Slide 1
advertisement

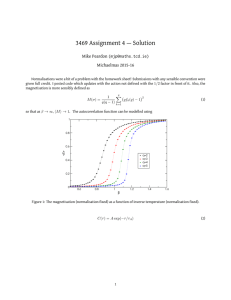
Critical Transitions in Nature and Society Marten Scheffer Chapter 14 How to Know if Alternative Basins of Attraction Exist ? 14.1 Hints from Field Data How one can tell if there are multiple attractors? • Jumps in time-series or regime shifts • Sharp boundaries and multimodality of frequency distributions • The shape of a catastrophe fold The evidence can never be conclusive. Discontinuities in time-series or spatial patterns can be due to discontinuities in environmental factors. Alternatively, the system might have a threshold response that is not related to alternative stability domains. 14.2 Experimental Evidence Experiments can provide evidence for multiple attractors. • Different initial states lead to different final states • Disturbance triggers a shift to another permanent state • Hysteresis in response to forward and backward changes in conditions A hysteretic pattern may not indicate alternative attractors if the response of the system is not fast enough relative to the rate of change in the controle factor. Experiments provide potentially powerful tests, but there are serious limitations to exploring large spatial scales and long time spans. 14.3 Mechanistic Insight Mechanistic models, formalized as graphs or equations, may explain observed behavior and allow us to extrapolate our findings. They allow us to predict that the system might have alternative stable states, chaotic attractors, or other interesting stability properties, even if those have not yet been detected in its behavior. We want such models to become as accurate as possible and should take their outcomes seriously, even though we have no comparable past events to validate this aspect of their predictions. Mapping mechanistic models to reality is the core of science. It is what allows moving from beliefs to true understanding of the complex world around us. Implications of positive feedbacks Minimal models and hypothesis testing Realistic simulation models To predict the consequences of the feedback, we need to take a more quantitative approach and analyze its interaction with other processes in the system. Minimal, or strategic, models focus on a minimal set of mechanisms needed to produce a certain behavior. However, in many cases we cannot identify one isolated casual factor. Predictive simulation models work surprisingly poorly for ecological problems. Tuning of complex ecological models easily leads to good results for the wrong reasons. The assumed casual relations need not be true, and extrapolation to new situations can lead to nonsense predictions. Chapter 15 How to Know if a Threshold is Near ? 15.1 The theory: Signs of Upcoming Transition Early warning signals as predicted from theory. • Slower recovery from perturbations • Increasing autocorrelation • Increasing variance • Flickering and stochastic resonance • Increased spatial coherence 15.2 Precursors of Transitions in Real Systems Ancient climate shifts: an increase in autocorrelation but no increase in variance. Lakes shifting from turbid to clear state: increase in variance but no rising autocorrelation. Epileptic seizures and heart failure: changes in the synchronization between oscillating cells corresponding to phase locking and resonance phenomena. 15.3 Reliability of the signals A shift due to a fast and permanent change of external conditions cannot be detected (?) Detecting increased autocorrelation requires long and good time-series. The external regime of perturbations can change over time distorting or counteracting the expected signals (?) The indicators will also signal a threshold that is not related to a catastrophic bifurcation but to a strong sensitivity of the system around a critical value. 15.3 Synthesis We are far from being able to develop accurate models to predict thresholds in most complex systems ranging from cells to organism, ecosystems, or the climate. We do not understand all relevant mechanisms and feedbacks sufficiently well in most cases. The generic character of early warning signals is reason for optimism, as they occur largely independent of the precise mechanism involved.