Intro to Humanities Arts
advertisement

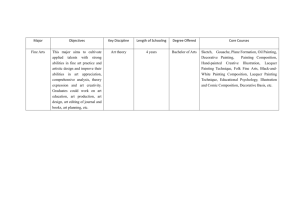
Introduction to Humanities Review Of the Arts PAINTING • Painting is the art that has most to do with revealing the visual appearance of objects and events. • The most basic elements of painting are line, shape, light, texture, and color. • The eye is the chief sense organ involved in our participation with painting… • Representational paintings furnishes the world with definite objects and events. • Abstract paintings offers us a complete rest from practical concerns. SCULPTURE • Along with painting and architecture is classified as one of the visual arts. • It engages our senses differently than painting does; because it occupies space as a three-dimensional mass. • Sunken-Relief Sculpture: carving cut grooves of various depths into the surface plane of the stone. • Surface-Relief; Low-Relief; High-Relief; etc. ARCHITECTURE • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. Is the creative conservation of space. Space is the material of the architect. Four necessities of architecture: Technical requirement – buildings must stand (and withstand). Functional requirements – they must stand in such a way that they reveal their function or use. Spatial requirements – relationships with surrounding buildings. Content – subject matter = relevant values of society. LITERATURE • Is an art whose medium is language used to affect the imagination. • Fiction writers and poets share many of the techniques of literature because their effects depend on universal language art. • Language has denotation: a literal level where words mean what they obviously say, and connotation; a subtler level at which words mean more than they obviously say. DRAMA • Is a species of literature whose basic medium is spoken language. • It can be read, somewhat like a poem or a novel. • The word “drama” comes from the Greek word meaning “act.” • Drama is spoken language acted, to be produced for public exhibition, usually upon a stage. MUSIC • Is one of the most powerful of the arts partly because sounds – more than any other sensory stimulus – create in us involuntary reactions, pleasant or unpleasant. • There is no escaping the effects of music except by turning off the source. • It can be experienced in two ways: “hearing” or “listening.” DANCE 1. Moving bodies shaping space. 2. At its most basic level, the subject matter of dance is abstract motion. 3. In abstract dance the center of interest is upon visual patterns. 4. It is rhythmic, unfolding in time, and thus has common ground with music. 5. Most is accompanied by music. FILM • When we evaluate a film, all of these elements come into play: • Cinematography, the care with which the film was photographed, • Structure, the completeness and excellence of the script or story line, • Acting and character development, • Editing of separate shots • Music, the way sound evokes emotion or establishes mood. PHOTOGRAPHY • When it became widely available in the 1940’s and 1950’s the images printed on paper were in black-andwhite or sepia (brown-and-white). • The success of photography in reproducing realistic scenes and people had an instant impact on painting.