B1: Creating a climate that promotes fairness
advertisement

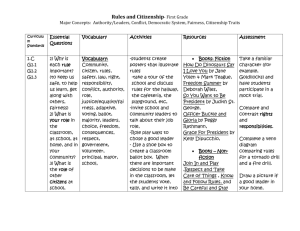
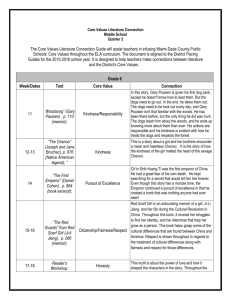
B1: Creating a climate that promotes fairness How does fairness contribute to teaching and learning? Ohio Teacher Standards: Components of fairness • All students have access to learning • Gender neutral instruction, assignments, language • Equity vs Equality – treat learners equitably • Respect for the rights and privacy of others • Respect for diversity through responses, posters, bulletin boards, materials Diversity Considerations • • • • • • Ethnicity Cultural background – values and norms Socioeconomic status Exceptional learners Gender Learning styles Bullet #1 Differentiates between equity and equality in a climate that promotes fairness In what ways are equity and equality different/similar in a classroom that promotes fairness? • Ultimately, equity is what we, as educators, seek. • Unfortunately, equity is not a very quantifiable measure. • By looking to equality and understanding the reasons behind inequalities, we can adjust our schools, our subjects, our very understanding to create equity (Jay Hill) • Complete the Venn Diagram on the differences/similarities of equity and equality Bullet #2 Describes a climate and rationale for promoting fairness What is fair is not always equal, and what is equal is not always fair. What does this principle look like, sound like, and feel like in a classroom that promotes fairness? • • • • • Respect for self and others Greater learning opportunities for all Trust in the teacher Appropriate behaviors based on respect Higher student achievement Why is this principle important for both the students and teachers in the teaching and learning process (rationale)? • • • • Respect for self and others Environment of trust and security Trust and respect of teacher Environment of trust = environment conducive to learning • Environment conducive to learning = academic risk taking • Academic risk taking = higher achievement Bullet #3 Illustrates how fairness can be actively encouraged How do effective teachers actively encourage fairness among students? • Teach children to avoid favoritism, prejudice and bias • Teach respect of diversity • Use teaching strategies to encourage children to be fair to each other – – – – Seating arrangements Spinners to select students Pull names Use games to ensure each learner has the opportunity to participate – Involve students in making classroom decisions to promote fairness for all How does the active encouragement AND practice of students being fair to each other impact the teaching AND learning process? • • • • Emotionally safe learning environment Greater academic risk taking Supportive and respectful learners More time engaged in learning Best Practice Example • What have you observed in your internships or with other teachers that demonstrates actively promoting fairness in the classroom? • What have YOU done to actively promote fairness in the classroom? Evidence (analysis) • What evidence could show fairness in the classroom? • How does this evidence selection create a climate that promotes fairness? • In what ways does the evidence apply to best practices in teaching? Give an example. • How does the evidence impact student achievement? Evidence (synthesis) • If you used this evidence in the classroom what do you think you would learn or discover from using it? • How would you use this learning in your own classroom or in future internship placements? Evidence (evaluation) • Do you think the evidence you selected would work to promote fairness in the classroom? • How? • Why or why not? • What expectations do you have of the students if you used this evidence? • If you used this evidence in the classroom do you think it would meet your expectations for the learners? • How? • Why or why not? Text Readings • Pg. 70 – 73 What is the Role of Schools in Today’s Society • Pg. 326 – 347 What Determines the Culture of the Classroom? • Chapter 5 Historical Foundations of U.S. Education • Chapter 8 Today’s Students • Chapter 9 Addressing Learner’s Individual Needs