Powerpoint
advertisement

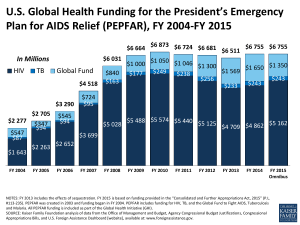
Ethiopia: Focusing our Program for Impact & Efficiency Jocelyn Felter Brown Acting Coordinator, PEPFAR Ethiopia AIDS 2014 – Stepping Up The Pace Ethiopia – Important Features • Population 90 million • Predominantly rural agrarian country • Growing economy with large infrastructure development projects • Low/decreasing national HIV/AIDS prevalence: 1.4% • Has reached the “Tipping Point” • Significant Urban to Rural HIV/AIDS disparity: mixed epidemic • Government is the primary service provider • Strong political commitment to health & equity of services • Significant Global Fund investment, but expected to decline with New Funding Model Ethiopia: Three Ways of Looking at HIV Distribution: Prevalence, No. Infected, and Density, 2011 PEPFAR Expenditures by Geographic Location & HIV Burden with Adult Prevalence FY13 PEPFAR Expenditures by Region vs. Prevalence and Disease Burden Bubble size = HIV Prevalence Among Adult Population, 2011 $50,000,000 Amhara PEPFAR Expenditures (FY2013 EA) $45,000,000 Oromiya $40,000,000 $35,000,000 Addis Ababa $30,000,000 $25,000,000 SNNPR Tigray $20,000,000 $15,000,000 Harari $10,000,000 Somali Dire Dawa $5,000,000 Benishangul-Gumuz Afar Gambela $0 0 50,000 100,000 150,000 200,000 250,000 300,000 People Living with HIV, 2011 Source: HIV Related Estimates and Projections for Ethiopia – 2012. Excludes National and Above National Spending 4 Focusing the Program: Start with Clinical Care & Treatment Number of Adults in need of ART* National Coverage Rate & Goals 2013 2014 2015 431,761 530,835 542,632 @69% = 298,336 *Source: Spectrum HIV Related Estimates and Projections for Ethiopia, 2014 80% 434,106 Focus on Clinical Care & Treatment • Historically…US University treatment partners led clinical care & treatment efforts • Partners accomplished what they were brought to Ethiopia to do; time to move more responsibility to Government of Ethiopia • Promising results from transition of University partners to Regional Health Bureaus in 3 regions demonstrated success and ability to manage funding • Assumption is that we can achieve same treatment goals, at same level of quality, but more efficiently – across all regions Achieving Efficiency in Clinical Care & Treatment USD, in millions 120 PEPFAR/HHS-Ethiopia Funding, by Partner Type 100 80 60 40 20 0 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014* US/Intl Local Total * 2014 reflects the COP14 submission, new funds only Defining Our Core We adapted the UNAIDS Investment Case Framework to further focus and rationalize our PEPFAR program in Ethiopia Understand: 1. Current state of epidemic—and how it’s expected to change 2. National Response: What is USG’s current role -- how might or should it change? 3. What are roles of other HIV Donors, Global Fund, Government, private sector -- how might they change? Design: 1. What are the core program elements/critical enablers required to Save Lives and Prevent New Infections? 2. What are the core program elements /critical enablers USG is uniquely qualified to deliver? 3. How and when and to whom should non-core programs/noncritical enablers transition or end? 4. What is the cost of the core program? 8 Prioritizing Activities Must Do Core • Activities critical to saving lives, preventing new infections - and/or which USG is uniquely qualified Near Core • Activities that directly support our goals and cannot yet be done well by other partners or host gov’t. Non Core • Activities that do not directly serve our HIV/AIDS goals and/or can be taken on by other partners or host gov’t or civil society. Should Do Nice to Do 9 Defining the Core: Results NonCore NearCore Core • Economic Strengthening (non-OVC) • TA In-school Youth prevention • Low-risk prevention (GPY) • • • • • • • • Blood Safety TA to Private Sector Health Svcs VMMC In-School Youth funding to MOE • Leadership and Governance (w/ transition plan) • Community/Peer Support • Ongoing Construction Commitments • • • • • Treatment Prevention (High & Med Risk) Targeted Testing Supply Chain TA HIV/AIDS Commodities • • • • PPP TA Infection Prevention Cross-border Cervical cancer screening Evidence Base (SI, SS, M&E) HC Financing/Insurance Training HMIS • OVC (incl. ES) Using Data to Maximize Program Investment Evidence Base Analysis • Utilized most current ANC surveillance data to ensure sufficient support in regions and refugee sites with increasing prevalence • Tracked those emerging regions transected by major transport corridors and targeted funding toward hottest Hot Spots • Assessed areas where HRH capacity is most limited and targeted ToT support Economic Analysis • We utilized national PEPFAR expenditure data to calculate unit expenditures, which allowed us to ‘cost’ our program’s core interventions • Expenditure data at regional and partner level prompted refinement to certain activities and regional interventions Site-Level Analysis • Directed spend toward highest-volume and highest-yield facilities; reduced spend to facilities with low-volume/low-yield Geographic Analysis: HIV+ yield distribution across PMTCT sites 90% 80% (14,260) of patients in 22% (371) of 1,668 sites 80% 80% 70% 60% 51% 50% Sites HIV+ 40% 30% 26% 22% 20% 20% 10% 0% 0% High Yield Key: High Yield = >1 patient/month Low Yield = <1 patient/month Low Yield No Yield Stakeholder Coordination With a more focused PEPFAR program, on-going stakeholder alignment is key to sustain gains and prevent service gaps Government Global Fund • Years of successful TA and strong Gov’t support ensure readiness to take over Cervical Cancer, Infection Prevention, VMMC, Blood Safety • Extensive Gov’t led Health Extension Worker program is able to take on more Community-focused activities • Revolving fund for ES allows PEPFAR to focus on OVC House Holds • On-going HSS funding can support health infrastructure needs • Commitment to significant funding of ARVs, RTKs Civil Society & Private Sector • Years of USG and Global Fund support have capacitated CSOs to take on more Community and Peer Support activities • Years of TA to Private Sector providers have strengthened their ability to serve clients and support business ETHIOPIA HAS A REAL CHANCE AT AN AIDS FREE GENERATION Thank You