Isolines
advertisement

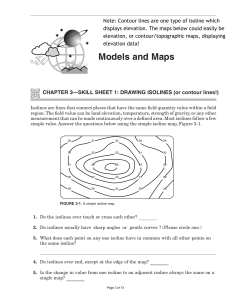
Drawing Isolines Aim: What do isolines represent? Objectives Draw isolines accurately on a field map Interpret field map data by reading isolines Calculate the gradient on an isoline field map Draw a profile of an isoline map Vocabulary: Isoline A line connecting points of equal value. Isotherm: A line connecting points of equal temperature Isobar: A line connecting points of equal barometric (air) pressure Contour: A line connecting points of equal altitude Anything else you can get a value for. Vocabulary: Interval The value from one line to the next Profile The side view represented by the isoline map Gradient The rate at which the values change on the map Field value What is represented by the map ( i.e. temperature, air pressure, altitude, air quality, etc.) Rules for Drawing Isolines: 1. Isolines connect points of equal value. 5 5 10 10 10 10 15 15 2. Isolines are gentle, curving lines- no sharp corners. 5 5 10 10 10 10 15 15 3. Isolines are always closed curves even though the map might only show part of it. 4. Isolines NEVER cross.- This would mean that one point has two different values. Ex: one spot has two temperatures? 40 ° 50 ° 30 ° 60 ° X 20° Y Z 5. Isolines usually are parallel. (They have a parallel trend.) Highlight data points. Isoline Practice #1 Fill in gaps in data. Connect the dots. Go on to the next value. Isoline Practice #2 Isoline Practice #3 Gradient Gradient shows how quickly the value changes from one point to another. Pg 1 of the ESRT – FIND Gradient value dis t anc e Example #1 Field Value = temperature = Isotherms The front of the room is 25oC and the back of the room is 20oC. The distance from the front to back of the room is 10m. What is the temperature gradient of the room? Example #3 Field value = air pressure = Isobars The air pressure in NY is 993 mb and the air pressure 500 km away in Chicago is 1007 mb. What is the pressure gradient between these two cities? Example #2 Field Value = elevation = Contour lines The bottom of a mountain is 100 m above seal level. The top of the mountain is 1500m. The distance from the bottom to top of the mountain is 700m. What is the elevation gradient? Lab – Temperature Field Map You need: Pencils Rulers Calculators How does a steep or gentle gradient look on a field map? A steep (high) gradient changes quickly and the isolines are close together. A gentle (low) gradient changes slowly and the lines are far apart. Steep area Gentle area