File - NYCNYS Science Resources for Teaching and PD
advertisement

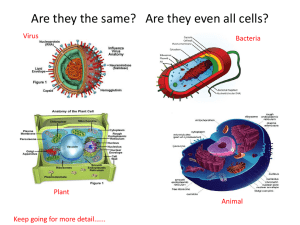
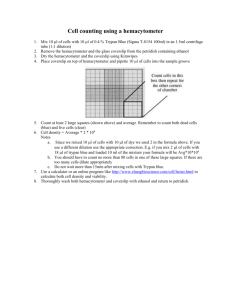
Teaching a Lesson LE Lesson Using Regents Diagrams Gary Carlin Leadership LSO April 23, 2010 M.S. 101 Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q ISLA – May 06 • 27 The diagram below shows a simple microscope. Four parts of the microscope are labeled A, B, C, and D. • Which part of the microscope is used to bring the image of the object on the slide into focus? (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D ISLA Spring 07 • 1 Three different human cells are shown below. • Which process occurs in all of these cells? • (1) metamorphosis (3) reproduction • (2) locomotion (4) photosynthesis ISLA – June 04 • 16 The diagram below shows a student making a wet-mount slide. • Why should the student make sure the edge of the coverslip touches the drop of water before setting the coverslip onto the slide? • (1) to increase evaporation • (2) to reduce air bubbles • (3) to clean the slide • (4) to prevent the coverslip from breaking LE Regents – June 09 • 3 Which cell structure contains information needed for protein synthesis? LE Regents – June 08 • 31 Which laboratory procedure is represented in the diagram below? • (1) placing a coverslip over a specimen • (2) removing a coverslip from a slide • (3) adding stain to a slide without removing the coverslip • (4) reducing the size of air bubbles under a coverslip Regents – June 08 • 79 A plant cell in a microscopic field of view is represented below. • • • • • The width (w) of this plant cell is closest to (1) 200 μm (2) 800 μm (3) 1200 μm (4) 1600 μm Regents – Jan 06 • 31 The diagram below shows how a coverslip should be lowered onto some single-celled organisms during the preparation of a wet mount. • • • • • Why is this a preferred procedure? (1) The coverslip will prevent the slide from breaking. (2) The organisms will be more evenly distributed. (3) The possibility of breaking the coverslip is reduced. (4) The possibility of trapping air bubbles is reduced. Regents – Jan 05 • 35 The diagrams below show four different onecelled organisms (shaded) in the field of view of the same microscope using different magnifications. • Which illustration shows the largest one-celled organism? Regents – June 04 • 56 Describe how structures 1 and 2 interact in the process of protein synthesis. [1] • 57 Choose either structure 3 or structure 4, write the number of the structure on the line below, and describe how it aids the process of protein synthesis. [1] • Structure: ________ Regents – Aug 02 • 39 The photograph below shows a microscopic view of the lower surface of a leaf. • What is the main function of the cells indicated by the black pointer? • (1) regulate the rate of gas exchange • (2) store food for winter dormancy • (3) undergo mitotic cell division • (4) give support to the veins in the leaf Regents – Jan 10 • 75 A laboratory technique is illustrated in the diagram below. • The technique of lowering the coverslip at an angle is used to • (1) make organelles more visible • (2) reduce the formation of air bubbles • (3) make the specimen transparent • (4) reduce the size of the specimen Regents – Jan 10 • 76 Information about which two lettered parts is needed in order to determine the total magnification of an object viewed with the microscope in the position shown? [1] • ____________ and ____________ • 77 Which lettered part should be used to focus the image while using high power? [1] • ____________ • 78 State two ways the image seen through the microscope differs from the actual • specimen being observed. [1] • ________________________________ and __________________________________ Regents – June 09 • 67 Which diagram best illustrates the technique that would most likely be used to add salt to these cells? • 68 In the space below, sketch what cell A would look like after the addition of the salt. [1] Regents – Jan 09 • 78 Identify a process that caused the change in the cells. [1] • ___________________________________ • 79 To observe the cells on this slide it is best to start out using the • (1) high-power objective and focus using the coarse adjustment, only • (2) low-power objective and focus using the fine adjustment, only • (3) high-power objective and focus using the fine adjustment • (4) low-power objective and focus using the coarse adjustment Regents – June 05 • 73 A student prepared a wet-mount slide of some red onion cells and then added some salt water to the slide. The student observed the slide using a compound light microscope. Diagram A is typical of what the student observed after adding salt water. • Complete diagram B to show how the contents of the red onion cells should appear if the cell were then rinsed with distilled water for several minutes. [1] Magnification Letter “e” – 40x & 100X Refraction: Loss of Light LP and HP Red Onion Cells Elodea Microscope Measurement Air Bubbles Stomates Animal Cell Simple Microscope A Wet Mount Depression Slide Onion Root Tip Epidermal Cells Solutions Cell Membrane Cell Communication Carrier Proteins State Lab: Diffusion Anton van Leeuwenhoek Robert Hooke Refraction of Light Refraction Analogy