醫療影像處理在診斷上之應用
advertisement

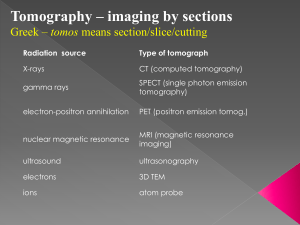
醫療影像處理在診斷上之應用 嘉義大學資工系 教授 時間: 2009年5月13日 柯建全 Outline Introduction Object of medical image processing Imaging devices applications Related techniques for Medical imaging Research Results Future works Introduction What is Medical imaging? Why do we need digital image processing? What kind of problems are often caused in medical images? Blurring caused by respiratory or motion Low contrast caused by imaging device or resolution Complicated textures Research trends have been transferred from 2-D to 3-D reconstruction Introduction (continue) Integrate all possible methods in the filed of DIP, pattern recognition, and computer graphics Qualitative Quantitative Three categories of imaging in different modalities Structural image Functional image Molecular image Object Help physicians diagnose Reduce inter- and intra-variability Produce qualitative and quantitative assessment by computer technologies Determine appropriate treatments according to the analyses Surgical simulation or skills to reduce possible erros Medical Imaging Modalities X-ray Ultrasound: non-invasive Computed tomography Magnetic resonance imaging SPECT (Single photon emission tomography) PET( Positron emission tomography) Microscopy X-ray Ultrasound 2-D sonography 3-D sonography Doppler color sonography A series of 2-D projection Reconstruction 4-D sonography Computed tomography MRI 可以觀察活體三度空間的斷層影像 磁振影像取影像時可以適當控制而得到不 同參數的影像,如溫度、流場(flow)、水 含量、分子擴散( diffusion)、 灌流 (perfusion)、化學位移(chemical shift)、 功能性(functional MRI) 及不同核種如 氫、碳、磷 MRI-structural and functional image Related techniques Image processing Segmentation Registration Feature Extraction Shape feature Texture Motion tracking Pattern recognition Supervised learning Un-supervised learning Neuro network Fuzzy Support vector machine(SVM) Genetic algorithm Related techniques 3-D graphic Virtual diagnose or visualization Fusion between different modalities Bio-medical visualization SPECT-functional image PET(Positron Emission Tomography ) PET以分子細胞學為基礎,將帶有特殊標記的葡 萄糖合成藥劑注入受檢者體內,利用PET掃瞄儀 的高解析度與靈敏度作全身的掃描,藉由癌細胞 分裂迅速,新陳代謝特別旺盛,攝取葡萄糖達到 正常細胞二至十倍,造成掃描圖像上出現明顯的 「光點」 能於癌細胞的早期(約0.5公分)準確地判定癌細 胞,提供醫師作為診斷及治療的依據,診斷率高 達87-91%,30歲以上的成年人及有癌症家族史 的民眾,建議每隔1~2年做一次PET檢查。 PET (Positron emission tomography) Applications in a hospital Assist surgeon plan surgical operation or diagnose Picture archiving system (PACS) 將醫療系統中所有的影像,以數位化的方式儲存,並經 由網路傳遞至同系統中,供使用者於遠側電腦螢幕閱讀 影像並判讀。 Telemedicine Surgical simulation: Medical Visualization, Surgical augmented Reality, Medicalpurpose robot, Surgery Simulation,Image Guided Surgery,Computer Aided Surgery Estimate the location, size and shape of tumor PACS System Virtual Surgery Related techniques Classification of normal or abnormal tissues such as carcinoma Pre-processing: Contrast enhancement, noise removal, and edge detection Lesion segmentation: extract contours of interest thresholding 2-D segmentation 3-D segmentation based on voxel data Color image processing Our study Contour detection and blood flow measurements in cardiac nuclear medical imaging Virtual colonoscopy Bone tumor segmentation with MRI and virtual display Breast carcinoma based on histology 原 始 系 列 影 像 影 像 放 大 影 像 強 化 影 像 去 雜 訊 影像前處理 左心室輪 廓偵測 心室功能 計算 (a)強化後影像 (b)心臟血流變化區域 (c)心臟區域輪廓 Background Region Contours within a sequence of frames Result No. EF ES ED PER PFR 1 16.3 558 ml 667ml -0.7 0.4 2 37.4 256ml 775ml -1.12 1.87 3 53.5 56ml 120ml -0.56 2.67 4 84.3 60ml 380ml -1.33 4.21 Tab 4.1 心室功能量測參數 Virtual colonscopy-Browsing or navigation within a colon Helical CT –patients injected contrast medium Re-sampling—Voxel-based Interpolation Automatic segmentation (seed) threshloding Determination of the skeleton of the colon Connected-Component Labeling Surface rendering and volume rendering Extraction of suspicious sub-volumes for diagnosis Automatic segmentation Determination of the skeleton of the colon Display and measurement Bone tumor segmentation with MRI and virtual display—Contrast medium Otsu thresholding Region growing Tri-linear interpolation Morphological post-processing Surface rendering Measurement Histogram of T1 weighted and T2 weighted Classification of Breast Carcinoma 開始 輸入組織影像 (1524*1012) 色彩分離 (RGB) 影像分割 (Gray level、Otsu、Laplacian) 特徵參數分析 (導管比例、管腔個數、組織紋理...) 貝式網路判斷 正常 異常 系統判斷為正常 12 6 系統判斷為異常 1 11 準確性 76.67% 敏感度 有效性 64.71% 92.31% Requirements for medical image processing system in clinical diagnosis Automatic and less human interaction Qualitative and quantitative measurements Stable and reliable (experiments with much more cases) Performance evaluation True positive, true negative, false positive, false negative Accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity Receiving operating characteristic curve (An index for evaluating the effectiveness of classification Optimal classification threshold Area under ROC approach 1 – better classification ROC curve Analyses of prognosis on breast cancer for a stained tissue Microscopy with different resolution (400 or 100) for a stained tissue Fluorescent microscopy in detecting the number of chromosome Immunohistochemistry(IHC) Preliminaries or problems ? Blurring often caused by patient motion or respiration Clinical opinion or idea obtained from an experienced surgeon Non-absolute answers at some specific conditions Trade-off between complexity and performance Large variations for different image modality Automation is necessary so as to help physicians Prove identification accuracy—comparison between manual and image processing Thanks for your attention!