Archimides
advertisement

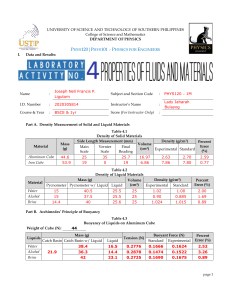
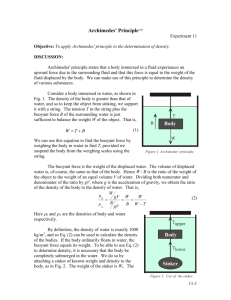
1. To observe the buoyant force acting on an object immersed in a liquid. 2. To prove that the amount of water displaced is equal to the buoyant force. Tools: - Beaker- ball –cube -dynamometerVernier Calliper- cube- ball water Theory: Archimedes’ principle states that a body immersed in a liquid is acted upon by a buoyant force F, the magnitude of which is equal to the weight G of the displaced liquid. :Laboratory results 1. Buoyant force = (the weight of the body in the air - the weight of the body in the liquid) 2. weight of water displaced = volume of the body × density of water× gravitational acceleration The Volume of the cube=L3 The Volume of the ball = π ×4/3 ×r 3 Steps: 1.Susbend a cube in the dynamometer and read its This is w1. 2.Submerge the cube in the water by raising the beaker and read its weight . This is w2 3. Repeat stes 1 and 2 using the metal ball . 4.Find the dimensions of the body using Vernier caliper and concluded the Volume. 5-Calculate Buoyant force and the weight of displaced water and then compare them Data. Table1 Fb= w3 Objects W1(air) W2(water) w3(airwater) 1.cube 2.ball Buoyant force Table2 W(H2Odisplaced ) =v . ρ . g Objects 1.cube 2.ball Volume(m3) ρ (kg /m3) g(kg .m/s2) Weight of water displaced