Switch Styles and Types
advertisement
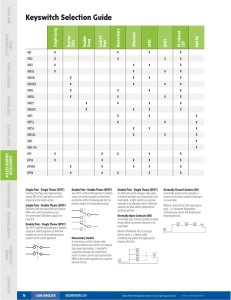
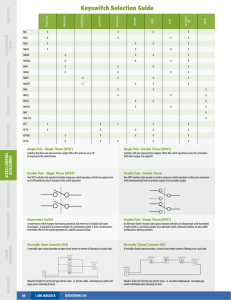
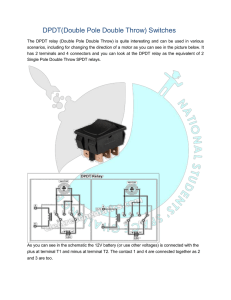
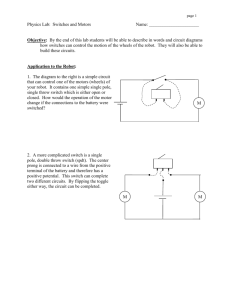
Switches Electronics 1 CVHS Basic Elements of a Circuit • Three Essential Elements – Load – Complete Path – Power Source • Additional Elements – Control Device – Protective Device Electricity Generation • Six Methods Used to Produce Electricity – Chemical – Magnetism – Heat – Friction – Light – Pressure Basic Switch Function • To open and close a circuit –Open (no connection) –Closed (connection) • Control device –Does not consume power Schematic Terms • Pole- what the switch armature is connected to • Throw- the closed position of the switch Pole Throw Single Pole, Single Throw • SPST • 1 pole, 1 throw • Example- room lights SPST Animation Single Pole, Double Throw • SPDT • 1 pole • 2 throws, 2 closed positions SPDT Animation Double Pole, Single Throw • DPST • 2 poles Double Pole, Single Throw • Not 2 throws because of mechanical connection • Both armatures make contact at same time- one closed position DPST DPST Animation Double Pole, Double Throw • DPDT • 2 poles • 2 separate closed positions DPDT Animation Switch Styles Toggle Slide Switch Styles Rocker Push On/Off Other Switches • Momentary contact switches –Push button switches • Rotary switches Momentary Contact • Push Button Normally Open • PBNO • Red in color PBNO Momentary Contact • Push Button Normally Closed • PBNC • Black in color PBNC Rotary Switches • Used for complex circuits • Can have multiple throws Rotary Switch • Example- Stereo input selector #1) ?P?T #2) ?P?T #3) ?P?T #4) ?P?T #1) 3P1T #2) 2P5T #3) 3P2T #4) 3P3T Review • • • • • What are the three basic parts of a circuit? What else can a circuit include? What are the six sources of energy? What is the main function of a switch? What is the difference between a throw and a pole? • What other types of switches are available?