waterfall spiral
advertisement

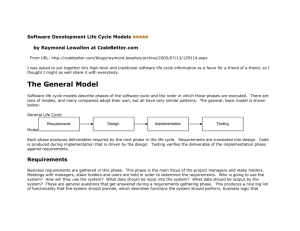
Software Development Life Cycle Lesson Objectives To understand the software development life cycle To be able to explain what commonly occurs at each stage of the software development life cycle To be able to identify at which stage of the software development life cycle a given step would occur To understand that there are several life cycle models that can be used (e.g. cyclical, waterfall, spiral) To be able to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of these lifecycle models How is software created? First comes the idea….everything has to start somewhere… Requirements / Analysis Testing Design Implementation Requirements/Analysis This is the first and most important step. Questions must be answered such as: Why is the software system required? Who is the software system for? What must the software system do? What are the constraints? (budget/timescale/particular needs) Design Now we know what the system is for, we must set about designing it. The aim being to achieve everything that we established in the previous phase. Again, more questions will need to be addressed: What programming language, operating system or hardware requirements are there? What data is required? What file structures are required? What user interface is there? ….and many more Implementation So now we actually create the software: Each step of the design is created using the appropriate technical capability Testing Obviously – need to test it works! Different Types of Approach Spiral / Cyclical Waterfall / Sequential Waterfall and spiral model are different types software development methodologies. These methodologies assist the developer in building a system efficiently. Each of the methodologies has a set of rules or discipline that needs to be followed in order to develop a system. Both of the methodologies posses their own pros and cons. Waterfall Model The waterfall model consists of the usual main phases, namely: Requirements/Analysis Design Analysis Implementation Testing Each phase has its own set of tasks that should be accomplished by the developer. The developer must complete each stage before moving to the next stage in a sequential manner. Due to this, the waterfall model is sometimes also referred to as sequential software development process. The model approach is from top to bottom as how a waterfall would flow down. Design Implementation Testing Spiral Model Analysis / Requirements Design Implementation Testing (next iteration planned here) Spiral Model The spiral model again contains four main stages. However the approach is more cyclical as seen in the diagram on the previous slide: It is an output driven methodology where each circle produces a prototype better than the previous one. In the spiral model, it is not necessary for the developer to complete each stage before moving to another stage. The developer can finish a short portion in a stage and shift to next stage and then come back again on next round to finish remaining task in the stages. It is a continuous process, in which each time the developed application gets more complex. At the same time the process also gets bigger and bigger. Waterfall or Spiral? WATERFALL SPIRAL Must complete a stage before moving onto next Can work on any stage at any time No feedback from client until software delivery Constant interaction with client – feedback and prototype development Document driven – well planned in advance (could result in less More ‘build it’ and see approach errors at later stages but time – less advance planning (could consuming at initial stages) result in problems – but more time to fix due to less planning at Sequential start) Cyclical Let’s Play A Game! Divide into teams (5 or 6 per team) Decide on a team manager Team manager to collect challenge resources and info from client (me!) You have 50 minutes to complete the challenge Test It!