Transducers/Sensors: Sample Device Thermistor
advertisement
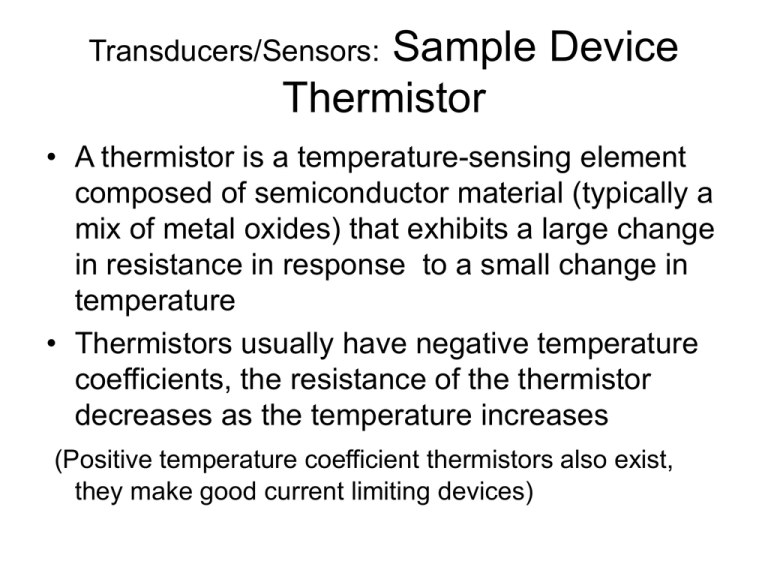
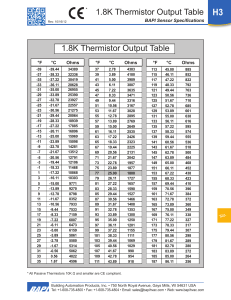
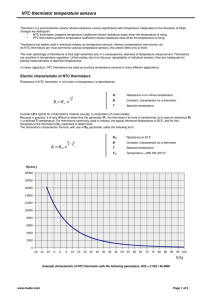
Sample Device Thermistor Transducers/Sensors: • A thermistor is a temperature-sensing element composed of semiconductor material (typically a mix of metal oxides) that exhibits a large change in resistance in response to a small change in temperature • Thermistors usually have negative temperature coefficients, the resistance of the thermistor decreases as the temperature increases (Positive temperature coefficient thermistors also exist, they make good current limiting devices) Sample Device Thermistor Transducers/Sensors: • Accuracy: Thermistors are one of the most accurate types of temperature sensors. Typical accuracy of ±0.2°C. • Range: Thermistors are fairly limited in their temperature range, working only over a nominal range of 0°C to 100°C . • Stability: Thermistors are chemically stable and not significantly affected by aging. Sample Device Thermistor Transducers/Sensors: Sample Device Thermistor Transducers/Sensors: • Linearity: Thermistors are highly non-linear, following a law called the Steinhart-Hart equation A, B and C are constants found experimentally by measuring R at three different temps and substituting back in the equation Graphs or tables of RvsT are usually used Sample Device Thermistor Transducers/Sensors: Typical Thermistors Sample Device Thermistor Transducers/Sensors: • Using a Thermistor to sense/measure temperature 1: If the thermistor is part of a potential divider then the output signal will vary with temperature. This simple circuit lacks precision, it’s often used in a set-point switch Sample Device Thermistor Transducers/Sensors: Using a Thermistor to sense/measure temperature 2: The thermistor is one of the resistors in a Wheatstone Bridge – say R4. The output voltage is now related to temperature and will vary as the temperature varies. Calibration will enable temperature to be measured.