Decision Making - Harris Academy
advertisement

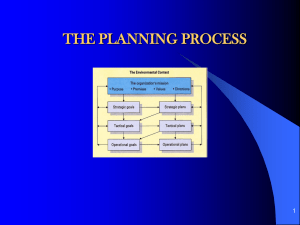
Business Enterprise Decision-making Learning and Teaching Scotland 1 Nature of decisions Decision-making is choosing between alternative courses of action. Typical decisions: • what to produce or provide • where to locate • what method of production to use • how many people to employ • what prices to charge. Objectives Objectives are the goals of the organisation: • survival • profit maximisation • growth • image and social responsibility. Objectives and strategy • Where are we? • Where do we want to be? • How do we get there? • Managers decide business objectives then organise objectives into targets. Mission statements • A company’s raison d’être. Why define aims/objectives? • An end result to work to. • Goals motivate people. • Keeps focus and direction. Click for Clip Mission statements • ‘We exist to refresh everyone we touch’ – Coca Cola • ‘We strive to lead in the invention, development and manufacture of the industry's most advanced information technologies’ – IBM Answer a question • Explain the reasons why some organisations produce a mission statement. (3 marks) 2010 • 6 minutes Peer marking • You are going to swap answers. • Has your partner answered well? • Does the answer make sense? • Is it worth a mark? Solution • Could be released to the press, which would help market the business and its products. • Issued to all employees, allowing them to see the firm’s aims and objectives linked to their roles as workers. • Shows the firm’s plans for the future and how the customers will be treated/affected. • Details social responsibilities of the organisation, which may attract customers to the organisation. • Could be used to attract quality staff, who would agree with the values created by the mission statement. • Improves image of the organisation, which could increase sales. Types of decision • Strategic • Tactical • Operational Strategic decisions • Long-term • Made by senior management • More general in nature • Major policy statements are strategic Examples • What products to make? • Increase market share • Which market segment will we target? Tactical decisions • Short-term • Made by middle managers in functional areas • Based on aims or goals of organisation • More detailed and specific • May change due to PESTEC factors Examples • Hire/fire employees • Instore promotions • To float a share issue • Re-brand the business Operational decisions • Day-to-day, routine decisions • Mainly made by lowlevel managers/supervisors • Respond to usually regular problems Examples • Arranging staff rotas • Procuring raw materials from suppliers • Payroll – paying wages and salaries • Dealing with customers enquiries (including complaints) Policy decisions Long-term Strategic (Senior management) Complex Non-routine How to achieve policy Medium-term Tactical Less complex (Middle management) Operational (Junior management) Day-to-day decisions Simple Routine Examples of decisions Bus company School Strategic Tactical Operational Expand market share by establishing a new route Increase attainment levels by 10% Develop new price structure to attract customers Make bus mgt compulsory Extra buses on due to increase in demand Arrange cover for Staff absences Strategic decision examples • Increase market share. • To grow by expanding and taking over firms. • Sell off an under-performing part of the company (divestment). • Invest new capital into business. Tactical decision examples • • • • Launch new product. Hire/fire employees. Buy or rent premises. Buy or lease equipment. Operational decision examples • • • • • • • • Arrange employee rotas. Training needs of employees. Layout of factory/office. Deal with customer enquiries. Payroll – payment of wages and salaries. Procure raw materials from suppliers. Implement methods of production. Make decisions on working hours. Answer a question (a) A manager decides to grant a worker’s request for a holiday. Identify and justify this type of decision. (2 marks) 2010 (b) Describe two other types of decisions and give an example of each. (4 marks) 2010 • 12 minutes Peer marking • You are going to swap answers. • Has your partner answered well? • Does the answer make sense? • Is it worth a mark? Solution to (a) • Operational decision. This is an operational decision because: • it is a decision made by a lower level/junior manager • it has little or no risk • it is made on a short-term basis. Solution to (b) • Tactical decision is medium-term/is made by middle level managers/has a slightly increased risk. • Any appropriate example. • Strategic decision is long-term/made by senior managers/has a greater risk. • Any appropriate example. What is management? • Managers are responsible for getting things done. • This involves delegation – passing responsibility onto others. • Managers act on behalf of owners and are accountable to shareholders. • Managers set objectives for the organisation and try to achieve them. History of management • Here is a short video outlining some of the major concepts of management history. Click for clip Henry Mintzberg’s nature of managers • Interpersonal role – relationships with others. • Informational role – collecting and passing on information. • Decisional role – making different kinds of decisions. Henri Fayol • (1841–1925) • French mining engineer and manager. • First to ask ‘What is management?’ Fayol’s role of manager • Plan – examining the future and drawing up a plan of action. • Organise – building up human and material resources and putting plan into action. • Command – maintaining worker activity. • Co-ordinate – unifying effort between departments. • Control – checks on efficiency of plan. • Implement – put into practice. Functions of management • • • • • • • Planning Organising Commanding Co-ordinating Controlling Motivation Delegation POGADSCIE • Identify the problem. • Identify the objectives of the solution. • Gather information. • Analyse information. POGADSCIE • • • • • Devise possible solutions. Select the best possible solution. Communicate the decision. Plan and implement the solution. Evaluate the effectiveness of the solution. Example of POGADSCIE Problem Select candidate Select solution Make final choice Objective Select suitable candidate Communicate Contact successful candidate Gather info CV, application forms Implement Appoint and training Analyse Info Look through above documents Evaluate Monitor new recruit’s progress Devise solution Produce short list Problems with structured models • Time. • Ability to collect all relevant information. • Lack of creativity of managers. • Changes might affect decision. Benefits of structured models • No hasty decisions will be made. • Quality/quantity of information you will have. • Availability of all alternative solutions. • Enhances innovation and responsiveness. SWOT analysis • • • • Strengths – strong points of business. Weaknesses – present problems. Opportunities – may arise in future. Threats – may arise in future and be avoided. • Strengths and weaknesses are internal. • Opportunities and threats are external. Click for clip SWOT analysis Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats SWOT analysis of 20th Century Fox Strengths • Talented workers • Merchandising • Back catalogue Weaknesses • No new movie blockbusters • Outdated studio facilities Opportunities • Blu-Ray • IMAX • 3-D • Asian market Threats • Competitors • TV • Piracy • Internet Recommendations • Next we try to form a strategy. Use your strengths to: • exploit opportunities • improve your weaknesses • eliminate/deal with threats. Recommendations for 20th Century Fox • Improve and update studio facilities. • Transfer back catalogue onto DVD. • Tailor more films for Asian market and push merchandising. • Tackle TV by creating IMAX spectaculars. • Increased copyright security tabs. Answer a question • Describe how a manager could evaluate the effectiveness of a decision. (4 marks) 2008 • 8 minutes Self-marking • You are to answer. • Have you answered well? • Does the answer make sense? • Is it worth a mark? Solution • Have the objectives been reached? • Is the organisation operating effectively? • Is there an increase in sales/profits? • Has staff turnover/absenteeism decreased? • Has staff morale improved? • They may issue questionnaires/interview staff/observe.