Introduction to SWOT Analysis - Siddaganga Institute of Technology
Introduction to SWOT
Analysis
Presentation by
Prof. M Ajoy Kumar &
Mr. Manu T U
What is SWOT?
• It is a planning tool used to identify
S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities and T hreats involved in a business. It is used as part of Strategic Planning
Process
Strategic Planning
Strategic Planning helps an organisation to answer some basic and critical questions like: a) Where we stand?
b) What is our goal?
c) How to reach the desired goal?
d) How to evaluate performance?
The Environment
The actions of an organisation /institution are influenced simultaneously by two factors: a) Internal Environment: People, systems, infrastructure, capabilities, culture etc.
b) External Environment: Political, legal, social, economical, technological etc.
Internal Environment
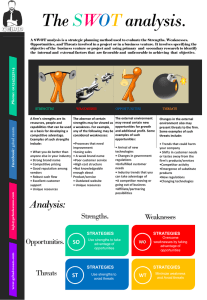
Analysis of Internal Environment leads to identification of: a) Strengths: Positive aspects which are within the control of the institution.
b) Weaknesses: Constraining factors that hinder the institution’s ability to achieve its desired goals.
Strengths & Weaknesses
Contributing Factors:
• People (Teachers/Staff/Students)
• Programmes (UG/PG/Doctoral)
• Properties (Assets/Infrastructure/Lab)
• Processes (Teaching/Research)
Strengths
• Highly competent faculty with Ph.D.
• Modern laboratories & equipments
• Unique programmes offered
• Value adding additional programmes
• Reputation & brand image
• Examination & Evaluation Process
• Research projects/Consultancy
• Industry interactions
Weaknesses
• Lack of competent/qualified staff
• Inadequate facilities/labs
• Outdated syllabus/courses
• Lack of industry orientation
• Weak employability of students
• Lack of research activities
• Internal Funding difficulties for projects
External Environment
Analysis of External Environment leads to identification of: a) Opportunities: Attractive factors that help an institution to develop & improve b) Threats: Factors beyond the control of an institution that potentially damage the present existence and future development
Opportunities & Threats
Contributing Factors:
• Technological
• Economic
• Legal/Regulatory
• Social
• Demographic
• Political
Opportunities
• Growing demand for various courses
• Growing demand for Technically qualified people
• New Technology Developments
• Research opportunities in specialised and niche areas
• Collaborations with industry
• Collaborations with institutes of higher learning (national & international)
Threats
• Competition from new entrants at local, national & international level
• Decreasing scope for some programmes
• Change in Technology
• Declining availability of qualified faculty
• Decline in the overall quality of student intake
• Tight regulatory measures
Why SWOT?
• Strengths – How to leverage?
• Weaknesses – How to overcome?
• Opportunities – How to exploit?
• Threats – How to defend?
SWOT provides clarity on where we stand & in which direction we should move
SWOT leads to development of shortterm & long-term objectives.
In the Absence
• Hidden strengths not utilised
• Weaknesses not identified & taken care
• Opportunities missed
• Unprepared to face threats
While doing SWOT
• Strengths – Modest & Clearly identifiable
• Weaknesses – Exhaustive
• Opportunities – Realistic & Identifiable
• Threats – Clearly identifiable
KRAs
• Enhancing quality of PG Programmes
• Starting new PG Programmes
• Strengthening Doctoral Programme
• Strengthening R & D activities
• Enhancing consultancy projects
• Industry Institute Interactions
• Collaboration with other institutes of higher learning (national & foreign)
• Centre of Excellence in a chosen area
After SWOT
• Link strengths to action plan to create sustainable competitive advantage
• Propose specific action plan to overcome weaknesses
• Develop action plan to take advantage of opportunities
• Develop action plan to defend the threats
How to proceed?
• Select a coordinator
• Create a SWOT Team
• Brainstorm (all stakeholders)
• Record all suggestions
• Consolidate ideas
• Clarify ideas & prioritise
• Summarise into a SWOT Document
• Questionnaire circulated
Practical Aspects
• Confusing factors
• Overlapping areas
• Identity Crisis
• Central Vs. Departmental Aspects