Software Development Models
advertisement

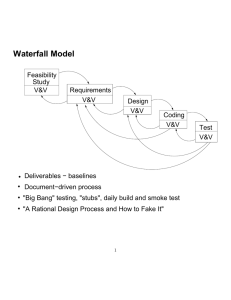
Sistemas de Información Agosto-Diciembre 2007 Sesión # 9 Software Development Process Planning Management Requirements Development Architecture Detailed Design Construction Quality Assurance and Testing User Documentation Time (McConnell, 1998) Evaluating the Software Development Process To assess the quality of the software development process: verify compliance with project schedule and budget verify compliance with initial requirements identify process metrics (SEI) coding testing Software Development Models Waterfall Model Spiral Model Structured Model Rapid Prototyping Model Rational MSF Waterfall Model Early focus on analysis of requirements and design Involves intensive documentation and testing Also known as “traditional model” or “linear model” Most widely used! Waterfall Model Systems Requirements Software Requirements Preliminary Design Detailed Design Code and Debug Test and Pre-operations Operations and Maintenance (Source: Dr. Szygenda, SMU) K90329_S_021 (2) Spiral Model Involves iterations of design, development, and testing Starts with a preliminary system version (v0.5) After intensive testing, a first version of the system (v1.0) is released Small changes on the first version are included, as necessary (v1.1, v1.2, etc..) Substantial changes will be included in a new release (2.0, 3.0, etc..) Works very well on incremental development projects (Source: Dr. Oard, LBSC-690) Spiral Model 1.2 2.3 0.5 1.0 2.0 (Source: Dr.Oard, LBSC-690) 3.0 1.1 2.1 2.2 Spiral Model Involves several task regions in each iteration: Customer communication Planning Risk analysis Engineering Release Customer evaluation (Pressman, 1997) Tends to be very expensive ! Structured Model Draws from structured analysis, structured design, and structured programming Involves parallel activities Requires several teams Works very well in large projects with self-directed teams Structured Model Users Management 1.0 Survey 2.0 Analysis Operations 8.0 Database Conversion 3.0 Design 7.0 Procedural Description 4.0 Implementation 5.0 Acceptance Test Generation (Source: Dr. Szygenda, SMU) 6.0 QA 9.0 Installation K90329_S_026 (2) Rapid Prototyping Model Goal: explore requirements Without building the complete product Start with part of the functionality That will (hopefully) yield significant insight Build a prototype Focus on core functionality, not in efficiency Use the prototype to refine the requirements Repeat the process, expanding functionality (Source: Dr. Oard, LBSC-690) Rapid Prototyping + Waterfall Update Requirements Initial Requirements Choose Functionality Write Specification Create Software Write Test Plan Build Prototype (Source: Dr. Oard, LBSC-690) Rational (IBM) A process for software engineering arranges in disciplines and phases Emerged in 1998, from the “Rational Approach” and the “Object Process 3.8”, from IBM Rational (IBM) • Core Process Workflows (6) • Core Supporting Workflows (3) MSF Microsoft Solutions Framework (MSF): An approach to IT project management Based on Microsoft best practices To improve project success rates To increase solution quality To increase business impact To improve process in terms of CMMi To support compliance with ISO standards MSF Models Software Development Models: Discussion How can we decide which model to use for a particular software development project? How can we assess the quality of: The software development process? The software product? Selecting a Software Development Model Choose a model, in terms of: the nature of the system to be designed and developed the time and budget restrictions the methods and tools available the required deliverables (Pressman, 1997)