Nervous & Endocrine Systems
advertisement
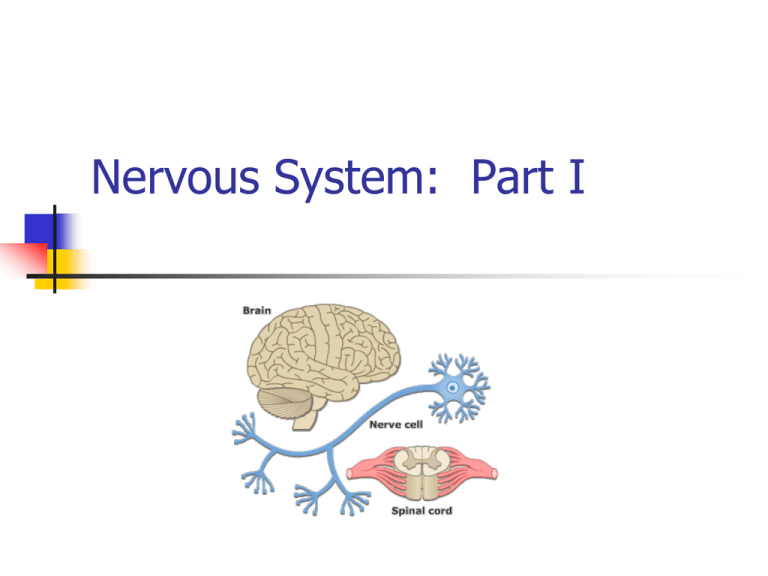
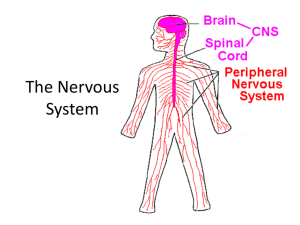
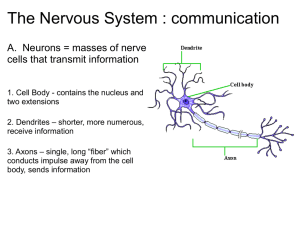
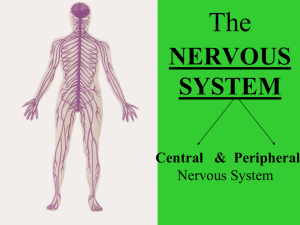
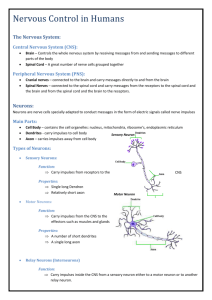
Nervous System: Part I The Nervous System Your body’s communication’s network & control center Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)-gathers info from inside & outside the body Central Nervous System (CNS)-receives this info & initiates a response-composed of the brain & spinal cord Messengers & receivers of these transmissions are NEURONS (nerve cell) Three Types of Neurons Sensory-carry from sense receptors to CNS (5 senses) Motor-carry signals from CNS to muscles or glands Interneurons-carry electrical connections within the CNS Functions of Neurons Cell body-contains nucleus & cell membrane Dendrites-branching projections of the cell body, carry impulses into the cell. Axon-Threadlike extension carries impulses to & from the cell, at the end of axon is the axon terminal Myelin Sheath-Insulates the axon & speeds up transmission of the impulses Synapse-point of contact at which impulses are passed from one cell to another Electrical impulse The Nerve Impulse Let’s draw neurons! Look at the drawing on page 517 of your health book. You will need 4 different colors markers/pencils, for the: cell body dendrites axon/terminal synapse Draw your neuron on a piece of paper color and label the parts Right Brain--- Left Brain Sitting at your desk, lift your right foot off the floor and make clockwise circles Now, while doing this, draw the number "6" in the air with your right hand. [Your foot will likely change direction, and there's nothing you can actually do about it.] Reflex Action (Unconscious) If the safety of our body requires a very quick response, the signals may pass directly to a motor neuron for instant, unthinking action. This is a reflex action. Signals sent via the spinal cord List as many examples of a reflex action as you can: http://www.bbc.co.u k/schools/gcsebitesi ze/biology/humansa sorganisms/4nervou ssystemrev4.shtml Part II: Nervous System Voluntary Actions (Conscious Act) Impulses passed via the brain What is the chain of events that happens from the instant you hear the phone ring until you pick up the phone? Every time a stimulus— such as a ringing telephone—is detected, the body's three kinds of neurons send a nerve impulse through the nervous system. Nerve Impulse Activity In groups put the following path of a nerve impulse in the correct order: 1.The nerve impulses pass to interneurons in the brain. 2.Receptors in your ear pick the sound of a ringing phone 3.Muscles in the arm carry out the response and you reach to pick up the phone 4. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the muscles 5. Receptors trigger nerve impulses in sensory neurons 6. Your brain interprets the impulses from many interneurons and you realize the phone is ringing. Your brain also decides that you should answer the phone. Correct order… 2. Receptors in your ear pick the sound of a ringing phone 5. Receptors trigger nerve impulses in sensory neurons 1. The nerve impulses pass to interneurons in the brain. 6. Your brain interprets the impulses from many interneurons and you realize the phone is ringing. Your brain also decides that you should answer the phone. 4. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the muscles 3. Muscles in the arm carry out the response and you reach to pick up the phone The Brain Largest, most complex part of the nervous system Weighs 3 pounds, contains billions of neurons Without oxygen it can only last 4-5 minutes Cerebrum Forms our intellect & personality Divided into two hemispheres Left-language & logic Right-imagination & emotional responses Does not fully develop until late teens or early-mid 20s!!! Phineas Gage If an explosion sent a steel rod through your head, would you be able to get up? Would you be able to walk and talk? Could you tell your doctor what happened to you? Amazingly, Phineas Gage did! But, could he make a complete recovery with a big hunk of his brain missing?