Lesson 3 Science Tools
advertisement

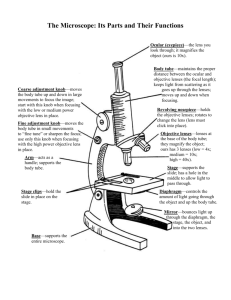
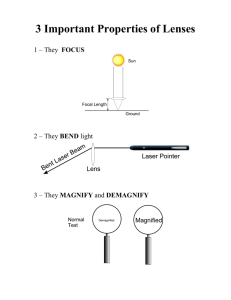
Lesson 3 Scientific Tools Organism(s) Living Things Microorganism(s) Living thing too small to see with the unaided eye. Compound Light Microscope Uses pairs of lenses to form a larger image. Eyepiece Coarse Adjustment Knob Fine Adjustment Knob Arm Clips Inclination Knob Ocular Lens Body Tube Revolving Nosepiece Low Power Objective Lens High Power Objective Lens Stage Diaphragm Base Mirror or Light Electron Microscope Uses electrons instead of light to make extremely small objects visible. Can magnify up to 2 million times their actual size! Ruler Measures length or distance. Thermometer Measures temperature. Graduated Cylinders and Beakers Measure Volume. Pan Balance Measures Mass Spring Scale Measures Weight. Stopwatch Measures Time. Microscopes and Hand Lenses Magnify Small Objects Telescopes and Binoculars Reveal details of faraway objects. Calculators and Computers Organize Data and Make Graphs. A Sieve Container with mesh or perforated bottom. Used to filter large particles out of a mixture. Magnets – Attract metal objects Petri Dish – Growing bacteria Line Graphs Visual display that uses 2 sets of data, like showing how a variable changes over time. Bar Graph Display that shows data as bars of different length. Circle Graph Display that shows data as parts of a whole. Diagrams Picture or group of pictures that display data. X – Axis Horizontal or bottom edge of a graph. Y – Axis Vertical or left edge of a graph. Prediction A guess about what is likely to happen. *Take out a sheet of paper. *Put your name in the upper right hand corner of this piece of paper. *Label the top of the paperGroup Discussion *Answer the discussion questions on your own paper. *When instructed—you will work with your group to answer the questions on the board. Discussion Questions #1 What tools would be useful for studying the planet Mars? Identify some of the things that can be learned by using different tools. #3 Make your own visual display of the data on the board. Quiz on Lesson 3 1. Which type of display is useful for showing parts of a whole? A. Line graph B. Bar graph C. Diagram D. Circle graph 2. Which type of display is BEST for showing how many rainy days there were in each month of one year? A. Line graph B. Bar graph C. Diagram D. Circle graph Lesson 3 Quiz 3. What is the dependent variable in this graph? A. Mass in g B. Volume in L C. Volume in mL D. The substance tested 4. Based on the data provided, what do you predict would be the mass of 50 mL of this substance? A. 30 g B. 50 g C. 400 g D. 500 g 5. Which of these tools should you use to measure the volume of a fluid? A. Graduated cylinder B. Pan balance C. Computer D. Stopwatch 6. A hand lens can be useful for studying A. The growth of a tree. B. The behavior of a squirrel. C. A bird’s feather. D. The density of a rock. 7. Suppose you want to compare the masses of 2 mineral samples. Which of these tools would you use? A. Pan balance B. Hand lens C. Thermometer D. Graduated cylinder 8. Describe which tools you would use and how you would find the volume of a piece of gold you found in a stream? 9. The ________ is the horizontal or bottom edge of the graph. 10. Charts and graphs allow scientists to visualize data. Using these tools they can make ________________ about what will happen in the future. **Listen carefully to the extra credit—your mouth should not open and your eyes should be on your own paper!!