1294036064Function of language
advertisement

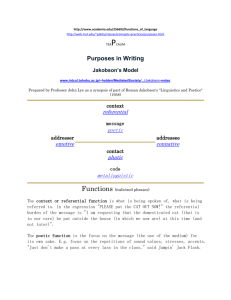
IV. Functions of Language Question: What do you think are the functions of language? Metafunctions of Language: Halliday’s Model 1. Ideational:( descriptive funtions) Constructs a model of experience and constructs logical relations ( through transitive system) 2. Interpersonal: (social function) enacts social relationships (through mood and modality) 3. Contextual: creates relevance to context (through coherence and cohesion) Elements of Communication: Jakobson’s Model (1960) Context Referential Addresser Emotive Message Poetic Contact Phatic Code Metalingual Addressee Conative Summary of the Functions of Language Emotive: the use of language to create or express certain feelings in the hearer. Through Jokes, Advertising, Propaganda, etc. Summary of the Functions of Language Conative : The use of language in order to achieve a result in an addressee, in accord with the speaker’s wishes. Its use is illustrated by a range of directive functions (e.g. commands, vocatives), but its precise sense needs to Summary of the Functions of Language Metalingual: The use of language to talk about language itself. This makes language infinitely selfreflexive: We human beings can talk about talk and think about thinking, and thus only humans can ask what it means to communicate, to think, to be human. Summary of the Functions of Language Poetic Function: This is the use of language in artistically. Example in the figure of speech in literary work or in normal conversation. E.g.. He talk a lot but his point couldn’t hold water Summary of the Functions of Language 3.5 Phatic: the use of language to establish an atmosphere or maintaining social contact. E.g. Greetings, Farewells, and Comments on the weather, etc. Summary of the Functions of Language 1. Informative : Language serves an informative function when it is used to tell what the speaker believes, to give information about facts, or to reason things out. By use of Declarative Sentences Summary of the Functions of Language 2. Interrogative: When language is used to get information from others, it serves an interrogative function Through Questions that expect answers. Summary of the Functions of Language 3. Interpersonal: Language serves an interpersonal function when it is used to establish and maintain their status in a society. Five sub-categories of interpersonal function: performative, directive, emotive, expressive, and phatic. Summary of the Functions of Language 3.1 Performative: (Declarative) the use of language to “do things”, to perform actions. Through quite formal and even ritualized language. E.g. in wedding and other religious ceremony Summary of the Functions of Language 3.2 Directive: (instrumental) When language is used to get the hearer do something, it serves a directive function. Most Imperative sentences. Summary of the Functions of Language 3.4 Expressive: the use of language to reveal something about the feelings and attitudes of the speaker. Through Exclamations, etc. Summary of the Functions of Language 4. Recreational: the use of language for the sheer joy of using it. E.g. baby’s babbling, poetry, etc. OTHER FUNCTIONS Recording function: (Keep record of the document, text or speech in brain) eg qur an bible etc. Identification faction. Use of language to identify with a group or to recognise a person due to his usage of language OTHER FUNCTIONS Regulatory Functions: The use of language to worn or impart discipline in the mind of people.