File - English Literature @ LCHS
advertisement

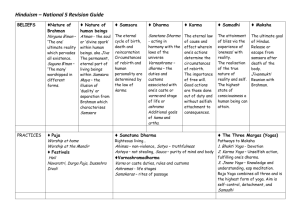
The Bhagavad-Gita English 10 Introduction -Objectives: -Students will understand the main characters in the Bhagavad-Gita -Students will be able to apply knowledge of prior texts (Illiad/Gilgamesh) to the story of Arjuna and Krishna Gandhi on the Gita “When disappointment stares me in the face and all alone I see not one ray of light, I go back to the Gita. I find a verse here and a verse there and I immediately begin to smile in the midst of overwhelming tragedies – and my life has been full of external tragedies – and if they have left no visible scar on me, I owe it all to the teachings of the Gita.” The Bhagavad-Gita: What is it? Meaning = “Song of the Lord” 700 verses in Sanskrit scripture of a Civil War Story of the Indian Epic, the Mahabharata – The war between two families, the Pandavas and the Kauravas (cousins) Main Characters: Arjuna (Pandavas hero) Lord Krishna (the God Vishnu) Arjuna – finest archer and warrior of the Pandavas: undefeated warrior 1. He is overcome with self-doubt and fear as he approaches the battle field. 2. Does not want to fight his own kin or his former Teacher. 3. Krishna gives advice, Arjuna listens and asks Questions 4.Text is a Philosophical dialogue between Arjuna and Krishna Lord Krishna ( the God Vishnu) 1. Supreme God of Vaishnavism 2. Explains to Arjuna that he should do his duty and fight in battle. 3. Teachings: The human soul is immortal – therefore – No one is actually “slain”. 4. If people live accordingly to their duties, they cannot be stained by action. 5. Known as “Guru” = the teacher/master The Teachings in Total… 18 Teachings ( we are reading only 5 total) In poetic form – usually chanted outloud The writings have influenced Gandhi, Albert Einstein, Herman Hesse, and Robert Oppenheimer to name a few… Each teaching is a separate “yoga” = (a prayer or hymn that is sung) st 1 Teaching The Distress of Arjuna 46 verses Arjuna requests Krishna on battlefield Moves chariot between both sides nd 2 Teaching –Summary of entire Gita Book of Doctrines – 72 verses Introduces Karma (concept of action/deed) – importance of cause and effect. Yoga and the immortal nature of the soul rd 3 Teaching (Karma Yoga) Virtue in Work 43 Verses Krishna explains performance of “duties” – actual performance that is practiced. th 6 Teaching Religion by Self Restraint 47 verses - Mastery of mind might be gained - Techniques to gain mastery of mind -Absolute reality is an illusion (concept known as “Maya”) th 11 Teaching Manifesting of the One and Many 55 verses Theophany – the appearance of a god/deity in human form – “universal form” Arjuna wants to find divine meaning of life The purpose of Beatific Visions – ability to see gods/goddess in living form, among the living. Vocab Words– On final (write down each word – leave a few lines in-between each for definition) 1. Dharma 2. Artha 3. Kama 4. Moksha 5. Karma 6. Puja 7. Ahimsa 8. Yoga (3 types) 9. Guru 10. Tilaka Dharma st 1 of the 4 goals in life Righteousness in religious life; sacredness of all life The principle/law that orders the universe Artha nd 2 of the 4 goals in life Success in economic life; material prosperity Achieving widespread fame, gaining wealth Having an elevated social standing Kama rd 3 of the 4 goals in life Eros – desire, pleasure of the senses Mental and intellectual fulfillment of love Passion – aesthetic enjoyment of life Moksha 4th of the 4 goals in life Liberation from the cycle of rebirth Freedom from the endless cycle of reincarnation Reincarnation – also known as Samsara (continuos flow) Karma The principle/law of cause and effect meaning: “deed”/ “act” “If one follows goodness, one will reap goodness.” “If one follows evil, one will reap evil” Puja – an expression of honor/worship A religious ritual; an offering to various gods, distinguished individuals, or guests. Daily puja can take place in varous settings: home, temple ceremonies, large festivals Ahimsa - “Do No Harm” The avoidance of violence – nonviolence Kindness to all living things, including animals Living beings as “unity” – everything is connected Yoga- “to unite” “to join” - The spiritual – mental - physical practice of attaining permanent peace. - Three Types (in 6th teaching/chapter) - 1. Karma Yoga: yoga of action - 2. Bhakti Yoga: yoga of devotion - 3. Jnana Yoga: yoga of knowledge Guru – “The wise ones who have realized the Truth will impart the Knowledge to you” - Krishna Meaning – “master” or “True teacher”. A respected instructor with saintly qualities. Enlightens the mind of followers – transmits wisdom from teacher to student A spiritual advisor; an enlightened master. One who “dispels the darkness of ignorance” Tilaka – a mark on the forehead or other part of body Worn daily or for special religious occasions Created by the smearing of powder or paste on the forehead Differs from a bindi, but similar – 19 different types of tilak The 4 Questions of The Gita…. 1. How can a Hindu warrior be liberated from rebirth? 2. If the soul is immortal, why is it involved in action (which will cause rebirth)? 3. If action is inevitable, how can the soul ever cease to be reborn? 4. How does one know right action from wrong?