lesson 6 neocolonialism
advertisement

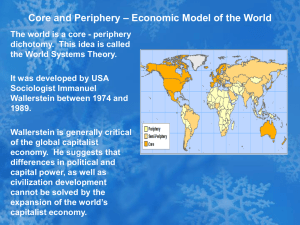
4.How can power be maintained? Modernisation World Systems Dependency • Based on three regions • Theory based on pure capitalism • Brain drain takes from periphery • Poorer countries will remain poor • USA - perfect example • Every country will develop • Based on core and periphery • A critique is that stages can be leapt over • Poorer countries will develop over time • Different stages of development evident • China upsets this theory • Poorer countries can break free of dependency • Africa is largely exploited in this theory • Semi periphery can exploit periphery • Colonial model • Criticised as too simplistic • Resources go to core • The existence of the core only occurs because of the periphery • Individuals are all consumers Warm up! Complete the sheet of heads and tails by matching the correct statements with a line – refer back to notes if stuck. If finished consider how the theories suggest power is or maintained (e.g. how are countries kept dependent/ low level of Rostow’s model?) How can power be maintained? Modernisation World Systems Dependency • Based on three regions • Theory based on pure capitalism • Brain drain takes from periphery • Poorer countries will remain poor • USA - perfect example • Every country will develop • Based on core and periphery • A critique is that stages can be leapt over • Poorer countries will develop over time • Different stages of development evident • China upsets this theory • Poorer countries can break free of dependency • Africa is largely exploited in this theory • Semi periphery can exploit periphery • Colonial model • Criticised as too simplistic • Resources go to core • The existence of the core only occurs because of the periphery • Individuals are all consumers Warm up! Complete the sheet of heads and tails by matching the correct statements with a line – refer back to notes if stuck. If finished consider how the theories suggest power is gained or maintained (e.g. how are countries kept dependent/ low level of Rostow’s model?) Superpower Geographies 2. Impacts and influences of Superpowers a) The changes from colonial rule to indirect neo-colonial rule b) Key roles in international decision making, policy and action c) Control of trade d) Superpower influence in the idea of developing a ‘global culture’ Learning Objectives: • Understand how superpower rule has changed from colonial rule to indirect neo-colonial rule • Assess the mechanisms of neo-colonial control – trade, aid and debt 4.2.1 How can power be maintained? Mechanism s of Colonial Control What mechanisms of control are there? These Images can help. 4.2.1 How can power be maintained? Imposition of an alien legal system and ownership rights Economic imperialism e.g. exporting to the home country Direct military conquest / occupation of territory Ethnic cleansing of difficult groups Mechanism s of Mechanisms of Colonial Colonial Control Control Government by dictat, through colonial administrator s Cultural imperialism through art, religion and language What mechanisms of control are there? These Images can help. Era of decolonialisation Independence brought about conflict rather than immediate freedom for 3 main reasons 1. Colonial borders did not match religious or ethnic boundaries = conflict 2. Colonies had a government but indigenous people excluded from running them = lack of experience 3. As colonial powers left, insurgents pushed them out = violence Neo-Colonialism • A form of indirect control over developing countries, most of them former colonies Direct political control decreased whilst economic control increased - Economic dependence on primary goods - Economic dominance of multinational companies - Impact of foreign aid and foreign debt How were they being indirectly controlled? 1) Aid Often given with ‘strings attached’ forcing the developing countries to spend it in particular ways 2) Trade Low raw material export prices contrast with high prices that developing countries have to pay for manufactured goods 3) Debt Many developing countries pay huge sums of money to developed countries each year in interest • • • • • • Neo-colonialism? Left-wing geographers argue that superpowers use subtle, indirect ways to maintain power today These ways are often termed neocolonialism Aid is often given to allies and ‘friends’ rather than the most needy countries (see table), and much aid is ‘tied’ in various ways. Debt repayments channel money from the developing to the developed world Even debt relief schemes, such as the HIPC scheme (see map) have been criticised For HIPC countries to qualify for debt relief, they must follow the economic policies of bankers in the developed world Top 10 Recipients of USA foreign aid Israel Egypt Colombia Jordan Pakistan Peru Indonesia Kenya Bolivia Ukraine 2006 ($ millions) 2,520 1,795 558 461 698 133 158 213 122 115 Note the total lack of overlap between the most indebted nations and the top 10 receivers of US aid. Ghana @ 50: success or failure? • In 1957 gained independence from British Colonial rule. • Read pg 152-157 Oxford and extra sheets on blog • Using table of development indicators for Ghana on p.152. In what ways has Ghana a) Made progress? b) Fallen behind? • Create a mind map around the key phrase ‘neo-colonialism a bridge between the developed and developing nations using Ghana as an example’ Exam Question • Using examples, assess the view that the relationship between the developed and the developing world is a neocolonial one’ (15 marks)