries Investigations
Type of
Investigations
Industry
Abuse of Dominance • Telecommunications
• Construction
• Oil Industry
Anti Competitive
Agreements
• Professional Services
• Shipping
• Commercial Banking
Merger
• Telecommunications
• Distribution
No.
Performance To Date
INVESTIGATIONS /Guidance
Abuse of Dominance Investigations
Agreements Investigations
Anti Competitive Conduct Guidance
Merger Investigations
Merger Guidance
Authorisation Investigations
Authorisation Guidance
Total
0
1
1
5
Future Work Focus
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Refine legislative framework
Inform and Educate businesses
Improve investigative procedures
Increase training of staff
Ensure Government Policy conforms with
Competition
Improve Knowledge of Judiciary
Provide Technical Assistance Regionally
Fair Trading Commission
Overview of Competition Law
The Experience of Barbados
Competition law and Policy Training Workshop
March 30-31, 2011
The Savannah Hotel