1. Explain how autotrophs/producers are different from
advertisement
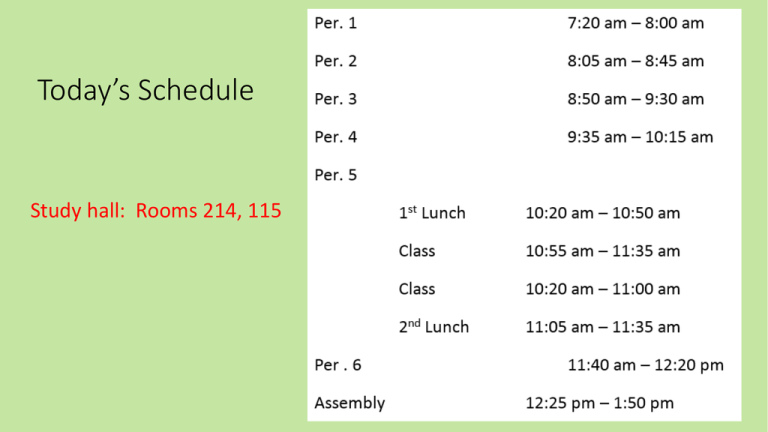
Today’s Schedule Study hall: Rooms 214, 115 1. Explain how autotrophs/producers are different from heterotrophs/consumers. Give examples of each. • Autotrophs/producers can make their own food, heterotrophs/consumers can’t. • Autotrophs/producers: plants, algae, phytoplankton • Heterotrophs/consumers: animals 2. What is a decomposer? Give three examples. • Eats dead things • Bacteria, fungi, worms, slugs, sea stars 3. What is an ecosystem? Give an example of one. • All living and non-living things in a particular place. • Forest, desert, coral reef, etc. 4. What is a species? Give an example of one. • Particular kind of living thing. • Dogs, cats, lions, tigers, humans, Douglas fir trees, etc. 5. Describe the flow of energy through the following members of an ecosystem: decomposers, autotrophs, heterotrophs, and the sun. • Energy goes from sun to autotrophs to heterotrophs to decomposers. 6. Explain what photosynthesis is and why it is important to all life on Earth. • Process by which producers use light energy to make their own food. • Photosynthesis at beginning of almost every food chain on Earth. • Without it, plants would starve. Without plants, animals would starve. 7. Explain the difference between photosynthesis and chemosynthesis. Where on Earth does chemosynthesis happen? • Photosynthesis: how organisms use light energy to make food. • Chemosynthesis: how organisms use chemical energy to make food. • At bottom of ocean, at hydrothermal vents. 8. Explain why each level of an ecological pyramid is smaller than the level below it. • Every animal has to eat several animals from level below it. • Every animal only gets 10% of energy from animals or plants they eat, so have to eat a lot of them. 9. What is biodiversity and why is it important for healthy ecosystems? • Variety of living things in an area. • More variety = more sources of food, shelter for animals. If one species disappears, there are still others. 10. Give example of an invasive species in the Pacific NW and explain it is a problem. • Himalayan blackberry. • Grows out of control, chokes out/kills all other plants. 11. How can you tell a Douglas fir tree from a Western red cedar? How can you tell red alder from Himalayan blackberry? • Douglas fir has seed cones with “mouse tails”, western red cedar has scaly leaves. • Red alder is tree with toothed, “ruffled” leaves. Blackberry is a shrub with thorns and berries. Red alder Douglas fir Himalayan blackberry Western red cedar 12. What is ecology and why is it important to learn about? • Study of how living things interact with their environments. • So we can understand how we are affecting our environment. • So we can understand how our environment works. • So we can understand how life on Earth works. 13. Name one Pacific NW plant that can convert nitrogen from the atmosphere into a form living things can use to make protein. How does this help other living things? • Red alder. • When leaves fall, they fertilize soil. Provide nitrogen for other plants and animals to make protein. 14. Constraints are things that limit how much you can do in an experiment. Suppose you wanted to find out how many orcas there are in Puget Sound. What would be some constraints on your ability to come up with an accurate count? • They’re always moving, hard to keep track of. • Hard to find when underwater. • New ones born, old ones dying.