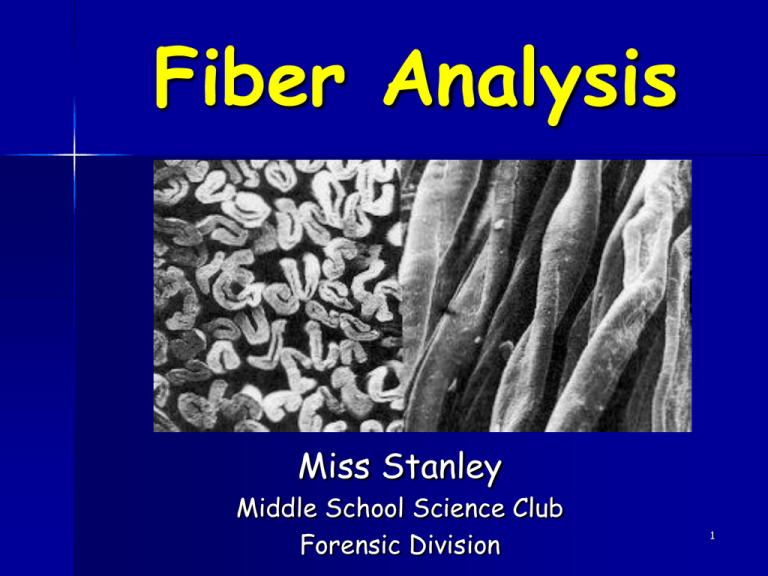
Fiber Analysis
Miss Stanley
Middle School Science Club
Forensic Division
1
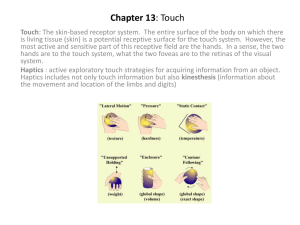
Textile Fiber
A textile fiber is the
basic unit or building
block of a fabric. Fibers
are produced naturally
by plants and animals and
synthetically by man.
2
3 Basic Fiber Categories
Natural
Manufactured,
or regenerated
Synthetic
3
Natural Fibers
Come from various animals, plants,
and minerals. Examiners can often
easily identify and compare these
fibers by microscopic inspection
alone. Animal hair that is woven into
fabric or used to manufacture
clothing and other household items is
considered natural fiber.
4
Natural Fiber - Cotton
By far, the most
commonly used
natural fiber is
cotton. When
examined under a
microscope, it has an
easily recognizable
twisted-ribbon
pattern.
5
Natural Fiber - Wool
The most common animal fiber
used in textile production is wool
originating from sheep.
6
Natural Fibers
Other examples are
mohair, cashmere,
and silk. Plant
fibers include
cotton, hemp, flax,
and jute.
7
Manufactured or
Regenerated Fibers
Are fabrics like rayon, acetate,
and triacetate. To make them, raw
cotton or wood pulp is dissolved,
and cellulose is extracted. The
cellulose is then regenerated into
fibers.
8
Synthetic Fibers
Come from polymers, which are
substances made up of a series of
monomers (single molecules) strung
together to make larger molecules
that can be thousands of
monomers long. Nylon and
polyester are synthetic fibers.
9
Textile Definitions
Fiber is smallest unit of a fabric.
Fibers are twisted into yarns.
Yarns are knit or woven into fabrics.
Known or Standard fibers make up
fabric of a donor or source garment.
Question or Transferred fibers are
found on or recovered from (the
debris from) a receptor garment.
10
Fiber Evidence
A fiber is the smallest unit of a textile material that
has a length many times greater than its diameter.
A fiber can be spun with other fibers to form a yarn
that can be woven or knitted to form a fabric.
The type and length of fiber used, the type of
spinning method, and the type of fabric
construction all affect the transfer of fibers and the
significance of fiber associations. This becomes
very important when there is a possibility of fiber
transfer between a suspect and a victim during the
commission of a crime.
Fiber Evidence
Matching unique fibers on the clothing of a victim
to fibers on a suspect’s clothing can be very helpful
to an investigation, whereas the matching of
common fibers such as white cotton or blue denim
fibers would be less helpful.
The discovery of cross transfers and multiple fiber
transfers between the suspect's clothing and the
victim's clothing dramatically increases the
likelihood that these two individuals had physical
contact.
Natural Fibers
Many different natural fibers that come from plants and animals are used in the
production of fabric.
Cotton fibers are the plant fibers most commonly used
in textile materials
The animal fiber most frequently used in the
production of textile materials is wool, and the most
common wool fibers originate from sheep.
Textiles Fibers as Evidence
Crimes Against Persons:
–Homicide, Assaults,
Sex Crimes - used to
indicate contact by
transfer of fibers
between V and S
clothing, transfer of
fibers between V/S
and scene.
14
Textiles Fibers as Evidence
Crimes Against Persons:
– Indication of Force in
Crimes Against Persons
- rips and tears.
–Sabotage - cut or tied
parachute lines.
15
Textile Fibers as Evidence
Crimes Against Property.
–Burglary, Larceny, - torn fabric
or loose fibers at point of entry,
fabric marks from gloves, fibers
from the scene transferred to
suspect.
16
Factors Influencing
Transfer and Persistence
Studies show within 2 hours of
transfer, 80% of fibers are gone.
Fiber type.
Weave or knit type.
Damage to the garment or fabric.
Amount or force of contact.
Garments vs. automobiles.
17
Laboratory Examinations
Color - Dyes
Size - Diameter
Cross Sectional
Shape
Transparent or
Opaque
Chemical
Composition
18
Fiber Reports / Conclusions
How common is the fiber?
How many were found?
Is there a combination of
fibers? (Consistent with one
garment or one set of
clothing?
19
Laboratory Tests We’ll Do
Burning Characteristics
Solubility
Staining
Microscopic Appearance
20