File
advertisement

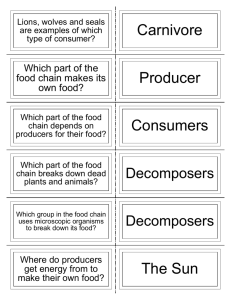
Materials: worksheet Catalyst: (5 min) 1. In which organelle does cellular respiration take place in eukaryotes? 2. In which organelle does photosynthesis take place in eukaryotes? 3. What is the energy storing molecule that has 3 phosphate groups? (formed in cellular respiration) 4.What is the chemical reaction for photosynthesis? 5.What is the chemical reaction for cellular respiration? Materials: none Catalyst: (5 min) 1. What is the difference between an autotroph and a heterotroph? 2. What is the primary source of food for small fish? 3. Where does all energy in this food chain originate? Elite Eight Trait Check-Up 1. Respect the Threshold • Everyone on time? • Silent for First Five? 2. Be Prepared (2 min) • Seated • Have materials • Working on catalyst Announcements • I will be emailing your science expo reports back this week with comments. • Final Draft Due in hard copy Monday, Dec 9! • Science Expo is Wednesday, Dec 11 • NEW TUTORIAL DAYS: Tuesday/Friday 3-4:30 Standard SB4. Students will assess the dependence of all organisms on one another and the flow of energy and matter within their ecosystems. b. Explain the flow of matter and energy through ecosystems by arranging components of a food chain according to energy flow. Objectives • I can differentiate between producers and consumers • I can interpret a food chain and food web. • I can explain the transfer of energy in both a food chain and a food web. Energy Transfer How do living things obtain and use energy? What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work Organisms use energy to eat, breathe, and move. The Transfer of Energy All the energy on Earth originates (comes from) the sun Review What is an autotroph? Autotrophs produce their own energy using sunlight What is an heterotroph? Heterotrophs obtain their energy from eating other organisms The Transfer of Energy Autotrophs obtain energy from the sun through photosynthesis Autotrophs are also called producers Why do you think autotrophs are called producers? The Transfer of Energy Heterotrophs obtain energy by eating other living organisms Heterotrophs are also called consumers What does it mean to be a consumer? Think! 1. What is a producer? Are producers and autotrophs the same thing? Explain. Producers make their own food from photosynthesis and is another name for autotrophs 2. What is an example of a producer? Grass, trees, and plants are all producers Think! 3. What is a consumer? Are consumers the same thing as heterotrophs? Explain. Consumers eat other organisms as their energy source and are another name for heterotrophs 4. What is an example of a consumer? Consumers include humans and all types of heterotrophs Heterotrophs What are the different types of Heterotrophs? Herbivores Herbivores: only eat autotrophs, such as grass, berries, and other plants. When you see herbivore think herbs and vegetarian! Examples: Rabbits, deer, horses, and elephants Can you think of any more herbivores? Carnivores Carnivores: eat only heterotrophs or other animals When you see carnivores think meat eater! Example: Lions, sharks, and snakes Omnivores Omnivores: eat both plants and animals Example: Humans, Rats, Mice, and Pigs Would a vegetarian still be considered an omnivore? Decomposers Decomposers: eats dead or dying animals Also known as Saprophytes or Scavengers Example: Bacteria and fungi Think: What type of heterotroph? Herbivores, Carnivores, Omnivores, or Decomposers Can eat both plants (autotrophs) and animals (heterotrophs) Herbivores, Carnivores, Omnivores, or Decomposers Herbivores, Carnivores, Omnivores, or Decomposers Can eat only animals (heterotrophs) Herbivores, Carnivore, Omnivore, or Decomposer Eats dead or dying organisms Herbivores, Carnivores, Omnivores, or Decomposers Herbivores, Carnivores, Omnivores, or Decomposers Can eat only plants (autotrophs) Herbivores, Carnivore, Omnivore, or Decomposer Flow of Matter and Energy in Ecosystems Energy Flow Energy flows (moves) in an ecosystem in the form of matter Matter - the physical substance that makes up everything (atoms) Food chain: is a model that shows how matter and energy move through an ecosystem berries mice Tiger The arrow shows who eats what or whom. The arrow points towards the predator and away from the prey Nutrients and energy move from: Producers Consumers Decomposers Think • In the food chain to the right, what is the producer? • Who eats the grass? • Who gets energy from the mouse? What is the producer, consumer, and decomposer in the food chain below? In which direction does the energy flow? Food Web: made up of multiple food chains Food webs show all the possible feeding relationships for each organism A food web is more realistic than a food chain because organisms depend on more than one other species for food 1. What does the rabbit eat? 2. What eats the rabbit? 3. What would happen to the mouse, rabbit, and goat if all the plants went extinct? How would this affect the lion? Food Web Levels Level 4: Tertiary Consumers (who eat Secondary consumers) Level 3: Secondary Consumers (who eat primary consumers) Level 2: Primary Consumers (who eat producers) Level 1: Producers Work Session Panther Pass Question 1 The owl is a nocturnal hunter of small mammals, insects and other birds. An owl is an example of a/an? A. Producer B. Omnivore C. Carnivore D. Decomposer Question 2 Which food would an herbivore always avoid? A. Worms B. Clover C. Pine nuts D. Grass Question 3 Many types of bacteria obtain nutrition from dead plants and animals. What type of heterotrophs are bacteria? A. Decomposers B. Producers C.Carnivores D. Viruses 4. Is the mouse a consumer or a producer? 5. What does the hawk eat? 6. What would happen to the lizard population if the caterpillars went extinct?