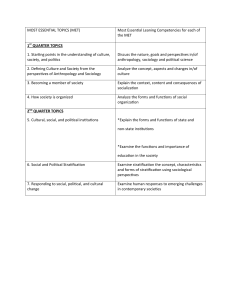
Social Stratification
advertisement

Social Differentiation and Social Stratification Status: socially defined position in a group or society. Social Differentiation: process by which different statuses in any group develop. Social Stratification: fixed arrangement in society by which groups have different access to resources, power, and perceived social worth. Forms of Stratification Estate System: the elite have total control over societal resources, including property Caste System: assigned to an individual at birth. Class System: possibility of changing over time, based on achieved status. Social class is the social structural position that groups hold relative to economic, social, and political, and cultural resources of society. Life Chances: opportunities that people in a particular class have in common, education, jobs, housing Measures that represent concepts: Income Education level Occupation Place of residence Material goods * Race * Gender * Ancestry 18-19th centuries in Western Europe Enlightenment (the Age of Reason) Positivism: accurate observation and description, not religious dogma or unfounded speculation Humanitarianism: human reason can improve society for all Auguste Comte (1789 – 1857) – coined the phrase “sociology” – believed in careful observation of human behavior to uncover laws of social behavior Alexis de Tocqueville (1805 – 1859) – Democracy in America Harriet Martineau (1802 – 1876) – Society in America Emile Durkheim (French, 1858 - 1917): People in society are held together by shared belief systems. Social facts exist outside individuals and exist to constrain behavior, a collective reality. Basis for “functionalism.” Karl Marx (German, 1818 - 1883) Society is shaped by economic forces, with the system of capitalism (which is class-based) dictating individual behavior. Max Weber (German, 1864 - 1920) Society has 3 basic dimensions: economic, political, and cultural. In looking at society, one is already a product of it, thus objectivity should be emphasized even though it is flawed. Verstehen = understanding social behavior from point of view of participants. Scientific approach. American and European sociologists both conceived society as an “organic metaphor” – society is constantly evolving. American sociology was built on the earlier work of the Europeans, but distinctive American flavor: Pragmatism Social Darwinism: e.g. William Graham Sumner (1840-1910) claimed that survival of the fittest=concept justified the inequities in society (social evolution) Social Telesis: e.g. Lester Frank Ward (18311914) claimed that human intervention in natural evolution of society would advance interests of society. industrialization, urbanization Method of approaching sociology that developed at the University of Chicago Charles Horton Cooley, George Herbert Mead: individual identity developed through people’s understanding of how they are perceived by others. Robert Park: city/neighborhood boundaries Jane Addams: founder of the Hull House W.E.B DU BOIS (1868 – 1963): cofounder of the NAACP (1909), Ph.D. from Harvard (first one awarded by Harvard to an African-American) Asst. Professor of Sociology at University of Pennsylvania (had to live in the settlement he was studying) Functionalism: emphasizes the stability and integration in society Conflict Theory: sees society as organized around the unequal distribution of resources, held together by power and coercion Symbolic Interaction: emphasizes role of individuals in giving meaning to social behavior, thereby creating society