The Basis for Business Decisions
15th /e Williams, Haka, Bettner, Carcello
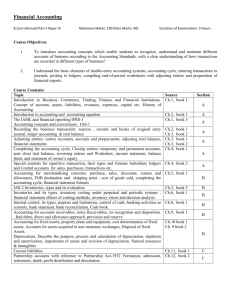
Financial Accounting
9th /e Meigs & Meigs
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2010 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Part I:Accounting & its Role
Accounting
Basic Financial Statements
1-3
Accounting
Profession Accountant Field?
No
“ Accounting is simply the means by which
we measure and describe the result of
economic activities”
Often Called
“ the Language of Business”
meigs & meigs
1-4
1-5
1-6
1-7
Purpose of Accounting
The basic purpose of accounting is to
provide decision makers with information
useful in making economic decisions.
1-8
Accounting from a User’s
Perspective
Individual need to understand:
The nature of economic activities that
accounting information describes
The assumption and measurement techniques
involved in developing accounting information
The accounting information that is most
relevant for various types of decisions
1-9
The
Accounting
Process
Economic
Activities
Actions
(decisions)
Accounting links
decision makers
with economic
activities and
with the results of
their decisions.
Decision
Makers
Accounting
Information
Reported
Results of
Actions
(decisions)
1-10
Types of Accounting Information
Financial
Tax
Management
1-11
Basic Functions of an Accounting
System
Interpret
and record
business
transactions.
Classify
similar
transactions
into useful
reports.
Summarize
and
communicate
information to
decision
makers.
1-12
Branches of Accounting
Financial
Accounting
Cost
Accounting
Managerial or
Management
Accounting
1-13
Areas of Accounting
1-14
Financial Accounting Information
Financial Accounting Provides information
about Financial resources, obligation, and
activities of an enterprise.
Financial
Position
Obligation
at point in
time
Result of
Operations
1-15
External Users of Accounting
Information
•Owners
•Creditors
•Potential investors
•Labor unions
•Governmental agencies
•Suppliers
•Customers
•Trade associations
•General public
1-16
Objectives of External Financial
Reporting
The primary financial
statements.
Balance
Sheet
Income
Statement
Statement
of Cash
Flows
1-17
Characteristics of Externally
Reported Information
A Means to an
End
Usefulness
Enhanced via
Explanation
Broader than
Financial
Statements
Based on GeneralPurpose
Assumption
Historical in
Nature
Results from Inexact and
Approximate Measures
1-18
Management Accounting Information
Create and use internal accounting
information not only for exclusive use
inside the organization but also to share
with external decision makers.
Example:
A producer may design an accounting
information system for suppliers detailing
its production plan.
1-19
Internal Users of Accounting
Information
•Owners
•Board of Director
•CEO & CFO
•Vice-presidents (information
services, human resources, ethics
and so forth)
•Business unit managers
•Plant managers
•Store managers
•Line supervisors
1-20
Objectives of Management
Accounting Information
Gather H&F
Information
from Both
sources
Objectives &
mission of
enterprise
Decision
Making
1-21
Characteristics of Management
Accounting Information
A means to an end
Identity of
Decision Maker
Importance of
Timelines
Oriented toward
the Future
Measures of Efficiency and
Effectiveness
1-22
Careers in Accounting
Public Accounting
Management Accounting
Governmental Accounting
Accounting Education
1-23
End of Chapter 1
1-24